Sialic Acid Microarray
Sialic acids are typically found as terminal residues on the glycan chains of vertebrate glycoconjugates and play important roles in protein recognition and immunization activities against exogenous virus. Sialic acids have the potential for more unique and varied biological functions due to their higher structural complexity. Sialic acids binding lectins can be found in many microbes, plants and animals. Studies of these sialic acids recognizing proteins by sialic acids microarrays are rapidly growing. As a leading supplier in the field of microarrays, Creative Biolabs is committed to designing and developing various effective biological microarray products for research. Our microarray test platform provides convenient and rapidly sialic acid binding analyzation with proteins, virus or other microorganism to help our global customers conduct relevant research and reduce research costs.
Introduction of Sialic Acid Microarray
Sialic acids are a group α-keto acids with a nine-carbon backbone, which display many types of modifications in nature. The diversity of natural sialic acid presentations is magnified by a variety of glycosidic linkages to underlying glycans, the sequences and classes of such glycans. The types of natural modifications found on sialic acids far exceed that of any other monosaccharides due to their nine-carbon backbone. This diversity is closely linked to the numerous and varied biological functions of sialic acids. However, the researches focus on the interaction between sialic acids and proteins or virus suffering from the lack of sialic acid derivative samples and throughput of the screen. Therefore, the sialic acid microarrays have proved to be valuable tools for the exploration of the diversity and biology of sialic acids. Due to the important effect of sialic acids in the immune system, sialic acid microarray is widely used in Glycoprotein-based Vaccine Development, Tumor Glyco-diag and Anti-Glycoprotein Antibody Development.
Applications of Sialic Acid Microarray
Based on the bioactivity of sialic acids in immunological recognition, sialic acid microarray technology has been commonly applied in the studies of sialic acid recognizing proteins or viruses. Through the screen of various sialic acid derivates, higher affinity sialic acid analogues have been picked out and shown potential to be used as sialic acid-binding immunoglobulin-like lectins inhibitors or for targeted therapeutic delivery to treat B cell leukemia. Another useful function of sialic acid microarray is to identify the virus type according to their combining capacity to different sialic acid analogues. One well-known example is the recognition of different sialic acid linkages by human and avian adapted influenza A viruses. Moreover, sialic acid microarray methods can combine with many other technologies to develop multifunctional chips such as SPRi, MALDI-TOF MS or Flow Cytometry.
The high flexibility of structure and function requires a rapid and high-throughput screen method to discover the carbohydrate-protein interactions. Our sialic acid microarray provides an approach to achieve these goals. If you are interested in our service or have any requirements in glycobiology research, please don't hesitate to contact us.
Published data
In recent years, the development of glycan microarray technology has made significant progress and is widely applied in high-throughput analysis of glycan-binding proteins. Sialic acid, a negatively charged α-ketogenic acid, is usually at the end of various sugar chains on the cell surface. In this study, the authors compared two different sialic acid glycan microarrays using a variety of sialic acid-binding proteins. The two arrays demonstrated the diversity of sialic acid in nature, including its modification, connection mode, and structural diversity of underlying glycans. The research team used a variety of printers, buffer conditions, and detection antibodies, and conducted a comprehensive analysis of the two arrays at different concentrations. The results revealed the diversity of sialic acid recognition and verified the analytical capabilities of glycan microarrays. Although a diverse array of formats improved the quality of information, it should be noted that there might be differences between different arrays. Therefore, it couldn’t be simply assumed that arrays with similar glycan structures produced similar results. In addition, they pointed out the challenges faced by glycan microarrays in data comparison and the problems that need to be solved in future technological development.
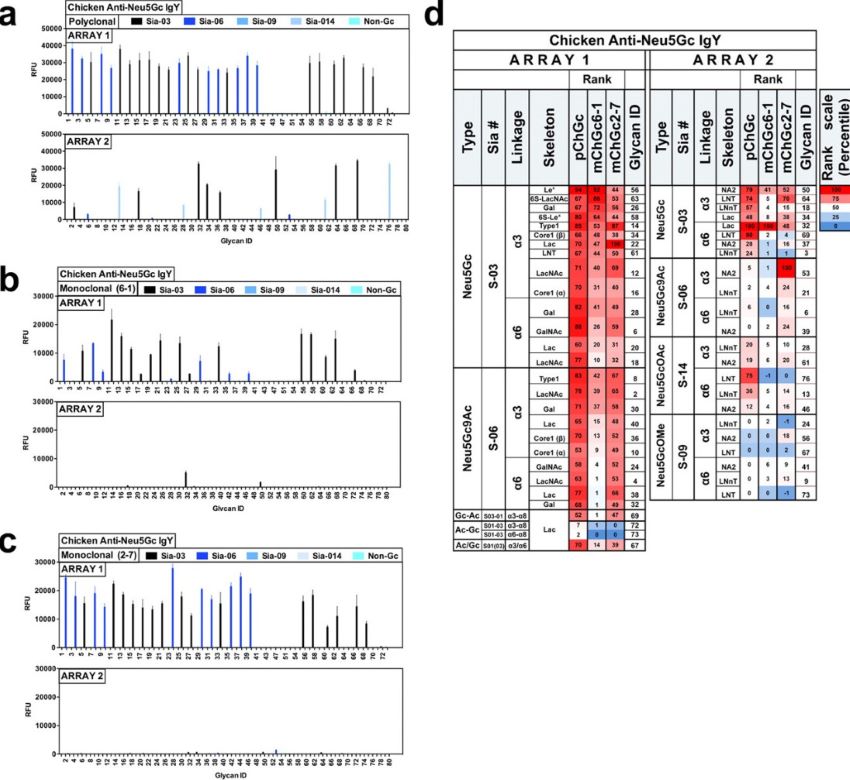 Fig.1 Selective recognition results of sialic acid glycan microarrays by specific antibodies.1
Fig.1 Selective recognition results of sialic acid glycan microarrays by specific antibodies.1
FAQ
Q1: How to design a sialic acid microarray?
A1: The design of a sialic acid microarray needs to consider the selection of appropriate sialic acid derivatives, the reasonable arrangement of their fixation on the microarray, and the optimization of the combination to ensure efficient capture of the target molecule. Our team provides customized services according to the specific needs of clients.
Q2: How can sialic acid microarrays help improve research efficiency?
A2: Sialic acid microarray technology has high-throughput screening capabilities and can analyze multiple samples at the same time, which can significantly improve experimental efficiency and data acquisition speed. This method quickly determines which sialic acid derivatives interact with the target molecule, thereby accelerating the research process.
Q3: What markers can be used to enhance the detection signal?
A3: Common markers include fluorescent dyes, enzyme markers, and radioactive isotopes. These markers can generate measurable signals after binding to the target, which is convenient for subsequent analysis.
Customer Review
High Accuracy of Analysis Results
“Through Creative Biolabs' sialic acid microarray analysis, we obtained very reliable data. We observed the binding of different sialic acid derivatives to the target protein, which provided a solid foundation for our research.”
Strong Experimental Repeatability
“We conducted multiple experimental verifications, and the results showed good repeatability. This proved the stability of Creative Biolabs' microarray technology and added credibility to our experimental data.”
Reference
-
Padler-Karavani, Vered, et al. "Cross-comparison of protein recognition of sialic acid diversity on two novel sialoglycan microarrays." Journal of Biological Chemistry 287.27 (2012): 22593-22608. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Selective recognition results of sialic acid glycan microarrays by specific antibodies.1
Fig.1 Selective recognition results of sialic acid glycan microarrays by specific antibodies.1

