Human Milk Oligosaccharide Microarray
Human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) are the most abundant carbohydrate component of breastmilk after lactose, and are composed of a heterogeneous mix of at least 200 distinct glycan structures. These glycans are unique to human milk, which can protect newborns from diseases and infections, build healthy intestinal bacteria, and are essential for the development of the baby's brain, intestines and immune system. Creative Biolabs provides high-quality products and customized services for the analysis of HMO-proteins interactions. We have successfully developed many human milk oligosaccharides microassay products and furtherly extent the application of this platform by combined with other support technologies. We guarantee to provide first-class products and excellent service to customers all over the world.
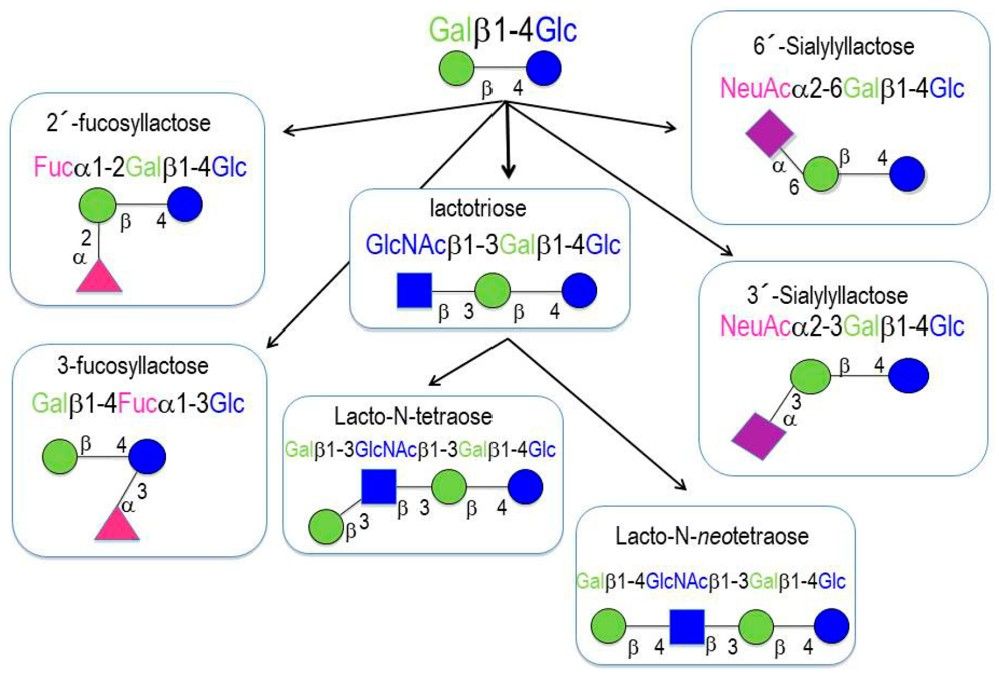 Fig.1 Basic structure of HMO.1, 4
Fig.1 Basic structure of HMO.1, 4
Introduction of Human Milk Oligosaccharide Microarray
The structural complexity of HMOs ranges from relatively simple glycans, such as lactose and sialyl- and fucosyl-lactose, to highly complex, multi-branched structures having different appendages at each branching point.
It currently is believed that HMOs can function both as prebiotics and as decoy receptors that inhibit the attachment of pathogenic microorganisms to the colonic mucosa. Given the importance of HMOs to infant health, there is currently considerable interest in identifying their protein receptors in humans, as well as those associated with viral and bacterial pathogens. However, virtually nothing is known about the importance of the molecular complexity of HMOs for binding and biological activity due to the difficulty to obtain the determined structural HMOs. However, the HMO microarrays provide a sensitive and high-throughput approach to HMO-binding proteins screening which uncover the binding selectivity controlled by glycan complexity.
Applications of Human Milk Oligosaccharide Microarray
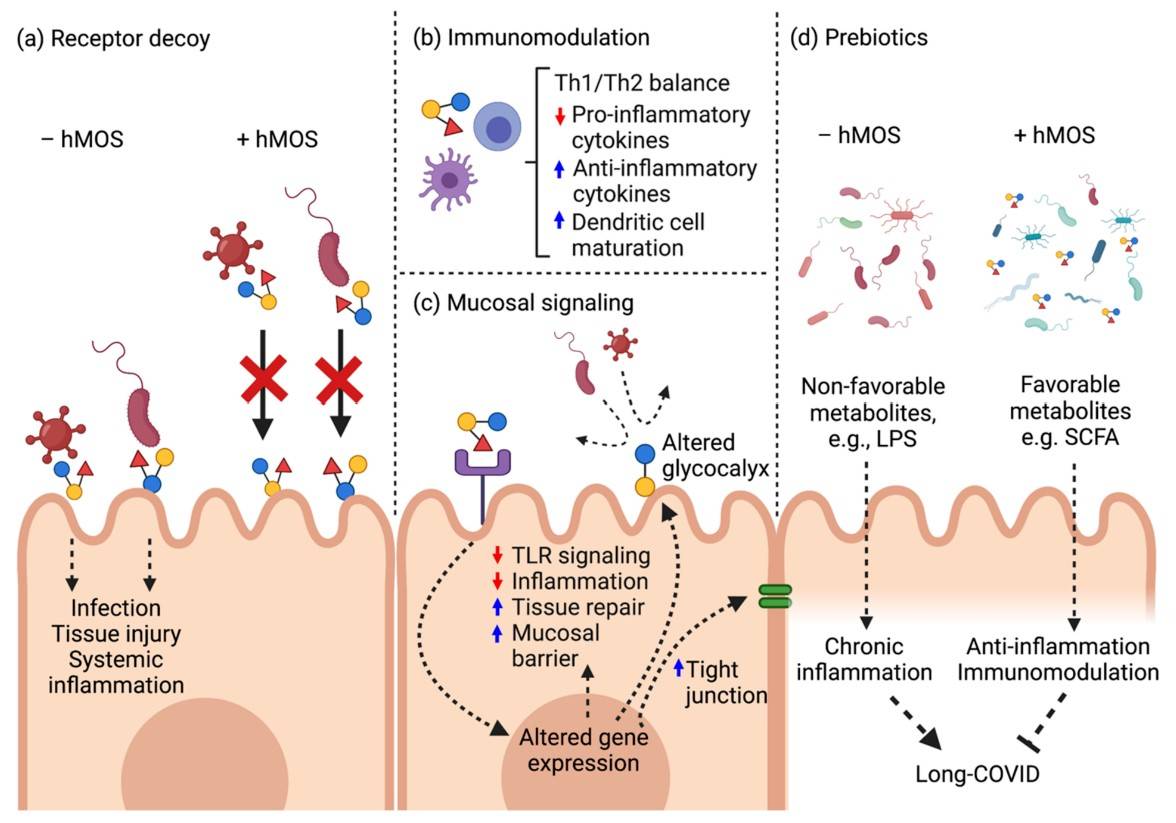 Fig.2 Potential action of hMOS for SARS-CoV-2.2, 4
Fig.2 Potential action of hMOS for SARS-CoV-2.2, 4
Except for its important effect on the immune system, recent studies have furthermore shown the beneficial properties of HMOs extending to protection against infant-associated gastrointestinal conditions with the binding ability of intestinal bacteria. Therefore, the screen of HMO-binding proteins ranges from endogenous protein to microorganism.
A novel study has shown the application of human milk oligosaccharide microarray technology. An HMO microassay chip containing more than fifty kinds of HMO was developed to detect the interactions between proteins and HMOs. The result uncovered that complex architectures of glycans can influence binding selectivity in unanticipated manners. Similarly, our HMO microassay also contains a series of classic glycan epitopes that have been widely reported. This product can accelerate the research of HMO and its interaction.
Because of the functional diversity, HMO-related research appears on high IF journals constantly. Creative Biolabs provides the most comprehensive Human Milk Oligosaccharide Microarray to meet your requirement. For more details, please feel free to contact us.
Published data
HMOs provide many health benefits such as modulating the immune system by forming non-covalent interactions with proteins. HMO microarray is an effective tool to study the interaction between HMOs and proteins. In this study, free glycans from breast milk were labeled and isolated to generate a library of labeled glycans, and an HMO microarray was constructed according to this library. After construction, the researchers also used the microarray to study the potential role of HMO as a rotavirus decoy receptor. This work provides a demonstration of the construction of HMO microarrays and the application of microarray-based research.
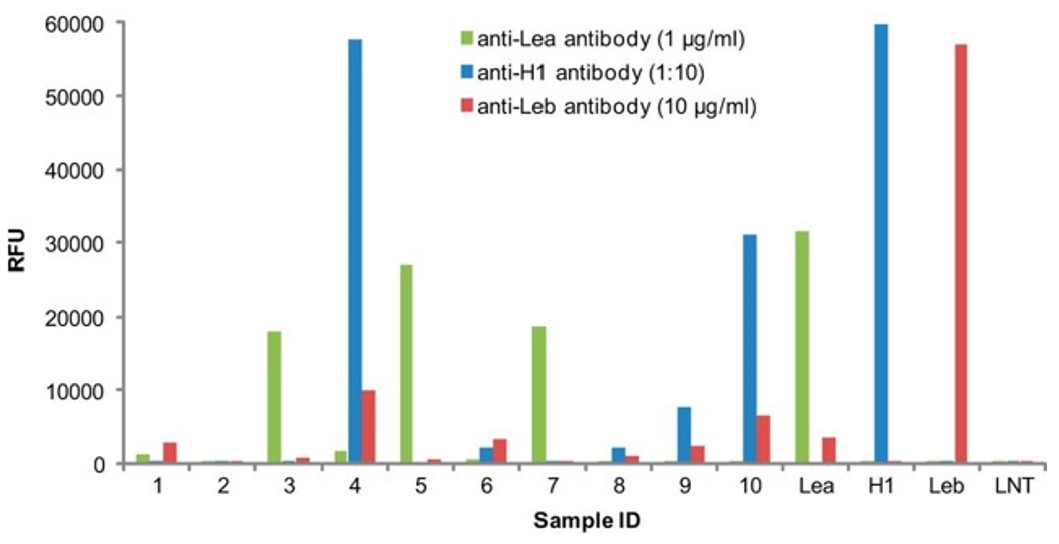 Fig.3 Lewis blood grouping is analyzed by microarray.3, 4
Fig.3 Lewis blood grouping is analyzed by microarray.3, 4
FAQs
Q1: How to analyze HMO-protein interactions using HMO microarrays?
A1: Specific HMO microarrays are constructed and analyzed according to the research objectives, including the following:
-
HMOs are labeled, isolated, and purified to generate labeled HMO libraries.
-
HMOs are printed onto substrates (slides) and are used to detect and analyze HMO-protein interactions.
-
HMO-protein interactions are analyzed according to experimental results.
Q2: What is the significance of HMO microarrays?
A2: HMOs have various functions such as immunomodulation, signaling, and antiviral and prebiotic effects. By analyzing the interactions between HMOs and molecules through HMO microarrays, researchers can identify specific HMOs that play key roles in infant health. The analysis also provides useful information for understanding the mechanisms of HMO functions and for developing milk formulas. In conclusion, HMO microarrays provide unlimited possibilities for deepening the understanding of infant nutrition and health.
Customer Review
Efficiently Analysis of HMO-protein Interactions
"Recently Creative Biolabs helped us to efficiently analyze the interactions between HMOs and proteins. We were very impressed with their high level and fast analysis. In addition to providing analysis results via HMO microarray assay, they were very willing to share their experience to help us analyze the results efficiently. We were very satisfied with their expertise and service."
A Range of HMO Microarray Products
"Creative Biolabs specialized in utilizing HMO microarrays for a variety of studies. They had a range of products to help us screen for HMO-binding proteins. In addition to meeting our research needs, they also provided some valuable insights that paved the way for our research. Their quality of work and commitment to client satisfaction were commendable."
References
-
Plaza-Díaz, Julio, Luis Fontana, and Angel Gil. "Human milk oligosaccharides and immune system development." Nutrients 10.8 (2018): 1038.
-
Chutipongtanate, Somchai, Ardythe L. Morrow, and David S. Newburg. "Human milk oligosaccharides: Potential applications in COVID-19." Biomedicines 10.2 (2022): 346.
-
Yu, Ying, et al. "Human milk contains novel glycans that are potential decoy receptors for neonatal rotaviruses." Molecular & cellular proteomics 13.11 (2014): 2944-2960.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Services

 Fig.1 Basic structure of HMO.1, 4
Fig.1 Basic structure of HMO.1, 4 Fig.2 Potential action of hMOS for SARS-CoV-2.2, 4
Fig.2 Potential action of hMOS for SARS-CoV-2.2, 4 Fig.3 Lewis blood grouping is analyzed by microarray.3, 4
Fig.3 Lewis blood grouping is analyzed by microarray.3, 4

