The liver is the largest organ in the body. It helps your body digest food, store energy, and eliminate poisons. If there is a problem with the liver, it can be a very difficult health problem.
Liver disease (also known as a hepatic disease) is a kind of liver damage or disease. The incidence rate of liver disease is one of the causes of global morbidity and mortality. Although the incidence of specific liver diseases varies by geographic location, the scope of liver diseases affecting underdeveloped, developing and developed countries is staggering, including liver infectious diseases to tumors and obesity-related diseases. According to different factors, liver diseases are classified as follows:
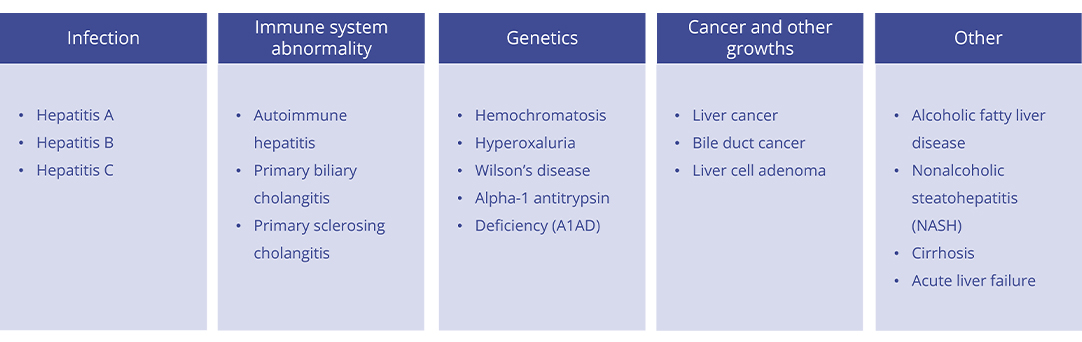
Symptoms of liver disease may vary, but usually include abdominal and leg swelling, bruising, color changes in stool and urine, jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and eyes. Sometimes there are no symptoms. Tests like imaging and liver function tests can detect liver damage and help diagnose liver disease.
The liver provides the basic functions needed to maintain homeostasis and the health of many organisms. At present, the treatment of liver disease lacks effective diagnosis and treatment methods. There is an urgent need for non-invasive markers to improve the diagnosis and prognosis of liver pathology, and to develop new drugs for liver disease treatment.
In the past decade, the development of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) has greatly expanded our ability to model and treat various diseases. In particular, iPSCs-derived hepatocytes have been used to simulate hepatotropic virus infection, virus-host interaction, high-throughput drug screening, and hepatocyte transplantation animal models. Hepatic stem cells are also a promising tool for gene modification, such as liver regeneration in patients with metabolic liver disease and acute liver failure, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
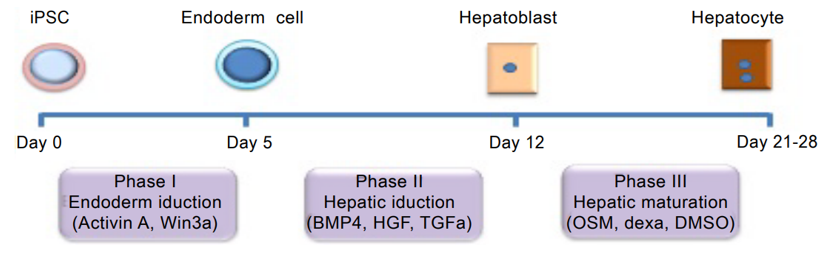 Fig.1 Schematic showing the experimental outline of differentiation of human iPS cells into functional hepatocytes.1
Fig.1 Schematic showing the experimental outline of differentiation of human iPS cells into functional hepatocytes.1
iPSCs are reprogrammed somatic cells in a dry state. They can produce cells of all three germ layers and provide an unlimited number of tissue-specific differentiated cell types for disease modeling and cell therapy. The use of differentiated hepatocytes in culture dishes to study patient-specific iPSC lines and disease phenotypes opens up a new way for personalized medicine.
Recent studies have shown that iPSCs-derived hepatocytes can be used for in vitro studies of genetic liver disease, drug screening and metabolism, hepatitis C virus infection, and evaluation of the efficacy of cell therapy. Disease-specific iPSC lines have been used to model inherited metabolic diseases including A1AD, familial hypercholesterolemia, glycogen storage disease type 1a and Wilson's disease. Advances in precise genetic engineering using designer nucleases have provided new tools for gene correction and reverse genetic engineering of disease-causing genotypes in iPSCs. In addition, iPSCs-derived hepatocytes from various genetic backgrounds are valuable resources for evaluating drug interactions and drug metabolism.
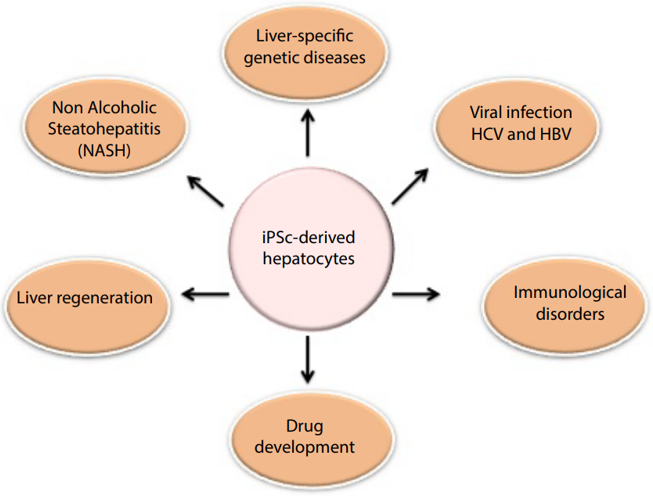 Fig.2 Utilities of iPSC-derived functional hepatocytes for disease modeling and other applications.1
Fig.2 Utilities of iPSC-derived functional hepatocytes for disease modeling and other applications.1
Besides, the use of iPSCs to study the genetic and molecular basis of NASH and alcoholic fatty liver disease also shows great potential. Metabolomics, genomics and proteomics analysis of iPSCs-derived hepatocytes exposed to nutrients, organic and inorganic compounds can elucidate the pathobiology of NASH. Overall, iPSCs technology provides new tools for advancing research in the field of liver biology. If you want to get more iPSCs treatment capabilities in liver diseases, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.