Therapeutic Glycoprotein Production in Human Cells
Animal cell expression systems are preferred for the production of large, complex proteins requiring post-translational modification (PTM) for their biological activity. Human cell-based expression systems are expected to produce proteins with PTM more similar to their natural counterpart as some sugar-transferring enzymes are lacking in BHK and CHO cells. Human cell lines with human glycosylation and other posttranslational modification machinery have become an attractive alternative for the biopharmaceutical industry. Currently, only a few cell lines are used to produce recombinant proteins at a large scale.
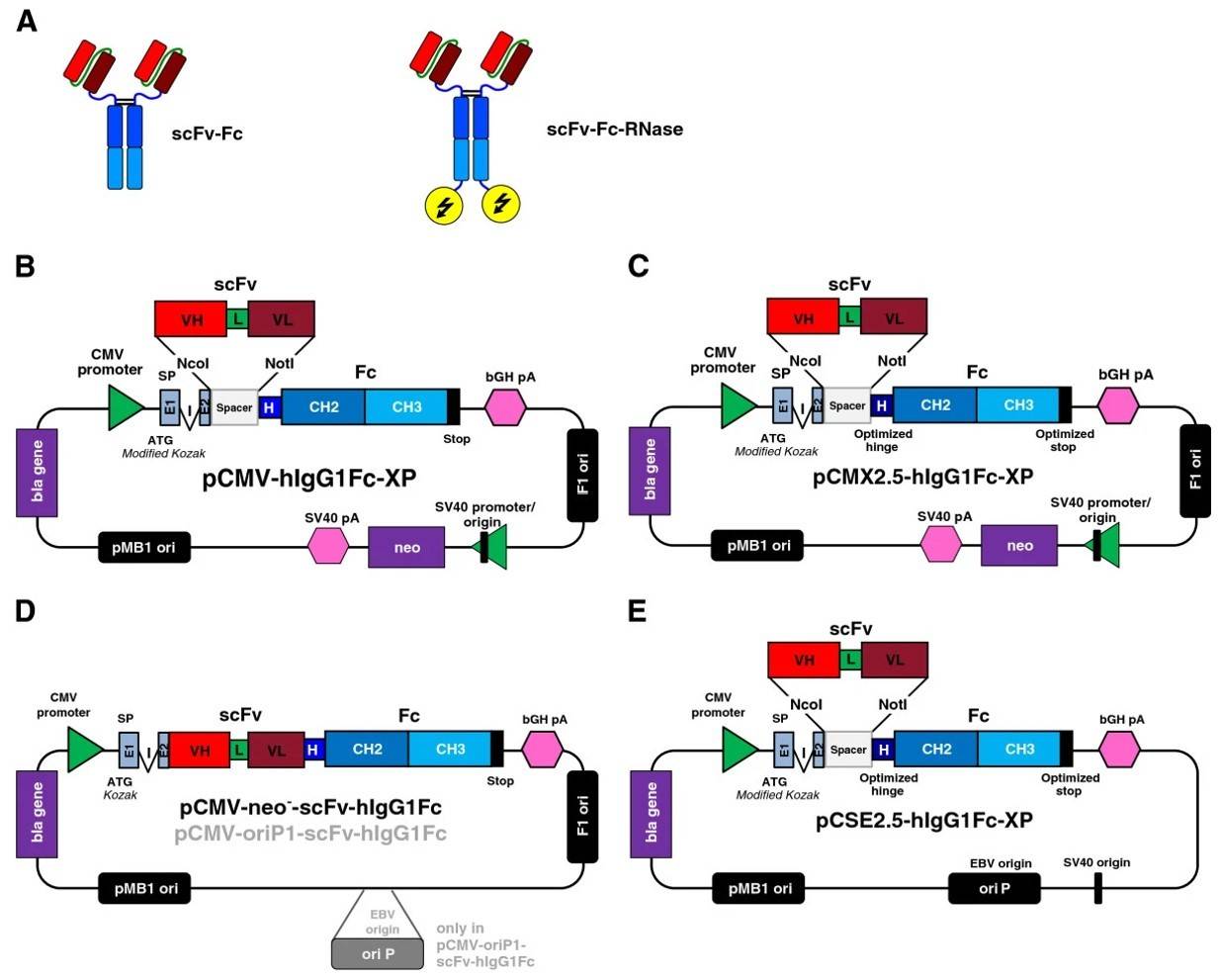 Fig.1 Development of vectors for expression of recombinant antibodies in HEK293 cell lines.1
Fig.1 Development of vectors for expression of recombinant antibodies in HEK293 cell lines.1
Human Cell Lines
HEK 293
One way to favor human-like glycosylation would be to use human cell lines for recombinant protein production. The HEK 293 cell line, derived from human embryonic kidney cells. This cell line has been used for a long time in the production of pseudotyped viral vectors and in the production of recombinant proteins to be used in research studies. Recently, this cell line has been the first human cell used to produce a commercial recombinant therapeutic product. The HEK 293E cell line is the most widely used cell line for large-scale transient gene expression. HEK 293 cell line is easily adapted to grow in serum-free suspension cultures and presents fast growth, and it is highly transfectable and transfusible, so these cells are a great candidates for use in high-throughput recombinant gene expression facilities.
CAP
CAP cells, which show humanlike posttranslational modifications and authentic human glycosylation patterns, also grow in serum-free suspension cultures, allowing stable protein production, and can be very efficiently transfected with commercially available transfection reagents.
HKB11
HKB11 is a human hybrid cell line. The hybrid cell line is capable of secreting high levels of recombinant proteins with human glycosylation profiles and non-aggregating properties. HKB11 clone was selected for nonaggregating properties and possesses typical human glycosylation enzymes such as α(2,3) and α(2,6) sialyltransferases. The main advantages of using these hybrid cells include: (1) the cells are negative for immunoglobulin expression; (2) they grow easily in plasma protein-free medium; (3) they are very susceptible for DNA transfection; (4) and they secrete high levels of recombinant proteins.
PER.C6
The PER.C6 cell line was established from human embryonic retinoblasts (PER.C6) transformed with adenovirus type 5. This cell line was initially developed for the safe production of pharmaceutical grade recombinant human adenoviral vectors used in vaccine and gene therapy purposes. PER.C6 was also used for producing classical vaccines including influenza and West Nile Virus. Recently, PER.C6 cells were also evaluated for the production of therapeutic proteins. PER.C6 cell line is considered one of the most advanced of the various human cell line alternatives to substitute CHO cells for recombinant therapeutic protein and antibody production.
Glycosylation Pattern in Human Cell Lines
While other expression systems allow the production of the target protein at high levels in low-cost culture media, mammalian cell cultures require complex and costly media to maintain their growth and protein expression. Most of the proteins used in human therapeutic approaches are glycol-proteins, such as coagulation factors and monoclonal antibodies. The oligosaccharides added to the primary chain of the protein directly affect the efficacy and safety of the biopharmaceutical product. Glycosylation is the most complex posttranslational protein modification. Mammalian cells can produce fully glycosylated proteins; however, there are differences in the glycosylation patterns intra- and interspecifically. Thus, human cell lines are more appropriate to be used in the production of recombinant human therapeutic proteins. Human cell lines are more suitable to produce human recombinant proteins, and the use of this expression system will diminish the presence of immunogenic glycan structures in the final recombinant proteins. However, the production in human cell lines does not avoid the presence of antigenic structures.
Advances in the production of biopharmaceuticals have evolved from cell engineering and bioprocess development of efficient expression systems that produce glycoproteins with appropriate structures for efficacious clinical application. Future developments in the expression systems will focus on the enhancement of productivity to meet the growing demand for these products and the refinement of their function so that the dosage requirements are minimized. You can choose from our mature mammalian cell expression system to get the high-quality glycoproteins you need.
Creative Biolabs is the premier glycoprotein expression contract manufacturer in the United States. We can accommodate your needs for a variety of expression systems. We are constantly improving our glycoprotein acquisition process and delivering products to you faster. If you are interested in our services and technologies, please feel free to contact us for more details.
Reference
-
Jäger, Volker, et al. "High level transient production of recombinant antibodies and antibody fusion proteins in HEK293 cells." BMC biotechnology 13 (2013): 1-20. Under Open Access license CC BY 2.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Development of vectors for expression of recombinant antibodies in HEK293 cell lines.1
Fig.1 Development of vectors for expression of recombinant antibodies in HEK293 cell lines.1

