Glycoprotein Function as Hormone
Creative Biolabs is a world-class biotechnology service company. We have more than ten years of experience in the field of biopharmaceuticals, with professional technical personnel and complete synthesis and analysis equipment. Based on these advantages, we have established a glycoprotein service platform that can provide several glycoproteins-related services.
Glycoprotein Function as Hormone
One of the important functions of glycoproteins as biologically active molecules is hormonal function. Glycoprotein hormones are a family of structurally similar hormones that are divided into two main groups: 1) gonadotropins, including luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and chorionic gonadotropin (CG), which play a key role in the control of reproductive function; and 2) thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is primarily used to control thyroid activity.
Primary Structure of Glycoprotein Hormones
In recent years, scientists have elucidated the structure of glycoprotein hormones and the mechanism of their receptor recognition activation, contributing to the clinical development of small molecule drugs to replace hormone therapy. Glycoprotein hormones are composed of two dissimilar subunits, named α and β, that are associated with noncovalent bonds. Within each species the amino acid sequence of the α-subunits of the different glycoprotein hormones was identical. The α-subunits of all glycoprotein hormones are coded by a single gene, separate from the β-genes. This gene is expressed in the various pituitary and placental cells secreting the different glycoprotein hormones. Nevertheless, although α-subunits exhibit identical amino acid sequences in a given species, their N-linked oligosaccharide chains are generally different. These are necessary for the conservation of the overall three-dimensional structure of the molecule, for the binding to the β-subunits, for the binding to the receptors, and also for the possible non-gonadotrope role of free α. Of course, the hormone-specific β-subunits of glycoprotein hormones exhibit different amino acid sequences.
Conformational changes occur when the α-subunit, responsible for high affinity for its receptor, binds with the β-subunit, responsible for specificity, which further leads to the active conformation of the hormone heterodimer.
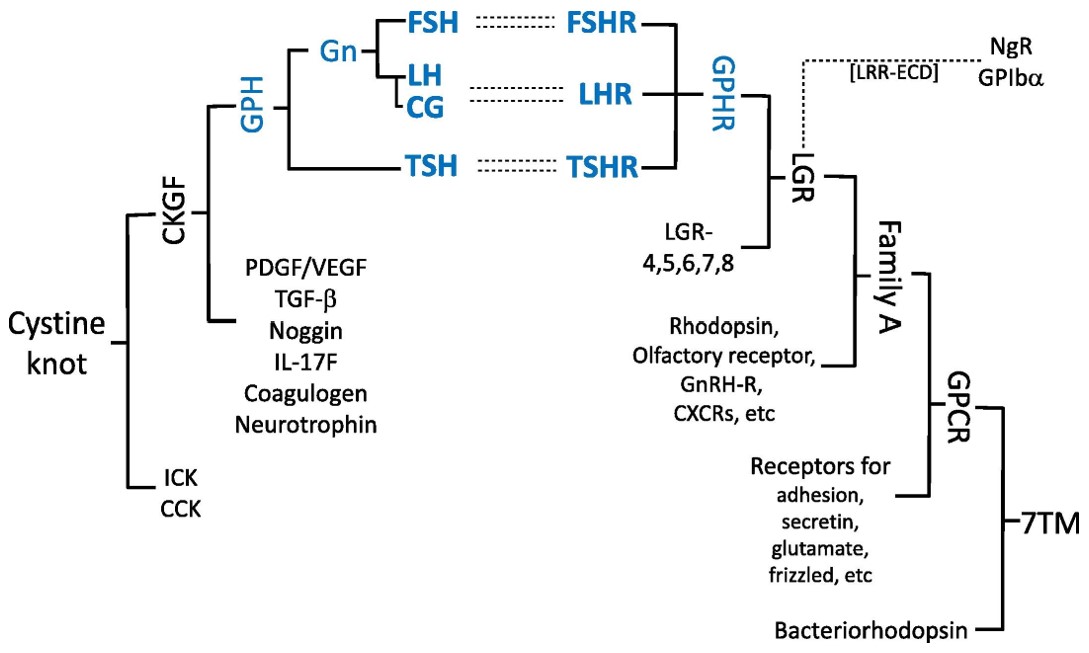 Fig.1 Glycoprotein hormones and their receptors.1, 2
Fig.1 Glycoprotein hormones and their receptors.1, 2
Services at Creative Biolabs
Glycoprotein hormone is a key drug for assisted reproduction and therapy of thyroid diseases. Its clinical application has been successful for decades and its annual sales reach billions of dollars.
Creative Biolabs owns lots of Ph.D. level scientists in the field of glycoprotein hormones and has extensive research on the structures and specific functions of different glycans of natural and recombinant glycoprotein hormones, which will be useful in the development of diagnostic and therapeutic applications of the glycoprotein hormones. We offer a range of Glycoengineering Services to meet a wide range of glycoprotein synthesis needs. If you have any questions about glycoprotein hormones, please contact us for more information.
References
-
Jiang, Xuliang, James A. Dias, and Xiaolin He. "Structural biology of glycoprotein hormones and their receptors: insights to signaling." Molecular and cellular endocrinology 382.1 (2014): 424-451.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Glycoprotein hormones and their receptors.1, 2
Fig.1 Glycoprotein hormones and their receptors.1, 2

