Glycoproteins Function as Transport Molecules
Equipped with professional scientific staff in glycoengineering of proteins and perfect equipment, Creative Biolabs has established a gycoengineering technology platform covering various services, which can provide our customers with personalized Glycoengineering Service.
Glycoproteins Function as Transport Molecules
Glycoproteins play an important role in a variety of biological processes. Among them, an important role of glycoprotein modified by N-glycosylation is its transport function. Many drugs rely on transport molecules on tissue membranes to mediate the passage of cell membranes to exert their pharmacological functions. Multispecific drug transporters usually come from two transporter superfamilies: the solute carrier transporters and the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. Among them, the ABC drug transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) is one of the best-studied mammalian transporters from the atomic level to clinical populations.
Introduction of P-gp
P-glycoprotein was first discovered in the colchicine-resistant Chinese hamster ovary in 1976. Initial studies found that this protein is mainly highly expressed in drug-resistant tumor cells. However, as the study progressed, it was found that there are also extensive P protein distributions in normal healthy tissues, mainly concentrated in absorption and excretion-related tissues and various barrier systems. Its main physiological function is to prevent the human body from absorbing harmful substances and regulate the output of substances, thereby protecting important tissues and organs such as the brain, testicles, fetus, bone marrow, etc.
The Effect of P-gp on Drug Absorption
P-gp is expressed in the small intestine of both humans and domestic animals and is localized to the intestinal villi epithelium, where it can influence drug absorption by recognizing substrates and excreting them into the intestinal lumen. During oral administration, the efflux of drugs by intestinal P-gp is an important reason for poor oral absorption and large variability. Substrate drugs with a narrow safety range may even cause poisoning. In addition, overexpression of P-gp by tumor cells may cause tumor multidrug resistance, which may lead to chemotherapy failure. Therefore, the use of P-gp inhibitors to reverse tumor multidrug resistance is the key to improving the efficacy of tumor chemotherapy.
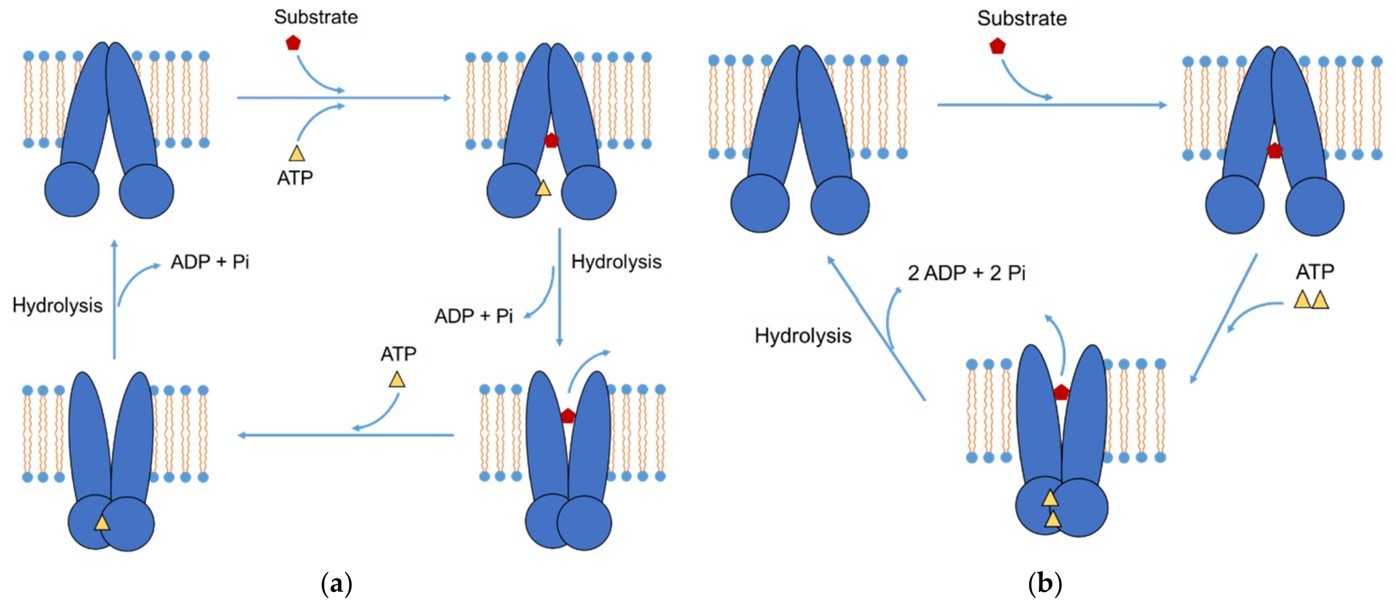 Fig.1 P-gp efflux mechanism.1, 2
Fig.1 P-gp efflux mechanism.1, 2
Substrates and Inhibitors of P-gp
The substrates of P-gp include natural products, antibacterial drugs, antiviral drugs, chemotherapeutics, peptides, steroids, ionophores and fluorescent dyes, etc. Most of these substrates are lipophilic compounds, often containing positively charged N atoms or aromatic rings. P-gp inhibitors are of various types and structures. It is mainly divided into three categories: small molecule inhibitors, natural product extracts and pharmaceutical excipients. In drug development, such excipients can be used to improve the bioavailability of difficult-to-absorb P-gp substrate drugs.
Services at Creative Biolabs
As a transport protein, P-glycoprotein can limit the absorption and distribution of drugs, which is an important factor affecting the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in the body. Therefore, P-glycoprotein inhibitors or inducers are very important in changing the effects of drugs, such as increasing drug absorption, reducing drug elimination and regulating the distribution in tissues.
Creative Biolabs has Ph.D. level technical personnel and years of research foundation in glycoprotein transport function, which can greatly promote your research progress in drug transport. Our services include but are not limited to Glyco-engineered Mammalian Cell Expression System, Glyco-engineered Pichia pastoris Expression System, Glyco-engineered Plant-based Expression System. If you have any questions about glycoengineering, please contact us for more information.
References
-
Nguyen, Thi-Thao-Linh, Van-An Duong, and Han-Joo Maeng. "Pharmaceutical formulations with P-glycoprotein inhibitory effect as promising approaches for enhancing oral drug absorption and bioavailability." Pharmaceutics 13.7 (2021): 1103.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 P-gp efflux mechanism.1, 2
Fig.1 P-gp efflux mechanism.1, 2

