Glycoprotein Function as Enzyme
Carbohydrates are ubiquitous in nature, and there is little doubt that the elaborate carbohydrate constructs observed on the surface of cells and proteins hold the key to understanding many complex biological processes. For example, glycoproteins have been reported to exhibit a pivotal role in processes as diverse as fertilization, neuronal development, hormone activities, immune surveillance, and inflammatory responses.
some examples of glycoproteins
Creative Biolabs offers custom services and technologies for glycoprotein study. Here are some examples of glycoproteins that function as enzymes.
Example One: Alkaline Phosphatases (ALPs)
ALPs are plasma membrane-bound glycoproteins. ALP forms a large family of dimeric enzymes, usually confined to the cell surface hydrolyzes various monophosphate esters at a high pH optimum with the release of inorganic phosphate.
-
Physiological Functions of ALP
ALP has been investigated continuously and extensively. But little is known regarding the physiological function of ALPs in most tissues except that the bone isoenzyme has long been thought to have a role in normal skeletal mineralization. A variety of mechanisms have been proposed to explain the role of ALP in bone mineralization. However, apart from its role in normal bone mineralization, the other functions of L/B/K remain obscure both in physiological and neoplastic conditions.
-
ALP in Health and Diseases
The activity of liver and bone ALPs in serum has been applied extensively in routine diagnosis. The enzyme ALP is an important serum analyte and its elevation in serum is correlated with the presence of bone, liver, and other diseases. High ALP levels can show that the bile ducts are obstructed. Levels are significantly higher in children and pregnant women. Also, elevated ALP indicates that there could be active bone formation occurring as ALP is a byproduct of osteoblast activity or a disease that affects blood calcium level, vitamin D deficiency, or damaged liver cells. Lowered levels of ALP are less common than elevated levels. Some conditions or diseases may lead to reduced levels of ALP. In addition, the drugs such as oral contraceptives have been demonstrated to reduce ALP.
Several studies have indicated the involvement of ALPs in cellular events such as the regulation of protein phosphorylation, cell growth, apoptosis, and cellular migration during embryonic development. The aberrant expression of ALP genes in cancer has led to the suggestion that ALP isozymes may be involved in tumorigenesis.
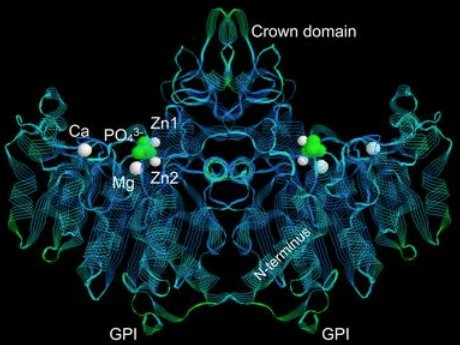 Fig.1 3D structure of alkaline phosphatase.1, 3
Fig.1 3D structure of alkaline phosphatase.1, 3
Example Two: Patatin Primary Structural Properties and Effects on Lipid Metabolism
Patatin is the trivial name given to a family of glycoproteins that make up >40% of the total soluble protein in potato tubers and serve as a storage protein. Patatin was an O-linked glycoprotein that contained fucose monosaccharides, as well as mannose, rhamnose, glucose, galactose, xylose, and arabinose. Patatin has antioxidant activity and potential anti-cancer effects. Patatin had a fucosylated glycan structural feature, which strongly bound AAL, a known fucose binding lectin. In addition, patatin is a lipid hydrolase whose folding topology is different from that of traditional lipases and is unique. In recent years, a family of mammalian lipid hydrolases called patatin-like phospholipase domains (PNPLA) has attracted widespread attention from researchers because researchers have found that members of this family play an important role in lipid metabolism and signal transduction.
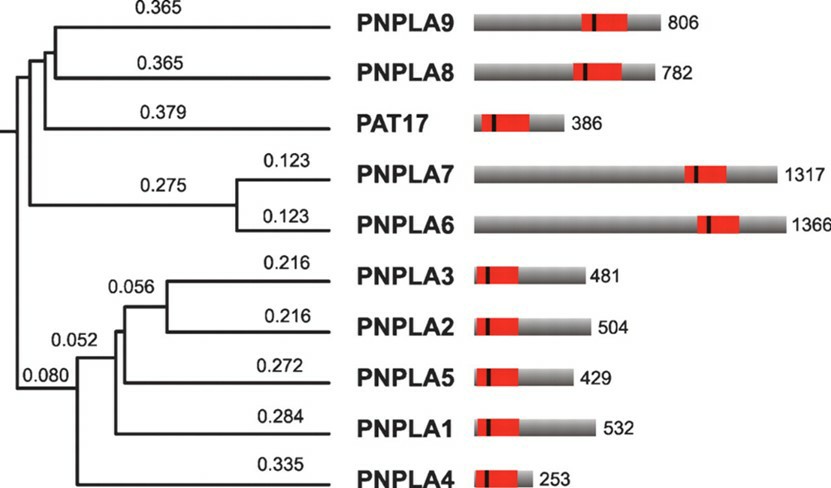 Fig.2 Phylogenetic relationships and structural comparison of PNPLA1-9.2, 3
Fig.2 Phylogenetic relationships and structural comparison of PNPLA1-9.2, 3
Custom Services for Glycoprotein With Enzyme Functions
Creative Biolabs is a comprehensive and leading biology company. When it comes to researching glycoprotein, you need to partner with a company with a proven track record of success and state-of-the-art technology that can get the job done quickly and efficiently. For these reasons, scientists consistently choose Creative Biolabs as the partner they want to work with. If you are interested in our services or technologies, please contact us for more details.
References
-
Millán, José Luis, and Michael P. Whyte. "Alkaline phosphatase and hypophosphatasia." Calcified tissue international 98 (2016): 398-416.
-
Kienesberger, Petra C., et al. "Mammalian patatin domain containing proteins: a family with diverse lipolytic activities involved in multiple biological functions." Journal of lipid research 50 (2009): S63-S68.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 3D structure of alkaline phosphatase.1, 3
Fig.1 3D structure of alkaline phosphatase.1, 3
 Fig.2 Phylogenetic relationships and structural comparison of PNPLA1-9.2, 3
Fig.2 Phylogenetic relationships and structural comparison of PNPLA1-9.2, 3

