Glycoproteins Interact with Specific Carbohydrates
The functions of glycoproteins are tremendously broad and include cell attachment recognition, homeostasis, transport of molecules, and enzymatic and immunology recognition domains. Also, they can interact with specific carbohydrates to play an important role, these glycoproteins include lectins, selectins (cell adhesion lectins), and antibodies.
What are Lectins?
The term lectin is generally applied to all proteins, excluding antibodies. Lectins and hemagglutinin are glycoproteins with at least one non-catalytic domain that can bind to specific monosaccharides or oligosaccharides. They can bind to the carbohydrate portion of the red blood cell surface and agglutinate the red blood cell without changing the carbohydrate properties. Over the years, hundreds of lectins have been isolated from different plants, invertebrates, and animals. Due to their ability to bind specifically to certain carbohydrate sequences, lectins are a frequently used tool in cytology, histology, and glycan analysis but also offer new options for drug targeting and drug delivery systems.
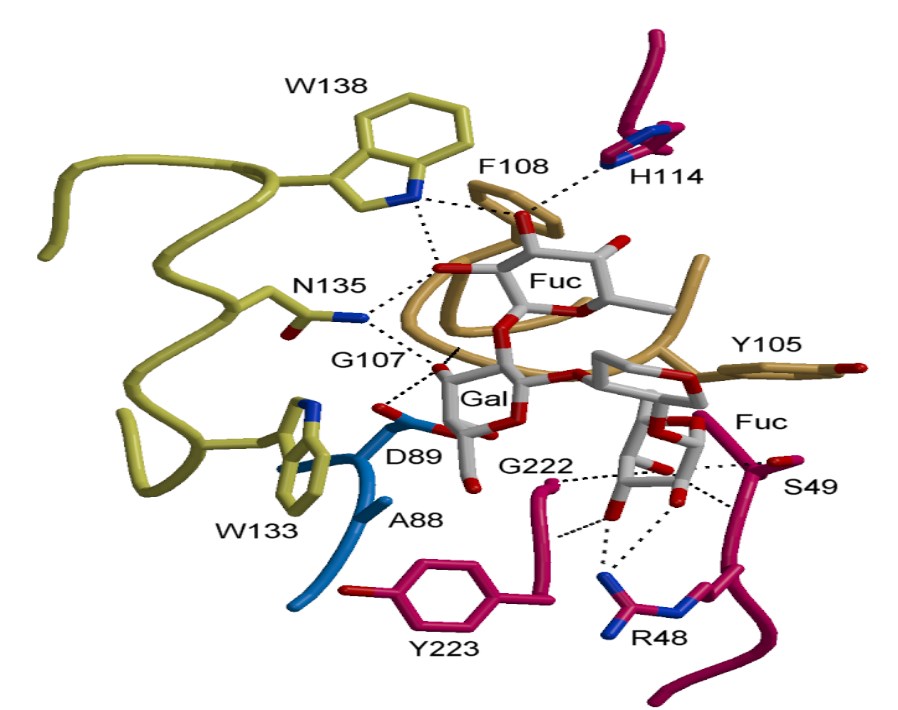 Fig.1 An oligosaccharide (shown in grey) bound in the binding site of a plant lectin.
Fig.1 An oligosaccharide (shown in grey) bound in the binding site of a plant lectin.
Practical Applications
-
Lectins-pathogen Management Strategies
Lectins have been suggested as one of the promising agents against insect pests. Lectins demonstrate anti-insect activity. They increase the mortality or delay the development of the insect. Lectins may also be introduced into plants to protect them from fungi. They cannot directly inhibit fungal growth by altering fungal membrane structure and/or permeability. However, there may be indirect effects produced by the binding of lectins to carbohydrates on the fungal cell wall surface.
It is well documented that lectins have an antitumor effect. Flammulina velutipes hemagglutinin inhibited proliferation of leukemia L1210 cells. Del Monte banana lectin retarded proliferation of (L1210) cells and hepatoma (HepG2) cells. Lectins can induce apoptosis in different cancer cell lines. Apoptosis can be mediated by lectin-induced death receptors. FAS receptor is the receptor with which lectins often interact. This interaction may be caused by protein interaction. Immunofluorescence and/or immunohistochemical studies using lectins can reveal the early precancerous stages of prostate cancer.
D-mannose-specific lectin can prevent H9 cells from infection with human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1. Lectins can inhibit syncytium formation in HTLV-IIIB/H9-Jurkat cell system and HIV-1/Human lymphocyte system through the side-chain reaction of oligosaccharide with HIV-1 GP120 envelope molecule. Later, it was found that concanavalin A, wheat germ agglutinin, lens culinaris agglutinin could also bind to gp120. Through carbohydrate-specific interactions with HIV-infected cells, they were able to inhibit the fusion of HIV-infected cells with CD4 cells.
Production of Lectins
Lectins occur in nature. It can be purified from different organisms. In addition, lectins can also be produced by recombinant techniques. To produce large quantities of lectin, large-scale fermentation under GMP conditions is the only method. E. coli is the most commonly used expression system. Different strains were selected to express different lectins. Creative Biolabs provides glycoengineering services to produce different glycoproteins.
Creative Biolabs has been focusing on glycoprotein research for many years. With a senior expert team, enthusiastic technical team, and cutting-edge technology, we have completed many glycoprotein projects. If you are interested in our services or technology, please contact us for more details.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 An oligosaccharide (shown in grey) bound in the binding site of a plant lectin.
Fig.1 An oligosaccharide (shown in grey) bound in the binding site of a plant lectin.

