Glycoprotein Structure
Glycoproteins are the carbohydrate conjugated complex biological macromolecules widely distributed in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Although biosynthetic studies have shown that glycoproteins from diverse sources have similar carbohydrate units and types of enzymatic machinery to attach the sugar residues to the completed peptide chain, glycoproteins are biologically diverse due to the difference of carbohydrate units, glycan-protein linkages, and peptide moieties. Because of these structural diversities, the synthesis and function research of glycoproteins attracts more attention in the field of protein engineering. Based on rich experience and an established platform in the protein research field, Creative Biolabs has developed different glycoprotein-related services to support your protein studies. Moreover, we have launched a customized glycosylation modification and detection service to meet the unique requirements of every client.
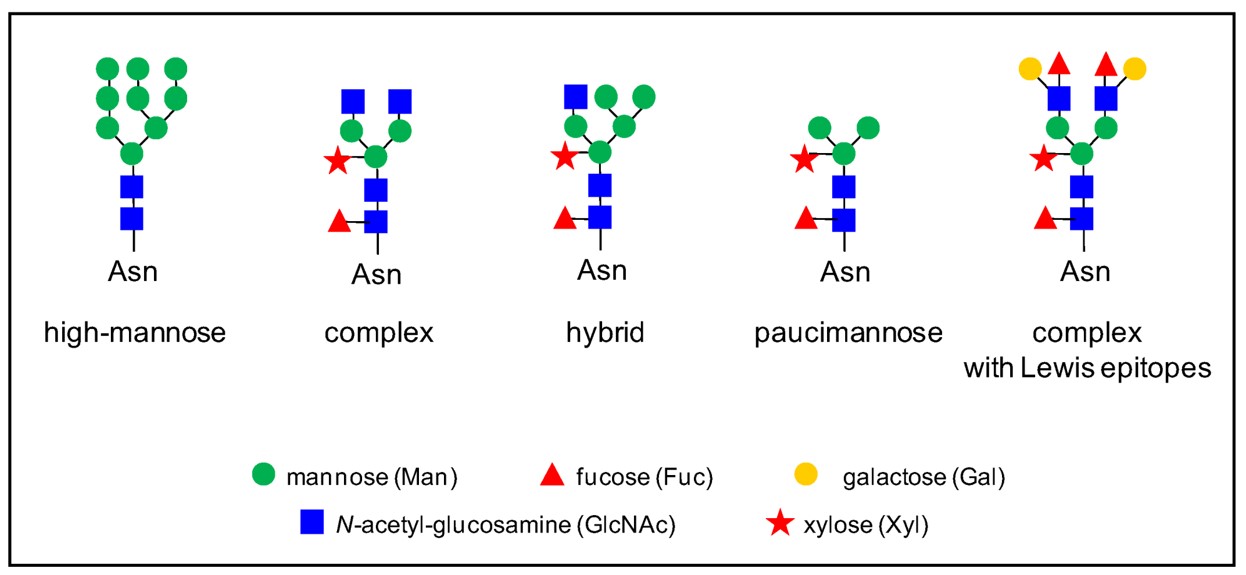 Fig.1 N-glycan structures on plant N-glycoproteins.1, 2
Fig.1 N-glycan structures on plant N-glycoproteins.1, 2
Introduction of Glycoprotein Structure
Various types of compounds consisting of carbohydrates covalently linked with other types of the chemical constituent are classified under the general name of glycoconjugates, among which glycoproteins occupied an important position due to their wide distribution and irreplaceable function. Glycoproteins can be simply defined as proteins to which carbohydrate is covalently attached. Over 40 different glycosidic bonds between sugars and amino acids, involving 8 amino acids and 13 different monosaccharides, have been identified. Glycan chains are assembled in the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi by a controlled sequence of glycosyltransferase and glycosidase processing reactions involving dolichol intermediates. However, the assembly of O-glycans occurs only in the Golgi and does not involve dolichol.
Classification of Glycoprotein Structure
There are several types of glycosylation while the O-glycans and N-glycans are the most common. The glycoproteins of these two types contain oligosaccharides based on N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) α-linked to serine or threonine (O-glycans), and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) β-linked to asparagine (N-glycans). Additional types of O-linked glycans have recently been described and include those based on Fucα, Glcβ or Manα linked glycoprotein. These complex glycans are synthesized by a series of glycosyltransferase reactions, and in the case of N-glycans, also glycosidase reactions that process glycan chains to their cell type-specific forms.
However, some unusual glycosylation also appears in vivo which is often via specific glycosidic bonds. For example, in the addition of mannose to tryptophan, mannose units are attached directly to carbon called C-glycosylation. Similarly, a β-GlcNAc is attached to the sulfur atom of a cysteine residue called S-glycosylation, and sugars are attached to phosphorus on a phosphoserine called P-glycosylation. Moreover, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) glycolipid is usually attached to the C-terminus of a polypeptide serving as a membrane anchor.
The research of structure-activity relationships of glycoproteins is important to understand the bioactivities of glycoproteins in vivo. Creative Biolabs offers all-sided and one-stop glycoprotein structure-related services to help your research. For more detail on glycoprotein structure or our company, please click follow key words or directly contact us.
References
-
San Clemente, Hélène, and Elisabeth Jamet. "N-Glycoproteins in plant cell Walls: a survey." Plants 11.23 (2022): 3204.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 N-glycan structures on plant N-glycoproteins.1, 2
Fig.1 N-glycan structures on plant N-glycoproteins.1, 2

