Current Detection Methods of Glycoprotein
Overview of Glycoprotein
Glycoproteins, the family of glycosylated proteins, are a kind of cis-diol-containing biomolecule. Large quantities of glycoproteins are found in nature, including enzymes, antigens, antibodies, and peptide hormones. As we can see, glycoproteins play a vital role in the biological activities of organisms, such as in cell recognition, immunomodulation, and growth regulation. Meanwhile, abnormal glycosylation of proteins in vivo is an important feature in disease progression, being related to the occurrence and development of many diseases, such as infections, tumors, cardiovascular diseases, liver diseases, kidney diseases, diabetes, and certain genetic diseases, so the detection of glycoproteins is of great value in clinical diagnosis, biological research, disease prevention, and so on. The traditional methods of glycoprotein detection, such as mass spectrometry, chromatography-mass spectrometry, and ELISA, are time-consuming, professional, and demanding for sample purity. So in recent studies, researchers developed various novel detection methods.
Current Detection Methods of Glycoprotein
-
Fluorescent boronic acid-based molecularly imprinted polymer
Glycoproteins, as key disease biomarkers, play a vital role in early diagnosis. Traditional glycoprotein detection methods rely on expensive biochemical reagents such as lectins and enzymes, so there is an urgent need to develop synthetic alternatives to simplify the detection process. In recent years, molecular imprinting technology has been applied to construct specific binding sites in polymers and extended to proteins and cell surfaces. These molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) show excellent stability and reusability. This study aims to evaluate the feasibility of using boronate-coupled fluorescent probes to detect glycoproteins captured by MIPs. The researchers selected three glycoproteins with different glycosylation patterns for experiments and successfully identified horseradish peroxidase. The results showed that imprinted nanoparticles suitable for sandwich detection could be prepared by covalently fixing glycoprotein templates and initiating dopamine polymerization. This method was not only low-cost and highly stable but also provided new possibilities for the development of simpler, faster, and more cost-effective glycoprotein analysis techniques.
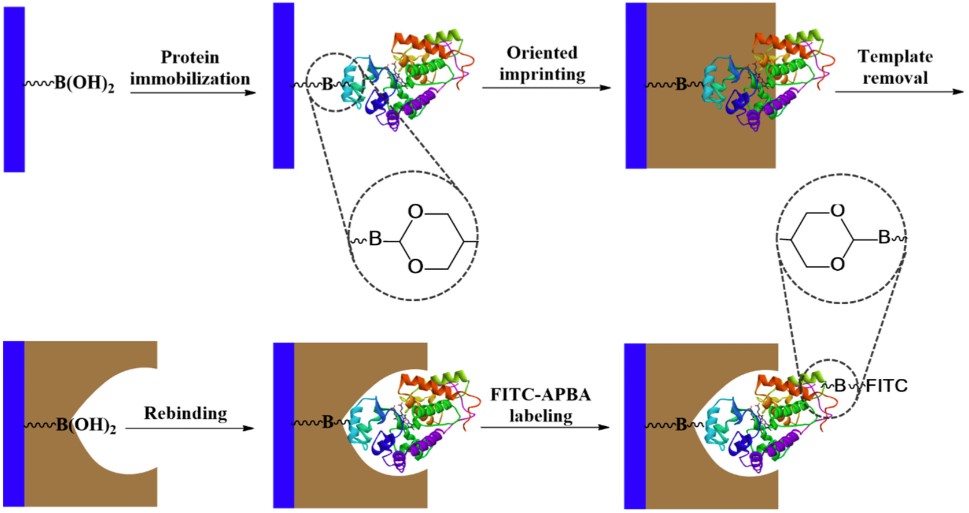 Fig.1 Boronic acid-fluorescein conjugate (BA-FITC) was used to detect glycoproteins captured by MIPs.1, 3
Fig.1 Boronic acid-fluorescein conjugate (BA-FITC) was used to detect glycoproteins captured by MIPs.1, 3
Boronate affinity materials (BAMs) are a kind of novel adsorbent material based on the properties of specific binding between boronic acid and cis diols, which actively contribute to the recognition, separation, enrichment, or detection of cis-diols. This study developed an innovative boric acid affinity three-dimensional ordered macroporous (3DOM) material, which combined boric acid affinity technology and colloidal crystal template method to simplify the preparation process. The material was characterized in detail by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, electron microscopy, and other methods. The results showed that it had a high specific surface area and porosity, and was rich in boric acid recognition sites. The experimental results showed that this 3DOM material could achieve an adsorption capacity of 438.79 mg/g for ovalbumin (OVA), showing excellent selectivity and kinetic properties. In addition, the material could also effectively capture glycoproteins containing cis-diols and had good selectivity and high-throughput potential for the separation and enrichment of cis-diol molecules in complex samples.
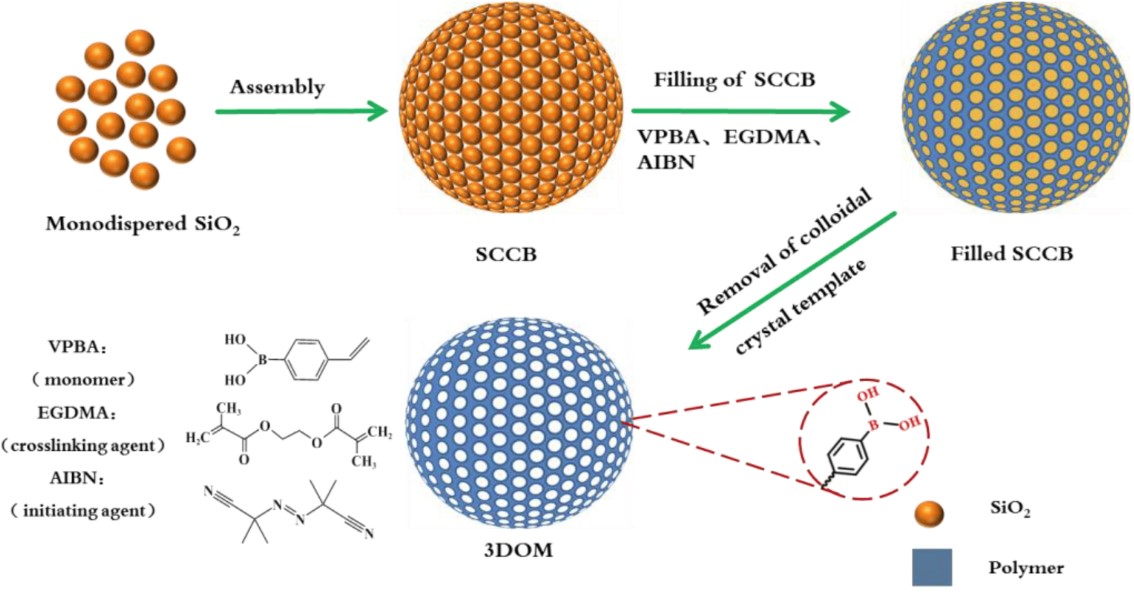 Fig.2 Preparation process of 3DOM materials.2, 3
Fig.2 Preparation process of 3DOM materials.2, 3
-
Multifunctional oligomer immobilized on quartz crystal microbalance
In another study, researchers developed a novel multifunction oligomer-modified QCM biosensor for glycoprotein. In this work, a multifunctional oligomer was prepared via free radical polymerization and a glycoprotein-imprinted crosslinked film was fabricated directly on the transducer surface of quartz crystal microbalance. Results of template rebinding tests had proven that the cross-linking process film could successfully conserve the orientation of imprinted sites in the aqueous environment and possessed a much higher affinity towards template OVA than that of the non-cross-linked assays. The specific binding affinity was further testified by three distinct control proteins, and the imprinted assay revealed large selectivity factors towards template glycoprotein. This facile and simple strategy holds great promise to fabricate efficient and specific devices for specific tumor marker detection.
Services at Creative Biolabs
With rich experience and advanced technology platform, Creative Biolabs is capable of offering global customers comprehensive glycoprotein-based services including but not limited to:
If you are interested in our services or you have any other questions, please don't hesitate to contact us for more information.
References
-
Jiang, Lingdong, Rui Lu, and Lei Ye. "Towards detection of glycoproteins using molecularly imprinted nanoparticles and boronic acid-modified fluorescent probe." Polymers 11.1 (2019): 173.
-
Li, Zhipeng, et al. "Synthesis and Characterization of Boronate Affinity Three-Dimensionally Ordered Macroporous Materials." Polymers 16.11 (2024): 1539.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Boronic acid-fluorescein conjugate (BA-FITC) was used to detect glycoproteins captured by MIPs.1, 3
Fig.1 Boronic acid-fluorescein conjugate (BA-FITC) was used to detect glycoproteins captured by MIPs.1, 3
 Fig.2 Preparation process of 3DOM materials.2, 3
Fig.2 Preparation process of 3DOM materials.2, 3

