Monosaccharide Types and Constituents
Monosaccharides are the basic components of glycan side chains on the glycoprotein. With the corresponding glycosyltransferase, monosaccharides are linked to oligosaccharides, which are then covalently attached to the binding sites of proteins or peptides. Although the different monosaccharide units constitute a wide variety of glycoproteins, the types and arrangements of these monosaccharides still showed certain conservation in different types of glycoproteins, which is closely related to the function of glycoproteins. While the research of monosaccharide units has been regarded as the basis of the glycoprotein structure-function relationship. Therefore, as an outstanding service provider, Creative Biolabs offers the most comprehensive and professional monosaccharides modification and analysis services to advance clients' projects all over the world.
Introduction of Monosaccharide
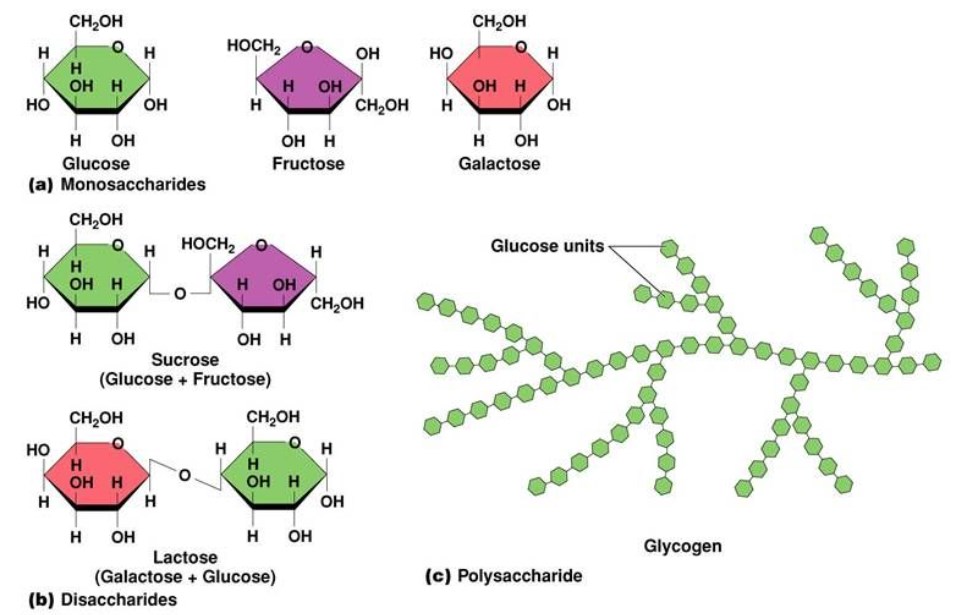 Fig.1 Typical structure of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polyaccharides.1, 2
Fig.1 Typical structure of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polyaccharides.1, 2
Monosaccharides are the simplest and smallest molecules of the carbohydrates and act as basic units in oligosaccharides and polysaccharides, both of which contain more than one sugar unit and can be hydrolyzed to release their constituent monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketoses with reactive carbonyl groups, which readily undergo nucleophilic attack by the unshared electrons of the oxygen atom of a hydroxyl group to produce a hemiacetal. Therefore, many monosaccharides form pyranose or furanose rings as stable structures. Saccharide units are joined together in a head-to-tail fashion by glycosidic linkages to compose oligosaccharides and polysaccharides chains. As a result, each oligosaccharide or polysaccharide molecule has one reducing end which can be attached to protein particularly amino acid residue covalently. While many carbohydrates are used to store and provide energy, the glycan chains of glycoproteins play important roles to maintain their biological functions such as cell recognition, fertilization, and development.
Common Monosaccharide Types in Glycoproteins
Since not all naturally occurring sugars have a hydroxyl group on every carbon atom, the monosaccharide units maintain diversity and form various polysaccharides. However, there are many monosaccharides commonly found in eukaryotic glycoproteins including β-D-glucose (Glc), β-D-galactose (Gal), β-D-mannose (Man), α-L-fucose (Fuc), N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuNAc), and β-D-xylose (Xyl). All of them contain pyranose rings and permute to form glycan chains on glycoproteins. The sugar group can assist in protein folding, improve proteins stability, and are involved in cell signaling.
Although single monosaccharides cannot maintain the complete biological function, the research of monosaccharide types and constituents leads to a clear understanding of the structure-function relationship of glycoproteins. Therefore, Creative Biolabs provides various services focusing on the detection, synthesis, and evaluation of glycoproteins. Moreover, we launched a customized glycosylation service including the introduction of unnatural monosaccharides and glycosylation modification on specific sites. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
References
-
Emsley, Paul, and Max Crispin. "Structural analysis of glycoproteins: building N-linked glycans with Coot." Acta Crystallographica Section D: Structural Biology 74.4 (2018): 256-263.
-
Under Open Access license CC BY 2.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Resources

 Fig.1 Typical structure of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polyaccharides.1, 2
Fig.1 Typical structure of monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polyaccharides.1, 2
