Sodium channel protein type 10 subunit alpha protein (SCN10A) encoded by the SCN10A gene is a tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunit. The protein contains 1956 amino acids, and molecular mass of the protein is 220 kDa. The sequence has 4 internal repeats, each with 5 hydrophobic segments (S1, S2, S3, S5, S6) and one positively charged segment (S4). S4 may be a voltage sensor characterized by a series of positively charged amino acids at every three positions. SCN10A is expressed in the dorsal root ganglia and sciatic nerve. The channel consists of an ion-conducting pore forming alpha-subunit regulated by one or more associated auxiliary subunits SCN1B, SCN2B and SCN3B; electrophysiological properties may vary depending on the type of the associated beta subunits.
| Basic Information of SCN10A | |
| Protein Name | Sodium channel protein type 10 subunit alpha |
| Gene Name | SCN10A |
| Aliases | Peripheral nerve sodium channel 3(PN3, hPN3), Sodium channel protein type X subunit alpha, Voltage-gated sodium channel subunit alpha Nav1 |
| Organism | Homo sapiens (Human) |
| UniProt ID | O60242 |
| Transmembrane Times | 24 |
| Length (aa) | 1956 |
| Sequence | MEFPIGSLETNNFRRFTPESLVEIEKQIAAKQGTKKAREKHREQKDQEEKPRPQLDLKACNQLPKFYGELPAELIGEPLEDLDPFYSTHRTFMVLNKGRTISRFSATRALWLFSPFNLIRRTAIKVSVHSWFSLFITVTILVNCVCMTRTDLPEKIEYVFTVIYTFEALIKILARGFCLNEFTYLRDPWNWLDFSVITLAYVGTAIDLRGISGLRTFRVLRALKTVSVIPGLKVIVGALIHSVKKLADVTILTIFCLSVFALVGLQLFKGNLKNKCVKNDMAVNETTNYSSHRKPDIYINKRGTSDPLLCGNGSDSGHCPDGYICLKTSDNPDFNYTSFDSFAWAFLSLFRLMTQDSWERLYQQTLRTSGKIYMIFFVLVIFLGSFYLVNLILAVVTMAYEEQNQATTDEIEAKEKKFQEALEMLRKEQEVLAALGIDTTSLHSHNGSPLTSKNASERRHRIKPRVSEGSTEDNKSPRSDPYNQRRMSFLGLASGKRRASHGSVFHFRSPGRDISLPEGVTDDGVFPGDHESHRGSLLLGGGAGQQGPLPRSPLPQPSNPDSRHGEDEHQPPPTSELAPGAVDVSAFDAGQKKTFLSAEYLDEPFRAQRAMSVVSIITSVLEELEESEQKCPPCLTSLSQKYLIWDCCPMWVKLKTILFGLVTDPFAELTITLCIVVNTIFMAMEHHGMSPTFEAMLQIGNIVFTIFFTAEMVFKIIAFDPYYYFQKKWNIFDCIIVTVSLLELGVAKKGSLSVLRSFRLLRVFKLAKSWPTLNTLIKIIGNSVGALGNLTIILAIIVFVFALVGKQLLGENYRNNRKNISAPHEDWPRWHMHDFFHSFLIVFRILCGEWIENMWACMEVGQKSICLILFLTVMVLGNLVVLNLFIALLLNSFSADNLTAPEDDGEVNNLQVALARIQVFGHRTKQALCSFFSRSCPFPQPKAEPELVVKLPLSSSKAENHIAANTARGSSGGLQAPRGPRDEHSDFIANPTVWVSVPIAEGESDLDDLEDDGGEDAQSFQQEVIPKGQQEQLQQVERCGDHLTPRSPGTGTSSEDLAPSLGETWKDESVPQVPAEGVDDTSSSEGSTVDCLDPEEILRKIPELADDLEEPDDCFTEGCIRHCPCCKLDTTKSPWDVGWQVRKTCYRIVEHSWFESFIIFMILLSSGSLAFEDYYLDQKPTVKALLEYTDRVFTFIFVFEMLLKWVAYGFKKYFTNAWCWLDFLIVNISLISLTAKILEYSEVAPIKALRTLRALRPLRALSRFEGMRVVVDALVGAIPSIMNVLLVCLIFWLIFSIMGVNLFAGKFWRCINYTDGEFSLVPLSIVNNKSDCKIQNSTGSFFWVNVKVNFDNVAMGYLALLQVATFKGWMDIMYAAVDSREVNMQPKWEDNVYMYLYFVIFIIFGGFFTLNLFVGVIIDNFNQQKKKLGGQDIFMTEEQKKYYNAMKKLGSKKPQKPIPRPLNKFQGFVFDIVTRQAFDITIMVLICLNMITMMVETDDQSEEKTKILGKINQFFVAVFTGECVMKMFALRQYYFTNGWNVFDFIVVVLSIASLIFSAILKSLQSYFSPTLFRVIRLARIGRILRLIRAAKGIRTLLFALMMSLPALFNIGLLLFLVMFIYSIFGMSSFPHVRWEAGIDDMFNFQTFANSMLCLFQITTSAGWDGLLSPILNTGPPYCDPNLPNSNGTRGDCGSPAVGIIFFTTYIIISFLIMVNMYIAVILENFNVATEESTEPLSEDDFDMFYETWEKFDPEATQFITFSALSDFADTLSGPLRIPKPNRNILIQMDLPLVPGDKIHCLDILFAFTKNVLGESGELDSLKANMEEKFMATNLSKSSYEPIATTLRWKQEDISATVIQKAYRSYVLHRSMALSNTPCVPRAEEEAASLPDEGFVAFTANENCVLPDKSETASATSFPPSYESVTRGLSDRVNMRTSSSIQNEDEATSMELIAPGP |
SCN10A mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming that in response to a voltage difference across the membrane, the conformation is turned on or off, and then, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which sodium ions can pass according to their electrochemical gradient. SCN10A may play a role in peripheral neuropathic pain mechanisms. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. Diseases associated with SCN10A include episodic pain syndrome, atrial fibrillation, and Brugada syndrome. These diseases are caused by mutations that affect SCN10A expression.
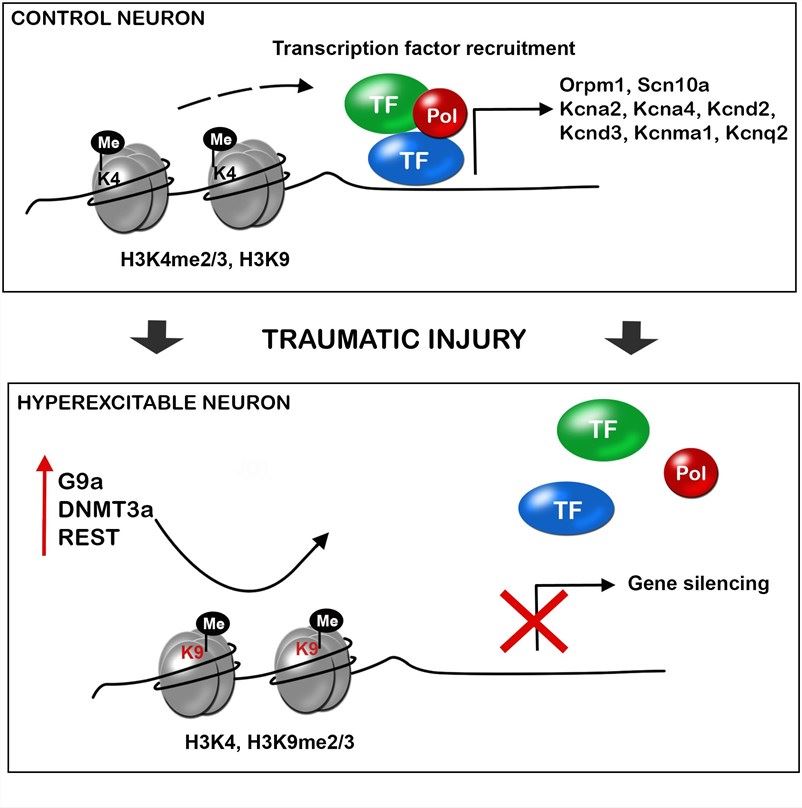 Fig.1 Traumatic injuries of the nervous system induce gene expression alteration in neurons triggering hyperexcitability and neuropathic pain. (Penas, 2018)
Fig.1 Traumatic injuries of the nervous system induce gene expression alteration in neurons triggering hyperexcitability and neuropathic pain. (Penas, 2018)
This article finds that the Brugada syndrome showing loss of NaV1.8 function, as well as rare variants in isolated patients is significantly related to common SNP SCN10A V1073.
This article explains SCN10A genetic variation has an effect on predisposes to arrhythmia and cardiac physiology.
This article suggests that SCN10A greatly improves our ability to genotype and risk stratify probands and family members.
This article reveals that rare and common variants of SCN10A have an effect on the function of the channel, indicating that these variants influence susceptibility to atrial fibrillation.
This article suggests that SCN5A as the key determining factor of cardiac conduction highlights the importance of deciphering the functionality of coding versus noncoding regions when interpreting GWAS data.
Membrane proteins play an important role in many fields. Based on our versatile Magic™ membrane protein production platform, we could offer a series of membrane protein preparation services for worldwide customers in reconstitution forms as well as multiple active formats. Aided by our versatile Magic™ anti-membrane protein antibody discovery platform, we also provide customized anti-SCN10A antibody development services.
During the past years, Creative Biolabs has successfully generated many functional membrane proteins for our global customers. We are happy to accelerate the development of our clients’ programs with our one-stop, custom-oriented service. For more detailed information, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
All listed services and products are For Research Use Only. Do Not use in any diagnostic or therapeutic applications.