A comprehensive catalog of pre-validated kits for synthesizing your own AOCs, enabling rapid prototyping and proof-of-concept studies.
Antibody-Oligonucleotide Conjugate (AOC) Development Service
Are you currently facing challenges with targeted delivery, poor cellular uptake of nucleic acids, or systemic toxicity in your therapeutic development? Creative Biolabs' AOC platform helps you overcome these hurdles and create highly specific therapeutics by combining the unparalleled targeting of antibodies with the potent therapeutic action of oligonucleotides through advanced conjugation technologies. Our solutions are designed to deliver your payload with precision, maximizing efficacy and minimizing off-target effects.
Antibody-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (AOC)
Antibody-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (AOCs) are an innovative class of bioconjugates designed to combine the strengths of two distinct molecular classes: monoclonal antibodies and oligonucleotides. Monoclonal antibodies are renowned for their exceptional specificity in binding to target antigens on cell surfaces, making them ideal for directing payloads to specific tissues or cell types. Oligonucleotides, such as siRNA and ASOs, are powerful therapeutic molecules that can modulate gene expression, but their large size and negative charge make them challenging to deliver into cells on their own. AOCs solve this fundamental delivery problem by using the antibody as a targeted vehicle. This approach ensures that the oligonucleotide payload is delivered directly to the intended cells, enhancing its therapeutic effect while significantly reducing systemic exposure and off-target side effects. This marriage of specific targeting and powerful genetic modulation represents a major advancement in the field of targeted medicine.
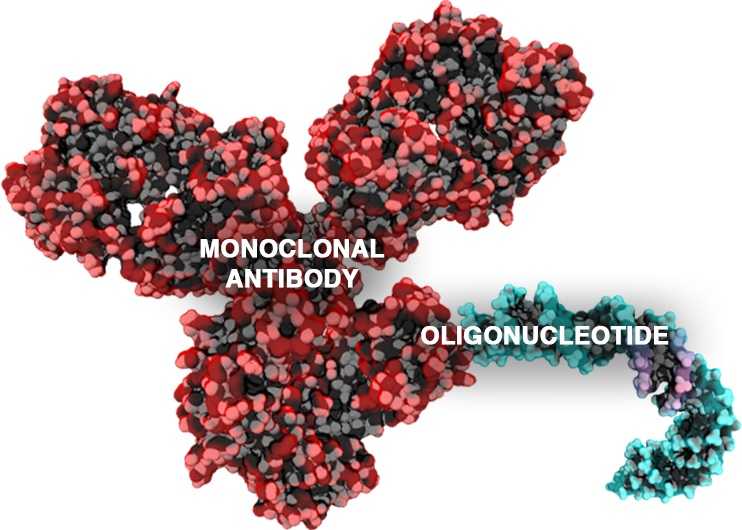 Fig.1 Antibody oligonucleotide conjugate.
Fig.1 Antibody oligonucleotide conjugate.
Our Antibody-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (AOC) Solution
Developing an effective AOC requires careful consideration of the conjugation strategy, which forms the critical link between the antibody and the oligonucleotide. There are several principal methods used to create these conjugates, each with its own advantages and considerations for stability and homogeneity.
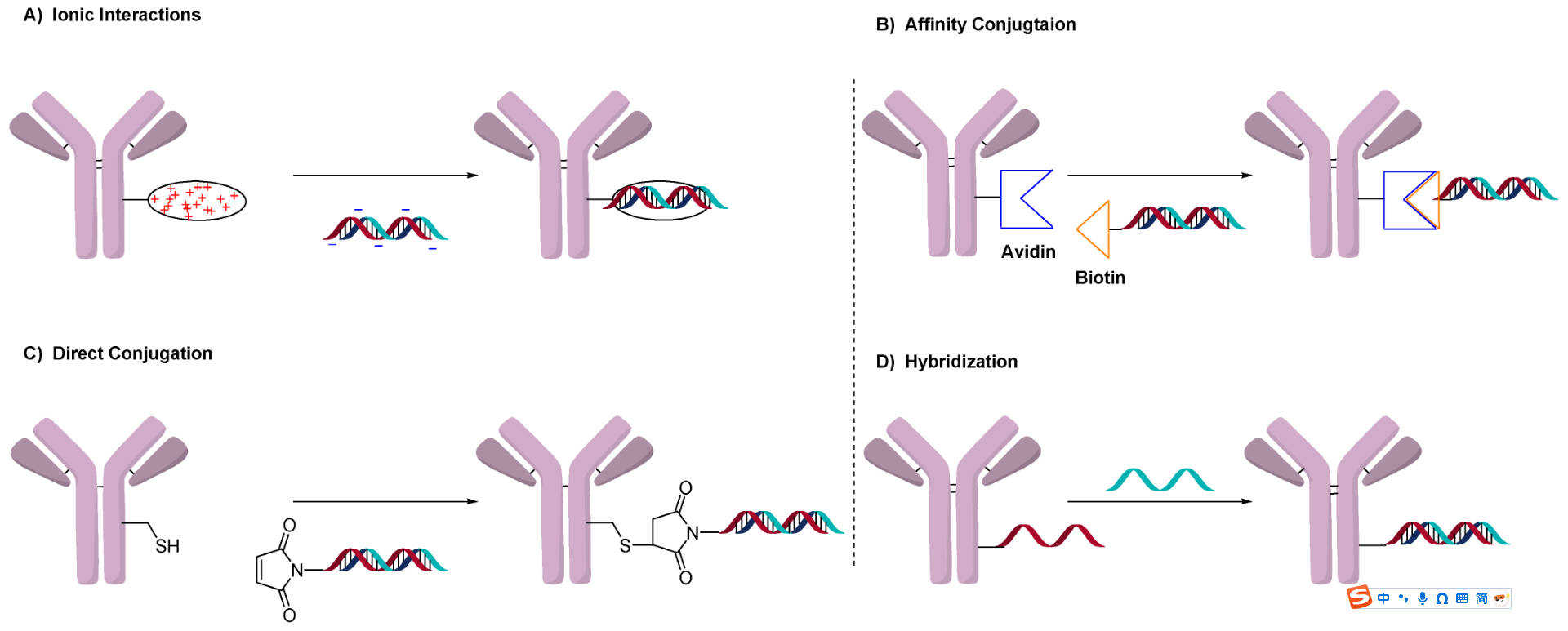 Fig.2 General methods to conjugate oligonucleotides.1,3
Fig.2 General methods to conjugate oligonucleotides.1,3
- Covalent Binding: This is the most common and robust method, involving a direct chemical bond between the antibody and oligonucleotide, often via a linker. These linkers can be cleavable, releasing the payload in a specific cellular compartment, or non-cleavable, which can be useful for certain mechanisms. This approach offers high stability and can be engineered for site-specific conjugation to achieve a well-defined drug-to-antibody ratio (DAR).
- Ionic Interactions: This strategy leverages the electrostatic attraction between a positively charged carrier molecule on the antibody and the negatively charged oligonucleotide. While simple and flexible, these conjugates may be less stable in vivo and could dissociate in different physiological environments.
- Affinity-Based Conjugation: This method, often using the strong biotin-avidin interaction, allows for the non-covalent, but highly stable, attachment of the oligonucleotide to the antibody. It offers a reliable way to create conjugates but can be complex to prepare and may face challenges in vivo.
- Hybridization: This approach involves conjugating a "carrier" oligonucleotide to the antibody, which then hybridizes with the therapeutic oligonucleotide. This allows for modularity and the use of different payloads, but the stability of the hybridization in a biological context must be carefully controlled.
Application
Targeted delivery systems like AOCs and other bioconjugates are transforming the landscape of medicine by enabling the precise delivery of therapeutic payloads. The applications are vast and rapidly expanding.
Contact Us About Bioconjugation Services
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs is a leader in targeted drug delivery innovation, with a team of experts dedicated to developing sophisticated AOC solutions. We offer a comprehensive suite of products and services designed to accelerate your research.
Ready-to-Use Conjugation Kits
Customized AOC Services
Our bespoke service allows us to develop tailored AOCs from concept to validation, precisely meeting your project's unique specifications. This includes custom oligonucleotide and antibody conjugation, as well as optimization for specific disease contexts.
Conjugation Services
Expertise in conjugating your chosen oligonucleotides to various antibody platforms, including full-length antibodies and smaller antibody fragments.
Pre-Clinical Validation
We offer comprehensive in vitro and in vivo testing to assess the targeting efficiency, cellular uptake, biodistribution, and therapeutic efficacy of your custom AOCs.
Comprehensive Scientific Support
Partner with us to leverage our deep scientific knowledge, state-of-the-art facilities, and rigorous quality control for your targeted delivery projects, from experimental design to data analysis.
Workflow
Why Choose Us?
Partnering with Creative Biolabs means choosing a path to accelerated drug development, enhanced therapeutic efficacy, and a significant reduction in off-target effects. Our commitment to innovation and scientific excellence ensures your therapeutic agents reach their targets with unprecedented precision.
Proven Expertise
Our team of highly specialized biologists, chemists, and engineers possesses deep scientific knowledge in both antibody engineering and oligonucleotide chemistry.
Innovative Technology
We leverage state-of-the-art platforms for oligonucleotide synthesis, antibody modification, and AOC characterization.
Tailored Customization & Flexibility
We provide custom oligonucleotide design and conjugation optimization to ensure your AOC perfectly aligns with your therapeutic goals.
Rigorous Quality & Reliability
Our commitment to scientific rigor ensures reliable, reproducible, and high-quality results for your critical projects.
Published Data
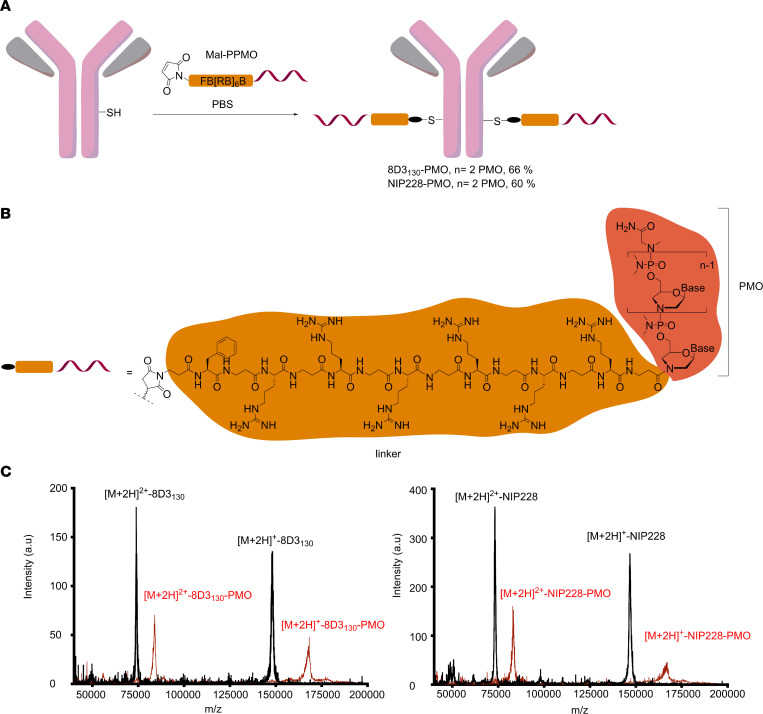 Fig.3 Synthesis of antibody-PMO conjugates.2,3
Fig.3 Synthesis of antibody-PMO conjugates.2,3
The study was centered on evaluating the efficacy of an antibody-oligonucleotide conjugate, referred to as 8D3130-ASO, in mouse models of spinal muscular atrophy. The conjugate was created by linking a brain-targeting antibody (8D3) to an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) designed to modulate the splicing of the human SMN2 gene, which is a key therapeutic target for SMA. The researchers conducted a series of experiments to assess the conjugate's pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and therapeutic effects compared to unconjugated ASOs.
In a key experiment, the 8D3130-ASO conjugate was administered systemically to human SMN2-transgenic mice. The results showed a significant increase in the bioavailability of the ASO in the brain and spinal cord—up to 10-fold higher than that achieved with unconjugated ASO. This enhanced delivery led to a dose-dependent increase in the levels of full-length SMN protein in the CNS. Furthermore, the conjugate was shown to improve SMN2 splicing in the CNS of adult mice, a finding that directly supports its therapeutic mechanism. In a severely affected SMA mouse model, a single dose of the 8D3130-ASO conjugate at postnatal day 2 resulted in a marked extension of the mice's lifespan. An analysis of cellular uptake revealed that the conjugate primarily colocalized with astrocytes, suggesting these cells play a critical role in mediating its delivery and distribution within the spinal cord. These findings collectively demonstrate that the antibody-mediated delivery of ASOs is a viable and effective strategy for CNS-targeted therapy in SMA.
FAQs
Q: How do you mitigate nuclease degradation, a common challenge for oligonucleotide stability?
A: We protect the oligonucleotide payload from enzymatic degradation by incorporating various chemical modifications into its backbone and sugar moieties. These can include phosphorothioate linkages or 2'-O-methyl modifications, which are designed to resist nuclease activity in circulation, ensuring the AOC remains intact and functional until it reaches its target cell.
Q: What is the key scientific advantage of using an AOC for targeted drug delivery?
A: The primary scientific advantage is the combination of high specificity and high payload delivery. The antibody ensures that the AOC binds exclusively to the intended target cells, concentrating the therapeutic oligonucleotide where it is needed most. This minimizes off-target interactions and systemic toxicity, leading to a much wider therapeutic window and improved patient safety.
Q: What is the process for developing a custom AOC for a novel or difficult-to-target antigen?
A: Our workflow commences with exhaustive assessment of your target antigen. We then select or engineer a high-affinity antibody, followed by the design and chemical synthesis of the optimal oligonucleotide payload. Our conjugation chemistry team then develops a robust and reproducible method to link these components, ensuring the final AOC maintains the functionality of both the antibody and the oligonucleotide.
Q: How do AOCs differ from Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) in their mechanism of action?
A: While both are targeted delivery systems, they have fundamentally different mechanisms. ADCs typically deliver a highly potent cytotoxic small molecule to kill a target cell. In contrast, AOCs deliver a nucleic acid payload (e.g., siRNA, ASO) that works by modulating gene expression. This allows for a wider range of therapeutic applications beyond cell killing, such as turning off a disease-causing protein or correcting a genetic defect.
Q: What scientific and technical factors influence the timeline of an AOC development project?
A: The temporal progression is chiefly dictated by project intricacy. Paramount determinants encompass the target antigen's biochemical properties, the prescribed molecular interaction strength for the antibody, the oligonucleotide payload's structural configuration, and requisite bioconjugation methodology. The scope of pre-clinical validation (e.g., in vitro vs. in vivo studies) also significantly impacts the overall project timeline.
Connect with our experts for project-specific consultation and detailed insights.
References
- Hammond, Suzan M et al. "Antibody-oligonucleotide conjugate achieves CNS delivery in animal models for spinal muscular atrophy." JCI insight vol. 7,24 e154142. 22 Dec. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.154142
- Dugal-Tessier, Julien et al. "Antibody-Oligonucleotide Conjugates: A Twist to Antibody-Drug Conjugates." Journal of clinical medicine vol. 10,4 838. 18 Feb. 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040838
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



