A comprehensive catalog of pre-formulated lipid-based delivery systems, including liposomes, exosomes, and polymeric nanoparticles, as well as a selection of validated targeted modules.
Lipid–Drug Conjugate (LDC) Development Service
Are you currently facing challenges such as poor drug bioavailability, systemic toxicity, and ineffective targeting? Creative Biolabs' LDC solutions help you overcome these hurdles and advance your drug development pipeline. By leveraging advanced lipid conjugation and nanocarrier platforms, we help you create therapies with improved stability, targeted delivery, and a wider therapeutic window.
Lipid-Drug Conjugates (LDCs)
Lipid-Drug Conjugates (LDCs) are a class of innovative prodrugs where a pharmacologically active compound is covalently linked to a lipid moiety. This conjugation is a strategic approach to modify a drug's physicochemical properties, particularly its lipophilicity, to enhance its therapeutic performance. The lipid component, which can be a fatty acid, glyceride, or phospholipid, is generally biocompatible and non-toxic, making it an excellent carrier. By increasing a drug's lipid solubility, LDCs can be more easily integrated into lipid-based delivery systems like liposomes, micelles, and nanoparticles, which serve as protective and targeting vehicles. The covalent bond between the drug and lipid is designed to be stable in circulation but is cleaved at the target site by specific enzymes or pH conditions, ensuring the controlled and localized release of the active drug. This mechanism is key to improving a drug's half-life, reducing its systemic exposure, and ultimately, broadening its therapeutic window.
Creative Biolabs offers a range of sophisticated conjugation solutions to create high-quality LDCs. The choice of lipid and conjugation strategy is critical to the success of the LDC, as it influences drug loading, stability, and release kinetics. Our solutions are tailored to your specific drug and therapeutic goal.
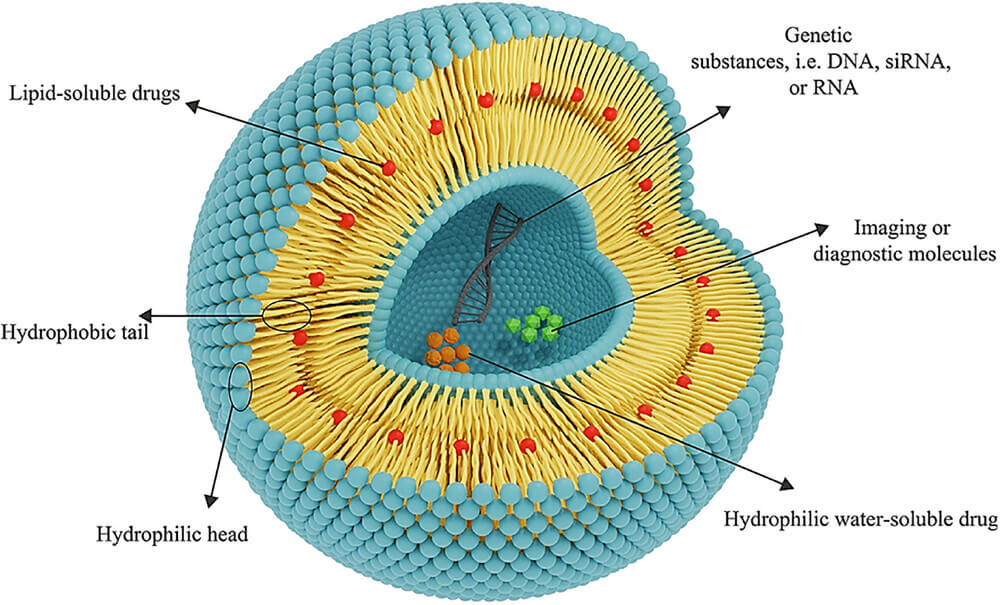 Fig.1 The general structure of the liposomes.1,3
Fig.1 The general structure of the liposomes.1,3
We leverage various lipid types for conjugation, including:
Drugs are typically linked to fatty acids via stable ester or amide bonds, often using active fatty acyl chlorides. This method is highly effective for increasing a drug's lipophilicity, which enables its seamless incorporation into nanocarriers such as liposomes or nanoemulsions. The fatty acid chain length and saturation can be tailored to optimize the drug's properties for specific applications, such as improving membrane permeability or lymphatic system targeting.
Contact Us About Bioconjugation Services
Application
Lipid–Drug Conjugates and their associated delivery systems are revolutionizing drug therapy by providing a versatile platform for a wide range of applications:
- Targeted Cancer Therapy: LDCs can be formulated into nanoparticles that preferentially accumulate in tumor tissues due to the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. This approach, combined with the controlled release of the drug payload, can significantly improve the efficacy of chemotherapy while reducing severe side effects.
- Oral Bioavailability Enhancement: Many drugs suffer from poor solubility and low absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. By conjugating these drugs with lipids, their lipophilicity is increased, which can lead to better absorption and overall oral bioavailability.
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Delivery: The blood-brain barrier poses a significant challenge for many therapeutic agents. LDCs can be engineered to bypass this barrier, enabling the effective delivery of drugs for neurological disorders by leveraging the lipid-based transport systems in the body.
- Anti-Inflammatory and Antiviral Treatments: The improved cellular uptake and sustained release offered by LDCs make them ideal for treating chronic inflammatory conditions and viral infections. The enhanced properties allow for lower dosing frequency and reduced systemic exposure, which is beneficial for long-term treatment.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs is positioned at the forefront of targeted drug delivery innovation. Our team of expert biologists, chemists, and engineers brings over two decades of collective experience in developing sophisticated delivery solutions. We offer a range of products and services designed to accelerate your research and development needs:
Ready-to-Use LDC Products
Customized LDC Services
Our bespoke service allows us to develop tailored LDC systems and novel targeted modules from concept to validation, precisely meeting your project's unique specifications. This includes custom lipid-drug conjugation, synthesis, and optimization of delivery system characteristics for specific disease contexts.
Conjugation Services
Expertise in conjugating selected ligands to various delivery platforms, including nanoparticles, liposomes, and polymers.
Preclinical Validation
We provide comprehensive in vitro and in vivo testing to assess targeting efficiency, cellular uptake, biodistribution, and therapeutic efficacy of your LDC candidates.
Comprehensive Scientific Support
Partner with us to leverage our deep scientific knowledge, state-of-the-art facilities, and rigorous quality control for your targeted delivery projects, from experimental design to data analysis.
Workflow
Why Choose Us?
Partnering with Creative Biolabs means choosing a path to accelerated drug development, enhanced therapeutic efficacy, and a significant reduction in off-target effects. Our commitment to innovation and scientific excellence ensures that your therapeutic agents reach their intended targets with unprecedented precision, unlocking new possibilities for disease treatment.
Demonstrated Proficiency
Our cohort of exceptionally skilled biologists, chemists, and engineers commands profound technical mastery in therapeutic conveyance platforms and ligand-carrier complex development.
Advanced Methodologies
We employ cutting-edge technological infrastructure for ligand-carrier compound synthesis, conjugation, and analysis, guaranteeing premium-grade and consistent replicability.
Bespoke Adaptation & Versatility
We deliver tailored lipid-therapeutic design solutions and delivery optimization aligned with precise treatment objectives.
Exacting Standards Assurance
Our dedication to uncompromising scientific precision and quality standards validates dependable outcomes for pivotal initiatives spanning discovery to clinical translation.
Published Data
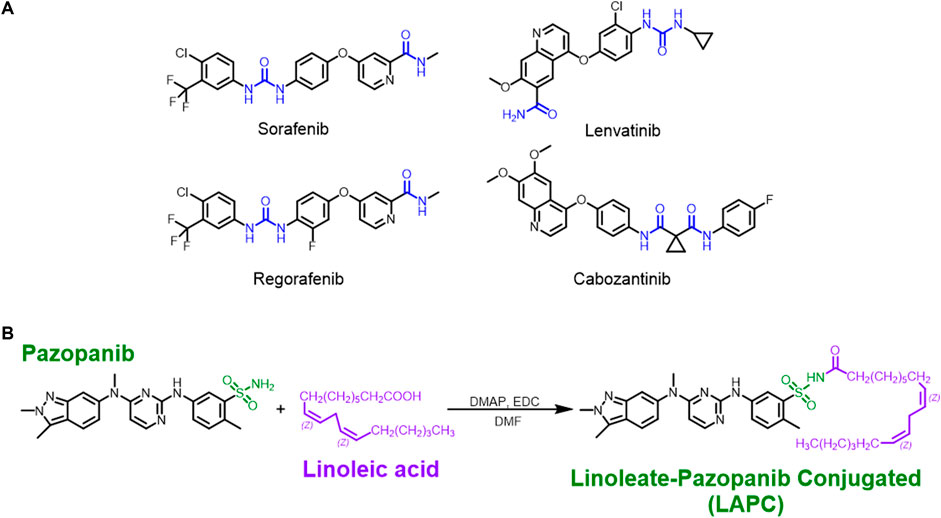 Fig.2 The structures of MKIs and synthesis of LA + pazopanib to produce LAPCs.2,3
Fig.2 The structures of MKIs and synthesis of LA + pazopanib to produce LAPCs.2,3
The study was conducted using a spontaneous HCC mouse model to evaluate the new drug conjugate, linoleate-pazopanib conjugate (LAPC), against the parental drug, pazopanib. The experimental results demonstrated that LAPC had a significantly superior therapeutic effect. While pazopanib primarily functions through an anti-angiogenic mechanism, LAPC was found to have improved cytotoxicity and to induce alternative cellular death pathways, specifically apoptosis and enhanced ferroptosis. Notably, these benefits were observed without any discernible systemic toxicity in the animal models. The researchers also highlighted that LAPC showed excellent properties for oral dosing and appeared to have a longer retention time in the blood, indicating improved pharmacokinetics. These findings collectively support the conclusion that the linoleate conjugation approach is a viable strategy for enhancing the efficacy and safety of existing VEGFR inhibitors.
FAQs
Q: How do Lipid-Drug Conjugates (LDCs) mitigate systemic toxicity?
A: LDCs are designed to reduce off-target toxicity by enhancing the drug's specificity and controlled release profile. By covalently linking a drug to a lipid, the conjugate can be formulated into a nanocarrier that circulates safely in the bloodstream. This protects the drug from premature degradation and minimizes its exposure to healthy tissues. The drug is then released at the intended site of action, often triggered by specific microenvironmental cues such as changes in pH or the presence of target-specific enzymes, thereby concentrating its therapeutic effect where it is needed most.
Q: What is the range of therapeutic agents that can be conjugated with lipids?
A: Our technology is highly adaptable and can be applied to a wide spectrum of therapeutic agents. We have successfully conjugated small molecule drugs, peptides, and even nucleic acid-based therapies. The conjugation strategy is meticulously customized for each unique molecule, considering its chemical properties, functional groups, and desired therapeutic outcome. This versatility allows us to develop optimized LDC solutions for diverse drug candidates.
Q: What are the primary mechanisms ensuring LDC stability and drug release in vivo?
A: The stability of an LDC in circulation is a critical design consideration. The linker connecting the lipid and the drug is engineered to be highly stable in the physiological environment of the bloodstream. Drug release is typically achieved via a cleavable linker that responds to specific biological triggers at the target site. These triggers can include enzymatic cleavage by intracellular enzymes (e.g., esterases or proteases), or hydrolysis in a low pH environment, such as in the acidic conditions of a tumor microenvironment. This precise control over drug release ensures therapeutic efficacy while minimizing systemic side effects.
Q: What are the key advantages of using LDCs over conventional drug encapsulation methods?
A: Unlike simple encapsulation, which relies on non-covalent interactions and is prone to drug leakage during circulation, LDC technology ensures a stable and robust association between the drug and its lipid carrier through a covalent bond. This leads to several key advantages: a significantly higher drug-loading efficiency, enhanced stability of the overall delivery system, and a more predictable, controlled release profile. This covalent approach provides a superior level of control and reproducibility, which is essential for developing reliable and effective therapeutic products.
Q: Can LDC technology address challenges with drug solubility?
A: Yes, improving drug solubility is one of the core benefits of LDC technology. By conjugating a poorly soluble drug with a biocompatible lipid, we can dramatically increase its lipophilicity. This modification makes it far easier to formulate the drug into a stable nanocarrier, which can then be delivered effectively. This strategy is a powerful tool for overcoming solubility-related bioavailability issues, thereby solving a major challenge in drug development and enabling the use of promising drug candidates that were previously unviable.
At Creative Biolabs, our mission is to provide you with innovative LDC solutions that accelerate your projects and lead to breakthrough therapies. Our team of experts is ready to partner with you and provide the scientific support you need.
Connect with our experts for project-specific consultation and detailed insights.
References
- Desai, Nimeet et al. "Nanoparticle Therapeutics in Clinical Perspective: Classification, Marketed Products, and Regulatory Landscape." Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) vol. 21,29 (2025): e2502315. DOI:10.1002/smll.202502315.
- Wang, Ke et al. "Linoleate-pazopanib conjugation as active pharmacological ingredient to abolish hepatocellular carcinoma growth." Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 14 1281067. 16 Jan. 2024, DOI:10.3389/fphar.2023.1281067.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



