Development of highly specific ligands (peptides, antibodies, small molecules, carbohydrates) tailored to your chosen liver cell target or receptor.
Liver Targeting Module Development Service
Accelerate Your Targeted Drug Delivery Research!
Creative Biolabs' Liver Targeting Module Development service provides bespoke solutions designed to significantly improve the specificity and efficacy of your therapeutic and diagnostic agents for liver-related applications. We deliver meticulously engineered targeting modules that guide your payload directly to desired liver cells, minimizing off-target accumulation and maximizing therapeutic impact. Our expertise ensures that your project benefits from enhanced drug concentration at the disease site, reduced systemic toxicity, and optimized patient outcomes.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Overview
Hepatic tissue serves as the primary organ for drug metabolism and elimination. Hepatocytes (70-85% of hepatic cellular mass) function as principal biosynthetic units, orchestrating metabolic regulation, endocrine signaling, and secretory activities. Kupffer cells constitute specialized macrophages executing immunoregulatory functions. Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) act as perivascular sentinels, transitioning to myofibroblastic phenotypes upon injury—driving collagen deposition that progresses to fibrotic/cirrhotic pathologies. Despite advances in hepatotherapeutic agents, nonspecific hepatic sequestration rapidly clears compounds from circulation, yielding subtherapeutic concentrations at pathological sites. These limitations necessitate cell type-selective pharmacodelivery platforms for precision hepatology.
Delivery System Targeting Liver
Recent advances in nanomedicine have yielded hepatic-targeted platforms leveraging lipid-based architectures for precise delivery of pharmaceuticals and genetic payloads to diseased liver tissue. Engineered nanovectors now enable dual diagnostic-therapeutic applications for hepatic pathologies, with gene-editing systems showing particular promise in managing hepatocellular carcinoma and fibrotic progression. Metabolic liver conditions like NAFLD are being addressed through selective hepatocyte vectorization using lipid-based nanoemulsions, self-assembling micelles, or polymeric nanogels. Concurrently, macrophage-centric strategies exploit Kupffer cell tropism—achieved via PLGA matrices or stealth liposomes—to deploy immunoregulatory, antifibrotic, or inflammation-resolving agents. For viral hepatitis management, advanced conjugated systems combine antiviral nucleoside analogs with RNA interference payloads through lipid-polymer hybrid engineering.
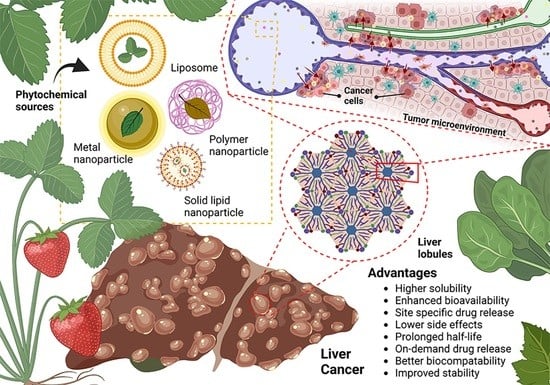 Fig 1. Plant-Based Anticancer Nanoparticles against Hepatocellular Carcinoma.1,3
Fig 1. Plant-Based Anticancer Nanoparticles against Hepatocellular Carcinoma.1,3
Liver cancer research has intensified focus on therapeutic delivery platforms requiring precise spatiotemporal control of tumor-selective biodistribution, payload liberation kinetics, and nanocarrier integrity. Emerging modalities encompass nanoscale immunotherapy vectors (primarily liposomal architectures) and viral-mediated gene-editing systems. Transarterial chemoembolization utilizing drug-eluting microspheres has emerged as a locoregional intervention for HCC. Contemporary approaches employ stimuli-responsive nanovectors and biofunctionalized architectures for chemotherapy/genetic payload deployment. Parallel diagnostic innovation leverages plasmonic gold nanostructures, superparamagnetic particles, and fluorescence-tagged nanoreporters for early lesion detection.
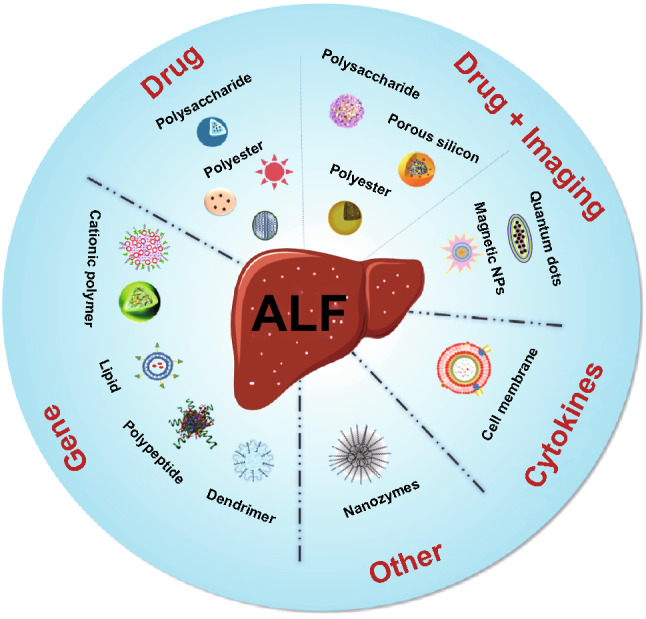 Fig 2. Diverse types of nanoparticles in the theranostics of liver.2,3
Fig 2. Diverse types of nanoparticles in the theranostics of liver.2,3
While hepatic tissues naturally accumulate pharmaceuticals at elevated levels, precision targeting remains critical due to the hepatic system's dominant role in xenobiotic processing—encompassing uptake, detoxification, biotransformation, and biliary excretion via transporter-mediated pathways. This results in rapid systemic clearance and pronounced first-pass elimination. Notably, hepatocyte-mediated internalization governs bulk hepatic assimilation, whereas Kupffer macrophages predominantly sequester particulate cargos. Thus, therapeutic agents—whether free molecules or carrier-conjugated formulations—may fail to achieve cell-selective biodistribution. Moreover, hepatic retention kinetics are governed by macrophage-vector interactions and compartmental pharmacokinetic parameters. The critical challenge lies in engineering cell type-specific accumulation while sustaining intracellular therapeutic concentrations over extended durations.
What We can Offer?
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive suite of services and products for Liver Targeting Module Development, designed to meet the diverse needs of your research and drug development programs. Our offerings are built upon a complete module delivery system and an experienced team of scientists dedicated to precision and innovation.
Custom Targeting Module Design & Synthesis
Module-Payload Conjugation Services
Expert conjugation of your therapeutic or diagnostic payload (e.g., small molecules, proteins, nucleic acids) to the synthesized targeting modules.
Diverse Carrier Complex Development
Creation of various module-payload/carrier complexes utilizing a wide range of delivery vehicles.
In vitro Efficacy Evaluation
Comprehensive assays to assess binding affinity, specificity, cellular uptake, and functional activity of targeting modules in relevant liver cell lines.
In vivo Efficacy & Biodistribution Studies
Preclinical evaluation in animal models to determine liver-specific accumulation, target cell distribution, and therapeutic outcomes of the targeted systems.
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of Liver Targeting Module Development, offering unparalleled expertise and a commitment to accelerating your research and development.
- Unrivaled Expertise: Over 20 years of specialized experience in targeted delivery systems and liver biology, ensuring deep scientific understanding and innovative solutions.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Access to advanced platforms for module design, synthesis, and comprehensive in vitro/in vivo evaluation, including state-of-the-art analytical instrumentation.
- Customizable Solutions: Our services are highly adaptable, allowing for the development of bespoke targeting modules tailored precisely to your unique payload and liver disease target.
- Comprehensive Approach: We offer end-to-end support, from initial target validation to preclinical evaluation, streamlining your development pipeline.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Our iterative design and rigorous testing methodologies are guided by robust data, ensuring optimal module performance and reliability.
- Proven Track Record: Our modules have demonstrated enhanced liver specificity and therapeutic efficacy across a range of preclinical models.
Workflow
FAQs
Here are some common questions we receive about Heart Targeting Module Development:
What types of liver cells can Creative Biolabs' targeting modules specifically address?
Our modules are highly customizable and can be designed to target a wide range of liver cell types, including hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells, Kupffer cells (hepatic macrophages), and liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. We encourage you to discuss your specific target with our scientific team to ensure optimal module design for your project.
How do Creative Biolabs' targeting modules enhance drug efficacy and reduce side effects?
By guiding your therapeutic payload directly to the intended liver cells, our modules significantly increase drug concentration at the disease site, leading to enhanced therapeutic efficacy. Simultaneously, this targeted delivery minimizes systemic exposure and accumulation in off-target tissues, thereby substantially reducing unwanted side effects and improving the overall safety profile of your therapeutic agent.
Can Creative Biolabs' service integrate with my existing drug delivery vehicle?
Yes, Our Liver Targeting Module Development service is designed for flexibility. We can work with a wide array of existing drug delivery vehicles, including various nanoparticles, liposomes, and viral vectors. Our team will collaborate with you to ensure seamless integration and optimal performance of our targeting modules with your chosen carrier system.
Creative Biolabs provide tailored targeted delivery solutions addressing unique research and therapeutic requirements. To explore these capabilities, please contact us for more information.
References
- Basu, Aalok, Thanaphon Namporn, and Pakatip Ruenraroengsak. "Critical review in designing plant-based anticancer nanoparticles against hepatocellular carcinoma." Pharmaceutics 15.6 (2023): 1611. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15061611
- Jin, Yuanyuan, et al. "Applications of nanobiomaterials in the therapy and imaging of acute liver failure." Nano-micro letters 13 (2021): 1-36. doi:10.1007/s40820-020-00550-x
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



