Hydrogel based Delivery System Development Service
Hydrogel delivery systems, defined by their highly hydrated, cross-linked polymer networks, are indispensable tools for achieving localized and sustained therapeutic release. However, the complexity of modern payloads like nucleic acids and protein degraders demands delivery vectors with intelligent targeting capabilities far beyond simple diffusion. Creative Biolabs specializes in engineering these next-generation systems. Our 20+ years of expertise ensure precision, scalability, and scientific excellence in every hydrogel-based solution.
The Role of Hydrogels in Next-Gen Therapeutics

Hydrogels are fascinating materials defined by a three-dimensional network of hydrophilic polymer chains, either natural (like hyaluronic acid) or synthetic (like PEG). These networks are held together by physical or chemical cross-links, enabling them to absorb and retain large volumes of water or biological fluid—often exceeding 90% of their total mass. This highly hydrated, soft structure closely mimics native extracellular matrix (ECM), providing unparalleled biocompatibility and making it ideal as a versatile delivery platform.
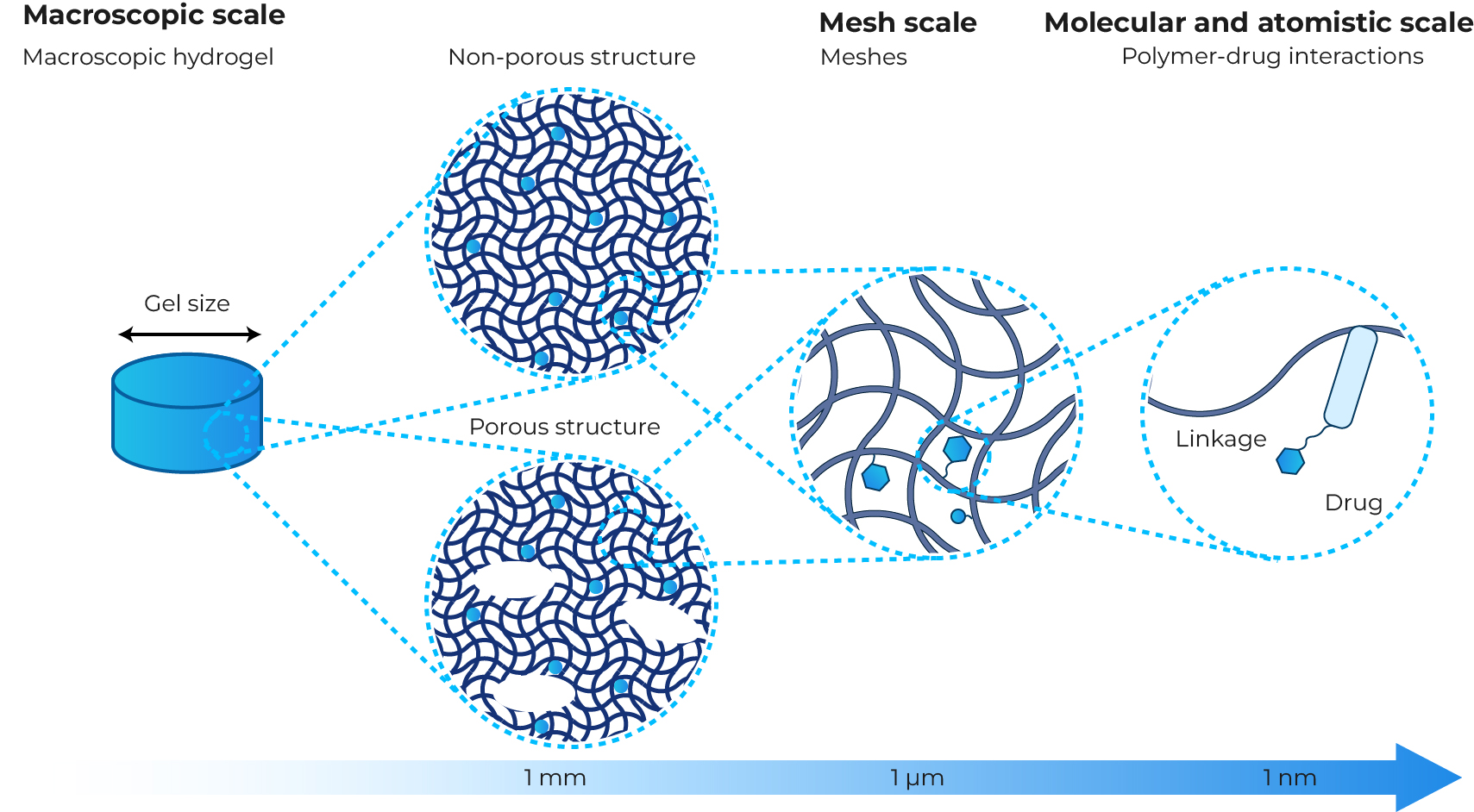 Fig. 1 The multi-scale properties of hydrogels.
Fig. 1 The multi-scale properties of hydrogels.
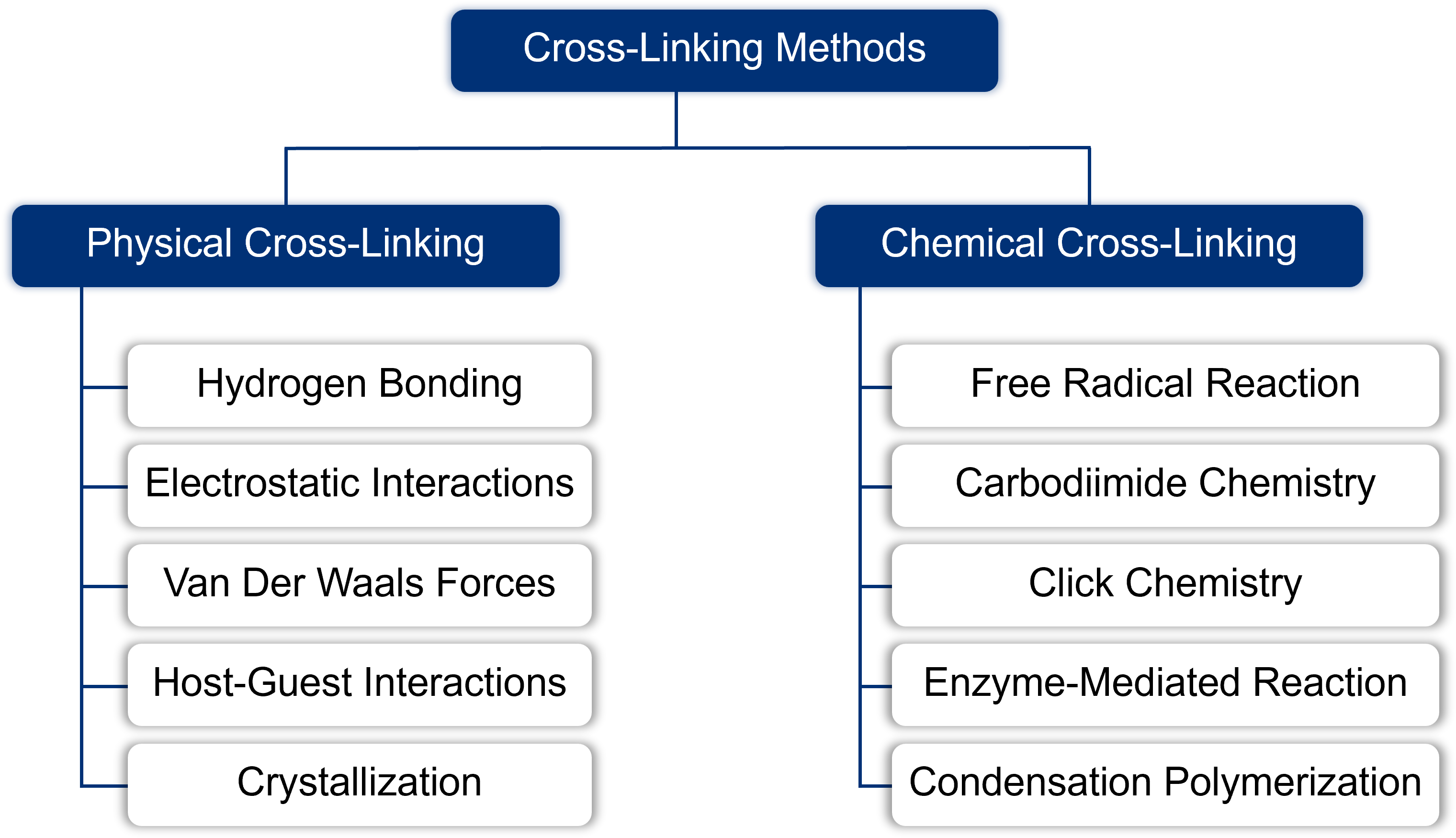
Hydrogel Classification and Material Diversity
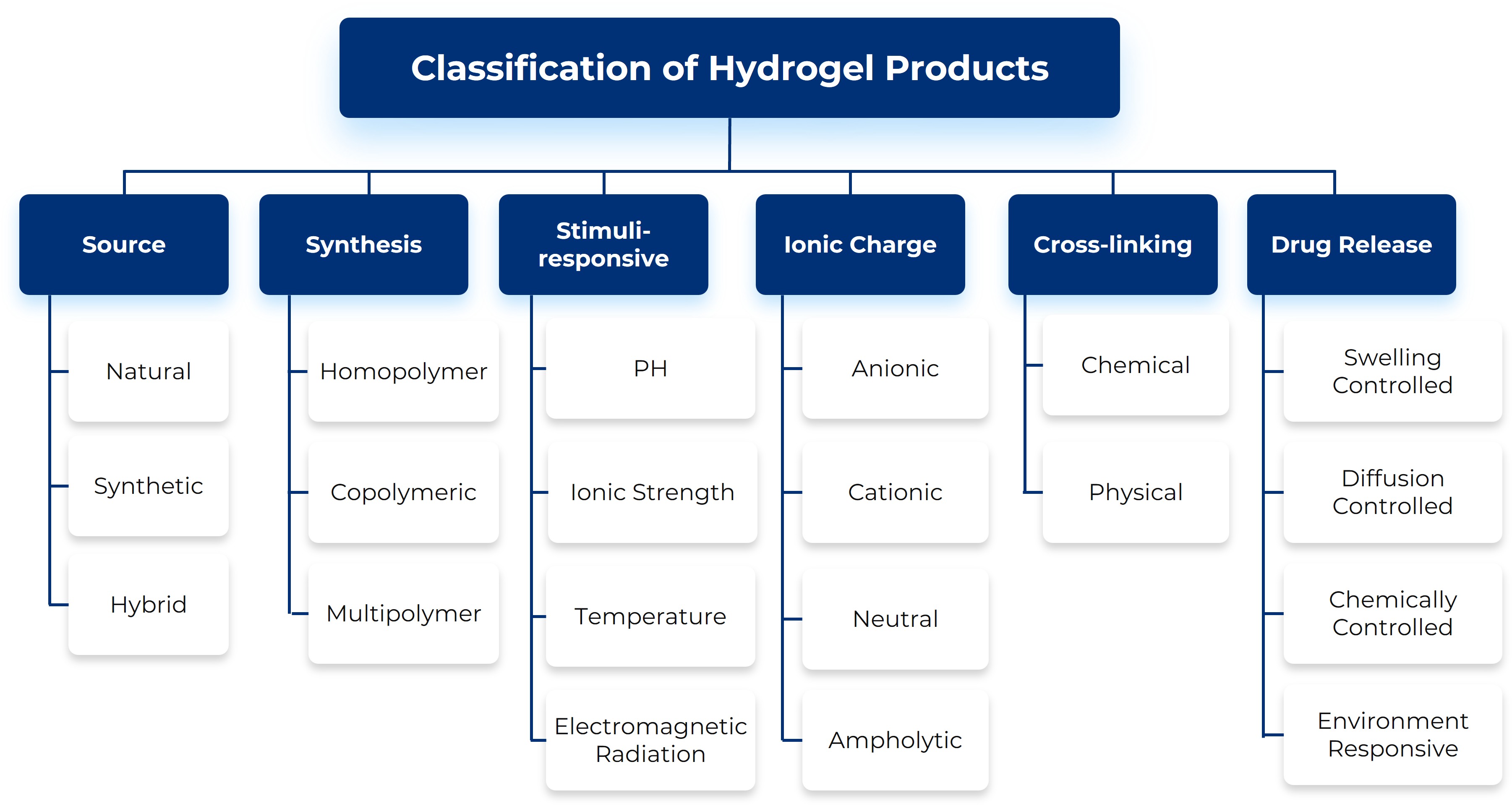
Designing successful hydrogel delivery systems requires a strategic understanding of their fundamental architecture. Hydrogels are not a monolithic material class; they are defined by multiple interacting properties. We classify these materials across several critical dimensions, including their Source (natural or synthetic), the method of Synthesis, the nature of their internal Cross-linking (physical or chemical), the material's Ionic Charge, its capacity for Stimuli-responsive changes, and the mechanism of Drug Release. A mastery of these design principles is the first critical step toward tailoring a system to meet specific therapeutic goals.
Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels: The Gateway to Smart Delivery
The most advanced hydrogel systems are "smart" or "responsive," meaning they are designed to release their payload only when triggered by specific biological or physical changes associated with the disease site. This enables active targeting and significantly reduces off-target effects.
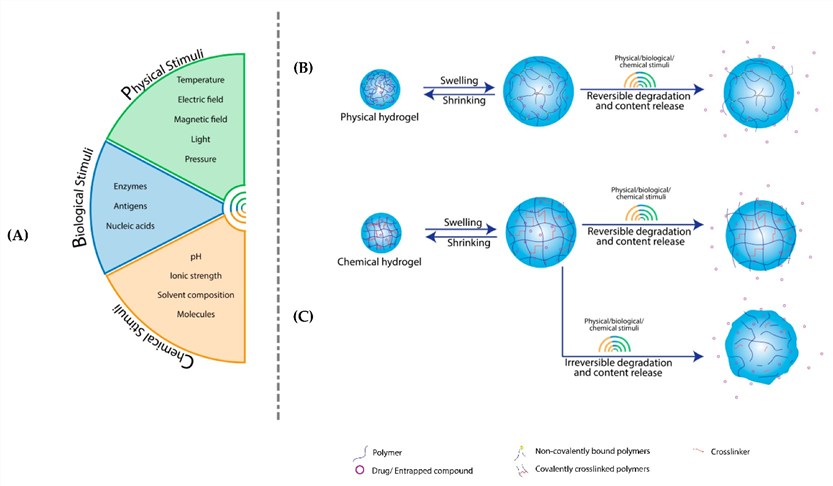 Fig. 2 Structural changes
in stimulus-responsive hydrogels.1,3
Fig. 2 Structural changes
in stimulus-responsive hydrogels.1,3
pH-Responsive Systems
Polymers incorporate weak acid or base groups (e.g., polyacrylic acid, chitosan) that ionize or protonate upon sensing a pH shift, leading to swelling or collapse of the matrix.
Temperature-Responsive Systems
A slight temperature shift past the Lower Critical Solution Temperature (LCST) triggers polymer collapse and rapid network de-swelling, efficiently expelling the drug payload.
Enzyme-Responsive Systems
Disease-specific enzymes (e.g., MMPs in cancer) cleave engineered peptide linkers within the polymer network, causing the hydrogel to degrade and release the payload locally.
ROS Responsive Systems
Chemical bonds (e.g., disulfide) degrade in response to high concentrations of ROS or reducing agents (glutathione) present in inflamed or intracellular environments.
Light-Responsive Systems
Light-sensitive chromophores (e.g., azobenzene) undergo cleavage or conformational change when exposed to specific UV/NIR light, enabling remote activation.
Glucose-Responsive Systems
Glucose oxidase or phenylboronic acid reacts with glucose, changing local osmotic pressure or pH, which then triggers polymer swelling or de-swelling for release.
Electric/Magnetic Field Responsive Systems
External fields (electric or magnetic) cause movement or localized heating of embedded components (polyelectrolytes/nanoparticles), triggering controlled drug release.
Pressure Responsive Systems
Cross-links within the hydrogel network are engineered to be sensitive to external mechanical stress or changes in local hydrostatic pressure, initiating release.
Molecule-Responsive Systems
Receptor sites in the network undergo competitive binding or chemical reaction when a specific target molecule (e.g., metabolite/antibody) is present, enabling release.
Other Responsive Systems
Polyelectrolyte hydrogels respond predictably to shifts in external salt ion concentration or solvent polarity, causing volume changes that modulate payload release.
Specialized Hydrogel Development Services
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of customized services, leveraging decades of material science and biology expertise to meet your specific R&D needs. Our services cover all major hydrogel classes, ensuring we can engineer the optimal system for your unique application.
High-Efficiency Payload Encapsulation
Design and synthesis of systems responsive to pH, Temperature, Enzyme Activity, and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) concentration for highly localized drug release.
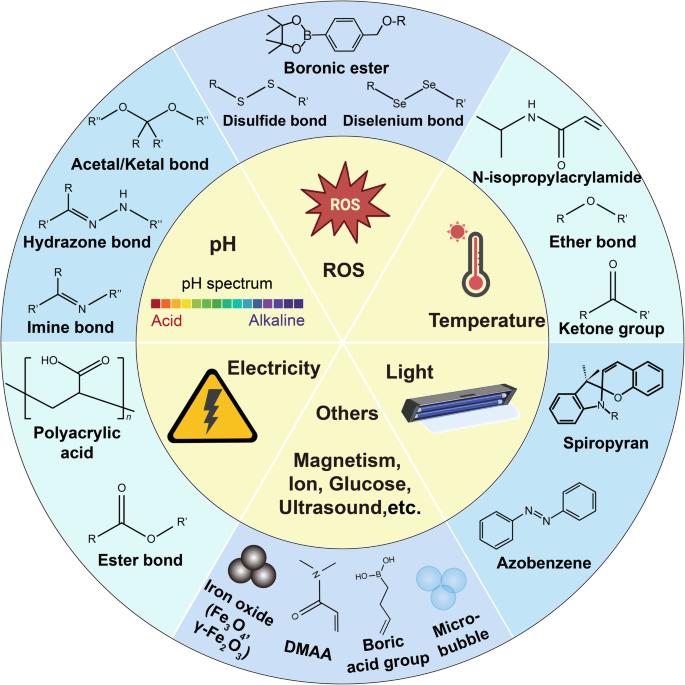 Fig. 3 Classification of various VLPs structure.2,3
Fig. 3 Classification of various VLPs structure.2,3
Trigger Specificity
Engineering of precise sensitivity thresholds for environmental cues (e.g., tumor microenvironment pH 6.5) and enzyme activity (e.g., specific MMP cleavage sites).
Release Kinetics
Guaranteed zero-order or pulsatile release profiles only upon activation, maximizing the therapeutic window and minimizing off-target effects.
Modified Hydrogels & Bioconjugation
Synthesis of functionalized polymers incorporating tags (e.g., Fluorescent for tracking) and reactive groups (Thiol, Azide, Acylhydrazine) for robust, bio-orthogonal conjugation via Click Chemistry.
Orthogonal Precision: Use of biocompatible, high-yield click chemistry (Cu-free) for precise attachment of targeting ligands or reporter tags without compromising payload integrity.
Imaging Readiness: Incorporation of NIR or fluorescent probes for real-time in vivo tracking and non-invasive monitoring of hydrogel localization and degradation.
Ligand Density Control: Fine-tuning of targeting ligand density on the polymer backbone to optimize receptor binding and internalization efficiency for active targeting.
Drug-Loading Hydrogels (Payload Versatility)

Dedicated formulation development for high-efficiency encapsulation of diverse therapeutics:
Payload Types: Supporting Small Molecule Drugs (hydrophobic and hydrophilic), Nucleic Acid Drugs (siRNA, mRNA, CRISPR components), Proteins/Antibodies, and Advanced Therapeutics (protein degrader/molecular glues).
High Efficiency & Stability: Guaranteed high drug loading capacity and encapsulation efficiency (EE) validated by HPLC/UPLC, along with long-term stability assessment for temperature-sensitive biologics.
Mild Encapsulation Methods: Employing non-covalent, solvent-free techniques (e.g., electrospraying, microfluidics) to maintain the bioactivity of fragile protein and nucleic acid payloads
Specialized Mechanical Hydrogels Development

Engineering advanced materials for dynamic biological environments, including Self-Healing Hydrogels (autonomous damage repair) and Super-Tough Hydrogels (enhanced strength and durability).
Super-Tough Hydrogels: Customized synthesis using specialized techniques (e.g., chemical or physical crosslinking) and reinforcement with materials like bacterial cellulose nanofibers or nanoparticles to achieve superior tensile, compressive strength, and toughness over traditional hydrogels.
Self-Healing Mechanisms: Expertise in dynamic network formation via dynamic covalent bonds (borate ester, disulfide bond, imine bonds) and non-covalent interactions (Hydrogen bonds, Host-Guest), enabling autonomous repair and restoration of mechanical properties.
Biomimetic Hydrogels Development

We design and engineer sophisticated 3D hydrogel systems inspired by natural biology, such as the architecture of the Extracellular Matrix (ECM) and the functional properties of biofilms.
Bio-Inspired Functionality: Development of systems using cellular membrane coatings (e.g., endosomal or stem cell membranes) for enhanced homologous targeting, and incorporation of competitive release mechanisms that mimic natural binding processes.
Advanced Delivery Systems: Specialized in creating tissue-specific microenvironments that reproduce the critical stiffness and cellular cues of native or diseased tissue (e.g., liver or tumor microenvironments) for predictive in vitro modeling and targeted research.
Composite Hydrogels (Hybrid Systems) Development
Integration of nano-scale delivery systems within the hydrogel matrix for multi-stage targeting and enhanced stability. Expertise includes combining hydrogels with Liposomes, LNP, PLGA microparticles, silica nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles, and quantum dots.
Multi-Stage Release: Design systems where the hydrogel provides local retention and the encapsulated nanocarrier (e.g., LNP) provides endosomal escape and intracellular targeting.
Carrier Stability: Validation of the long-term stability and non-aggregation of the encapsulated nanocarriers within the hydrogel network prior to deployment.
Workflow
Applications of Hydrogel in Modern Research
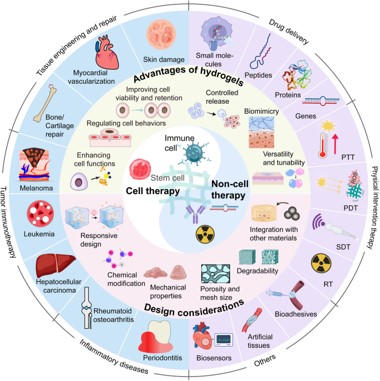 Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of the application of hydrogels
in cell therapy and non-cell therapy.2,3
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of the application of hydrogels
in cell therapy and non-cell therapy.2,3
- Ophthalmic & Dermal Delivery: Hydrogel-based ocular inserts or drops designed for extended residence time, providing controlled delivery of anti-inflammatory or anti-VEGF agents. Dermal patches for enhanced, sustained transdermal drug penetration.
- Regenerative Medicine & Tissue Engineering: Utilizing biomimetic, injectable scaffolds that deliver growth factors and cells (e.g., mesenchymal stem cells) to damaged tissues (cartilage, bone, skin), guiding cell differentiation and supporting complex tissue repair and regeneration.
- Oncology and Targeted Therapy: Localized, sustained, and responsive delivery of small molecule chemotherapeutics and immunomodulators (e.g., checkpoint inhibitors) directly into the tumor microenvironment to maximize efficacy while minimizing systemic toxicities.
- Photo/Sono/Radiation Therapy: Integration of photothermal agents (photothermal therapy, PTT), photosensitizers (photodynamic therapy, PDT), or sonosensitizers (sonodynamic therapy, SDT) within the hydrogel matrix, allowing for localized, triggered release and synergistic therapeutic effects combined with radiation therapy (RT).
- Wound Healing: Development of adhesive, bioactive hydrogel patches that accelerate tissue repair, minimize scarring, and provide sustained release of antimicrobial agents or growth factors.
- Artificial Tissue/Organoids: Engineering complex, 3D hydrogel microenvironments that support the growth, maturation, and function of organoids and artificial tissues for disease modeling and transplantation.
- Cell Therapy Platforms: Hydrogel scaffolds support diverse cell therapies, providing niches for Stem Cells, Targeted Cell Replacement, and localized Immunotherapies (CAR-T, TCR-T, TIL, Treg, NK, APC).
- Biosensors: Hydrogel matrices designed for integration with sensing elements (e.g., electrodes, functionalized nanomaterials) to create implantable or wearable biosensors for real-time monitoring of biomarkers (e.g., glucose, pH, enzymes).
Why Choose Creative Biolabs for Hydrogel Development?
Hydrogel technology is a highly versatile delivery system. Choosing Creative Biolabs means gaining a strategic advantage in a highly competitive drug delivery landscape. Our expertise ensures your success.
Precision Targeting Mastery
We are unique in our ability to seamlessly integrate advanced targeted modules (targeted peptides, etc.) within the hydrogel scaffold, enabling true cellular and subcellular specificity—a critical requirement for gene therapies.
Full-Spectrum Scientific Validation
Our characterization goes beyond basic swelling tests. We provide advanced analytics, including rheology, microstructure imaging (SEM/TEM), and mathematically modeled in vitro release kinetics, guaranteeing data integrity.
Decades of Specialty Expertise
Our team comprises biology specialists with 20+ years of focused experience in polymer chemistry, drug delivery mechanisms, and biological barriers, translating complex challenges into clear, viable solutions.
Comprehensive Material Library
Access our extensive portfolio of natural (gelatin, hyaluronic acid, chitosan) and synthetic (PVA, PEG) polymers, including specialized functionalized materials like cRGD-Chitosan.
Validated Preparation Methods
Our proficiency spans all mature hydrogel preparation methods, encompassing both diverse Physical Crosslinking (ionic, thermal) and advanced Chemical Crosslinking (Click Chemistry, enzymatic gelation) techniques, ensuring optimal mechanical stability and tunable degradation.
Biomimetic and Cell-Specific Design
We engineer hydrogels with tunable stiffness and ligand presentation to accurately mimic native ECM, critical for cell therapy and tissue engineering success.
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner for translating complex biological challenges into successful therapeutic delivery systems. Our service encompasses everything from cutting-edge stimulus-responsive polymers and multifunctional composite formulations to comprehensive characterization and scale-up readiness. We provide the scientific mastery and proven processes required to elevate your research from the bench to the preclinic. Ready to enhance your therapeutic delivery precision? Contact us today to leverage our 20+ years of expertise and begin designing your custom hydrogel solution.
Related Services
FAQs
What types of therapeutic payloads can be encapsulated in your hydrogels?
We successfully encapsulate a wide array, including small molecule drugs, diverse nucleic acids (siRNA, mRNA, DNA plasmids), proteins, antibodies, and advanced therapeutics like protein degraders. Our methods are tailored to preserve the bioactivity of each payload.
How do you guarantee targeted release over a simple sustained release?
We achieve true targeting through our modular platform by integrating stimuli-responsive elements (pH, enzyme activation) with surface-functionalized Targeted Modules (aptamers or peptides) that bind specifically to receptors on the diseased tissue or cell type.
How is the hydrogel's mesh size and mechanical stiffness controlled?
We control mesh size and mechanical stiffness primarily by adjusting the polymer concentration and the degree of cross-linking. We use advanced rheology to precisely quantify viscoelastic properties and ensure they align with the requirements of the target tissue environment.
Can your hydrogel systems be administered via injection?
Absolutely. A key focus of our development is Injectable & In Situ Gelling Systems. We formulate liquid precursors that rapidly solidify into a stable hydrogel upon reaching physiological conditions in vivo, enabling minimally invasive administration.
Which advanced cross-linking chemistries do you utilize for demanding applications?
For high-precision applications requiring rapid and biocompatible gelation, we routinely employ bio-orthogonal reactions such as Copper-free Click Chemistry (e.g., strain-promoted cycloaddition) and Michael-type Addition to ensure controlled and cell-friendly polymerization in situ.
References
- Onaciu, Anca, et al. "Hydrogels based drug delivery synthesis, characterization and administration." Pharmaceutics 11.9 (2019): 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11090432
- Lu, Peilin, et al. "Harnessing the potential of hydrogels for advanced therapeutic applications: Current achievements and future directions." Signal transduction and targeted therapy 9.1 (2024): 166. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-024-01852-x
- Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.