Microsphere-Based Delivery Strategies: A Complete, Easy-to-Understand Guide
Microsphere-based delivery strategies are reshaping the future of drug formulation by making treatments last longer, work more precisely, and stay more stable. These tiny carriers can protect sensitive drugs, control how fast they are released, and even target specific tissues. Because of their flexibility and proven success in long-acting injectables and vaccines, microspheres have become a leading platform in modern therapeutics. This article breaks down how they work, why they matter, and how Creative Biolabs supports their development from concept to application.
What Are Microsphere-Based Drug Delivery Systems?
Microsphere-based drug delivery systems use tiny spherical particles to carry active ingredients and release them over time. These microspheres usually range from 1 to 1000 micrometers in diameter. Inside or within their matrix, they hold drugs, peptides, proteins, or nucleic acids.
Because of their design, microsphere-based delivery strategies can:
- Control how fast the drug leaves the carrier.
- Protect sensitive molecules from enzymes or harsh environments.
- Target specific tissues by changing surface chemistry or adding ligands.
Microspheres can be made from:
- Biodegradable polymers: PLGA, PLA, PCL, alginate, chitosan, gelatin.
- Lipids: for softer, more flexible carriers.
- Ceramic or inorganic materials: for special imaging or bone-related uses.
- Hybrid systems: combining polymers, lipids, or inorganic components.
They support many administration routes, including oral, injectable, ocular, nasal, pulmonary, implantable, and even mucosal delivery.
Mechanisms of Drug Release from Microspheres
Microsphere-based delivery strategies rely on well-defined release mechanisms. Understanding these helps you tune how long a treatment will last.
Fickian Diffusion
In many systems, drugs move out of the microsphere by diffusion through the polymer matrix. The rate depends on:
- Drug solubility in the polymer and the surrounding fluid.
- Polymer density and crystallinity.
- Particle size and surface area.
Polymer Degradation and Erosion
For biodegradable polymers like PLGA or PLA, the polymer itself slowly degrades and erodes. Two main patterns appear:
- Bulk erosion: water penetrates the entire sphere, and degradation happens throughout.
- Surface erosion: only the outer layer erodes, keeping the size more constant.
Combined Diffusion–Erosion Systems
Most real formulations show a combination of diffusion and degradation (Figure 1). For example, microspheres made by double emulsion or spray drying often show:
- An initial burst as the surface drug diffuses out.
- A slower sustained phase as the polymer breaks down.
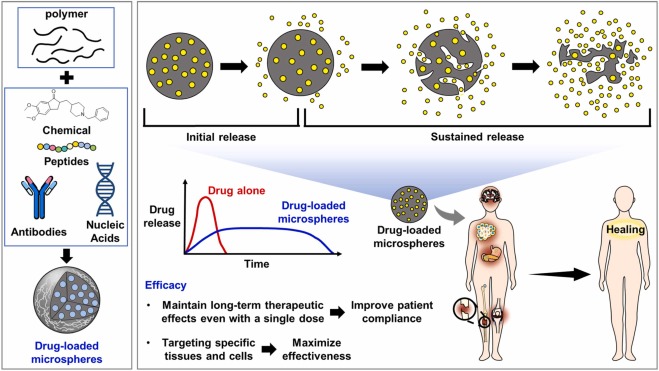 Fig.1 The mechanism of the microsphere-based drug delivery.3
Fig.1 The mechanism of the microsphere-based drug delivery.3
Advantages and Limitations of Microsphere Delivery Systems
A clear understanding of the advantages and limitations of microsphere-based delivery systems can help researchers choose the right formulation strategy and anticipate potential development challenges.
Key Advantages
Microsphere-based delivery strategies offer several clear benefits:
- Prolonged therapeutic effect with fewer injections or doses.
- Smoother pharmacokinetics, reducing peak-related side effects.
- Local depots for site-specific therapy.
- High formulation flexibility across small molecules and biologics.
- Options for targeted delivery using ligands or magnetic fields.
Major Limitations
However, they also present challenges:
- Manufacturing can be complex and multi-step.
- Scale-up often needs tight control of mixing, solvents, and drying.
- Residual solvent levels must be carefully monitored.
- Proteins and peptides may face stability issues in the polymer matrix.
- Overall costs are usually higher than simple injections or tablets.
Types of Microspheres in Drug Delivery
Microsphere-based delivery strategies are not "one size fits all". Different types of microspheres are designed for different routes, drugs, and clinical goals.
Polymeric Microspheres (PLGA, PLA, PCL)
Polymeric microspheres are the workhorses of modern microsphere drug delivery. They are made from biodegradable polymers such as:
- PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid))
- PLA (polylactic acid)
- PCL (polycaprolactone)
These materials slowly break down in the body into safe metabolites like lactic and glycolic acid. They are widely used for:
- Long-acting injectables in oncology, endocrinology, and psychiatry.
- Local depots for joint, eye, or tumor sites.
- Controlled release of peptides and proteins.
Mucoadhesive Microspheres
Mucoadhesive microspheres are designed to stick to mucosal surfaces. They often use polymers like chitosan, carbomers, alginate, or other hydrophilic materials.
They are used for:
- Nasal delivery to bypass first-pass metabolism.
- Buccal or sublingual delivery for rapid uptake.
- Ocular administration to improve residence time.
- Gastrointestinal delivery to extend contact with the GI tract.
Floating / Gastro-Retentive Microspheres
Floating microspheres are low-density systems that stay on top of gastric fluids. Some use gas-generating cores or swellable shells.
They are useful when drugs:
- Are best absorbed in the stomach or upper small intestine.
- Have a narrow absorption window.
- Need more time in the stomach to reach effective levels.
Lipid Microspheres
Lipid microspheres are based on oils or phospholipids. They can solubilize hydrophobic drugs and may provide:
- Improved bioavailability of poorly soluble compounds.
- Enhanced tolerability for parenteral administration.
- Opportunities for parenteral nutrition and specialty formulations.
Magnetic Microspheres
Magnetic microspheres contain magnetic particles such as iron oxides inside a polymer or lipid shell. With an external magnetic field, they can be:
- Guided to a specific site in the body.
- Used for localized hyperthermia or combined therapy and imaging.
Ceramic / Inorganic Microspheres
Ceramic or inorganic microspheres often use materials like calcium phosphate or silica. They are especially attractive for:
- Bone or dental applications.
- Imaging contrast or theranostic systems.
- Slowly resorbing scaffolds in tissue engineering.
To explore additional carrier formats and advanced targeting options, visit our comprehensive Module Delivery Systems platform at Creative Biolabs.
Applications of Microsphere Platforms
Microsphere platforms unlock a wide range of practical and clinically meaningful applications, offering versatile solutions for long-acting injectables, biologic stabilization, targeted delivery, and advanced gastrointestinal or mucosal drug administration.
PLGA/PLA Microspheres for Long-Acting Injectables
PLGA/PLA-based LAI formulations have transformed many chronic therapies, such as diabetes treatment (Figure 2). In these microsphere-based delivery strategies, the product is:
- Injected intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
- Slowly releases the drug over weeks or months.
- Maintains more stable plasma concentrations.
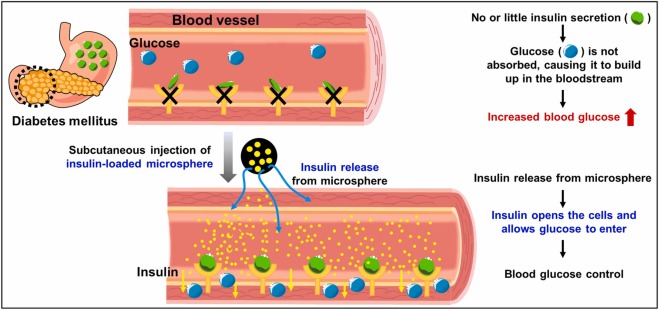 Fig.2 Application of insulin-loaded microspheres in diabetes treatment.3
Fig.2 Application of insulin-loaded microspheres in diabetes treatment.3
This approach can:
- Reduce dosing from daily to weekly or monthly.
- Improve adherence in conditions like schizophrenia or hormone disorders.
- Decrease peaks and troughs that cause side effects.
Several FDA-approved depot products already rely on PLGA or PLA microspheres, demonstrating that this technology is not only promising but also proven.
Microsphere Platforms for Vaccines, Proteins, and Gene Delivery
Microsphere-based delivery strategies are especially powerful for biologics and vaccines.
They can:
Shield antigens or proteins from degradation.
- Create a depot effect, mimicking prime–boost schedules from a single injection.
- Support mucosal vaccines via nasal, pulmonary, or oral routes.
- Co-deliver adjuvants and targeting ligands for stronger, more focused immune responses.
Emerging systems use polymer or polysaccharide microspheres for:
- DNA and mRNA constructs.
- Growth factors and cytokines.
- Gene-modulating agents for local, sustained effects.
Mucoadhesive, Floating, and Gastro-Retentive Systems
Mucoadhesive, floating, and gastro-retentive microspheres adapt the basic technology to the complex GI and mucosal environments.
Mucoadhesion for Nasal, Ocular, Buccal, and GI Delivery
Mucoadhesive microspheres are coated or formed with polymers that interact with mucus, such as chitosan or carbomers. This:
- Extends contact time with the epithelium.
- Improves absorption of drugs with low permeability.
- Supports site-specific delivery, for example, to nasal or colonic tissues.
Floating Systems for Gastric Retention
Floating microspheres stay in the stomach by having a lower density than gastric fluid or releasing gas. They are helpful when:
- Drugs are best absorbed in the stomach or upper intestine.
- Local action in the stomach is desired, as in certain infections.
Expanding Interest in Oral Biologic Delivery
By combining mucoadhesion, protection from acid, and controlled release, microsphere-based delivery strategies are increasingly explored for oral biologics, a long-standing challenge in drug development.
Design, Testing, and Regulatory Considerations
Successful development of microsphere-based delivery systems depends on rigorous design, thorough testing, and careful regulatory alignment to ensure each formulation meets the safety, quality, and performance standards required for clinical translation.
For more advanced formulation options and related technologies, explore our full suite of targeted delivery platforms at Creative Biolabs Module Delivery Systems.
Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs)
For microsphere-based delivery strategies to succeed, several critical quality attributes must be defined and tightly controlled:
- Particle size and size distribution (polydispersity).
- Encapsulation efficiency and loading.
- In vitro release profile and correlation with in vivo behavior.
- Residual solvents and impurities.
- Sterility and endotoxin levels for parenteral products.
Regulatory Challenges
Regulators focus strongly on:
- Reproducible release kinetics from batch to batch.
- Long-term stability of encapsulated biologics.
- Robust, scalable manufacturing processes.
These requirements help explain why the number of approved microsphere depots remains modest, even after decades of research.
How Creative Biolabs Supports Microsphere-Based Delivery Development
Creative Biolabs offers an integrated targeted delivery platform to help you design, optimize, and validate microsphere-based delivery strategies from concept to preclinical evaluation.
Material and Polymer Selection
We help you choose the right polymer or hybrid system, considering:
- PLGA, PLA, PCL grades and ratios.
- Natural polymers like alginate, chitosan, and gelatin.
- Magnetic or lipid components when targeting or imaging is required.
Microsphere Fabrication Technologies
Our scientists design and optimize microspheres using multiple fabrication routes, such as:
- Double emulsion (W/O/W) for hydrophilic drugs and peptides.
- Microfluidic encapsulation for precise, monodisperse microspheres.
- Spray drying for scalable, industrially relevant processes.
These processes are tuned to your desired release profile, particle size, and route of administration.
Advanced Characterization & In Vitro Release Testing
We provide detailed characterization, including:
- Particle size and morphology.
- Encapsulation efficiency and loading.
- In vitro release testing under biorelevant conditions.
- Stability studies for sensitive molecules.
These data support regulatory submissions and process refinement.
Targeting Ligands and Surface Engineering
To unlock true targeted delivery, Creative Biolabs can:
- Attach antibodies, peptides, sugars, or small molecules to microsphere surfaces.
- Design mucoadhesive or stealth coatings.
- Tailor zeta potential and hydrophilicity for circulation or mucosal retention.
In Vivo Evaluation and Preclinical Support
Finally, we help bridge the gap to the clinic by:
- Designing relevant in vivo models for your indication.
- Assessing biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics.
- Supporting iterative optimization between formulation and biology.
Together, these services connect seamlessly with the broader Targeted Delivery solutions offered by Creative Biolabs.
For Research Use Only. Not for Clinical Use.
Related Services You May Be Interested in
FAQs
What are microspheres in drug delivery?
Microspheres are tiny spherical carriers that encapsulate drugs in a polymer, lipid, or inorganic matrix to provide controlled, targeted, or sustained release.
What are the advantages of microsphere-based delivery strategies?
They extend drug action, reduce dosing frequency, smooth blood levels, and support localized or targeted therapy for many diseases.
How do microspheres control drug release?
They release drugs by diffusion, polymer erosion, or both, with the rate controlled by polymer type, particle size, porosity, and formulation method.
What polymers are commonly used for microsphere drug delivery?
PLGA, PLA, PCL, alginate, chitosan, and gelatin are widely used because they are biodegradable and can be tuned for different release times.
Why are biodegradable polymers important for long-acting treatments?
They allow drug release over weeks or months, improve adherence, and reduce clinic visits by transforming frequent injections into infrequent long-acting regimens.
Conclusion
Microsphere-based delivery strategies are reshaping how we think about dosing, patient adherence, and targeted therapy. By combining smart polymers, precise fabrication, and robust testing, they turn ordinary pharmaceuticals into long-acting, high-performance treatments that fit real-world patient needs.
As new biologics, vaccines, and gene therapies enter the pipeline, demand for reliable, scalable microsphere platforms will only grow. Partnering with Creative Biolabs means working with a team that understands both the science of microsphere drug delivery systems and the practical steps needed to translate them into advanced products.
If you are planning your next sustained-release depot, vaccine, or targeted delivery program, we invite you to contact Creative Biolabs today to discuss how our microsphere-based delivery strategies and targeted delivery platforms can accelerate your innovation.
References
- Su, Y. et al. "PLGA-based biodegradable microspheres in drug delivery: recent advances in research and application." Drug Delivery 28, 1397–1418 (2021). https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10717544.2021.1938756.
- Lengyel, M., Kállai-Szabó, N., Antal, V., Laki, A. J. & Antal, I. "Microparticles, Microspheres, and Microcapsules for Advanced Drug Delivery." Sci. Pharm. 87, 20 (2019). https://www.mdpi.com/2218-0532/87/3/20.
- Lee, Y. J. & Kim, M. S. "Advances in drug-loaded microspheres for targeted, controlled, and sustained drug delivery: Potential, applications, and future directions." Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 189, 118244 (2025). https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S075333222500438X. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



