Nucleus Targeting Module Development Service
Accelerate Your Targeted Drug Delivery Research!
Are you currently facing challenges in delivering your therapeutic agents precisely to the cell nucleus? Do you struggle with poor drug efficacy and significant off-target effects? Creative Biolabs' Nucleus Targeting Module Development service empowers you to overcome these obstacles. We help you enhance drug efficacy and minimize adverse reactions through advanced drug delivery systems. Our expertise in developing cutting-edge nucleus targeting modules ensures your therapeutics reach their intended target, maximizing their impact.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Overview
As the genomic command hub of eukaryotes, the nucleus governs critical cellular processes. Pharmacological agents targeting nucleic acids aim to block DNA replication and suppress transcriptional activity of key genetic elements. Yet even when intracellular delivery occurs, most therapeutics exhibit limited nuclear bioavailability—only 0.1% of cytosolically introduced plasmid vectors achieve nuclear localization. Furthermore, malignant proliferation in oncological contexts drives genomic adaptations conferring therapeutic resistance, perpetuating refractory cell lineages. This necessitates nanoscale delivery platforms enabling direct nuclear transport of payloads to enforce mitotic arrest while circumventing off-target cytotoxicity.
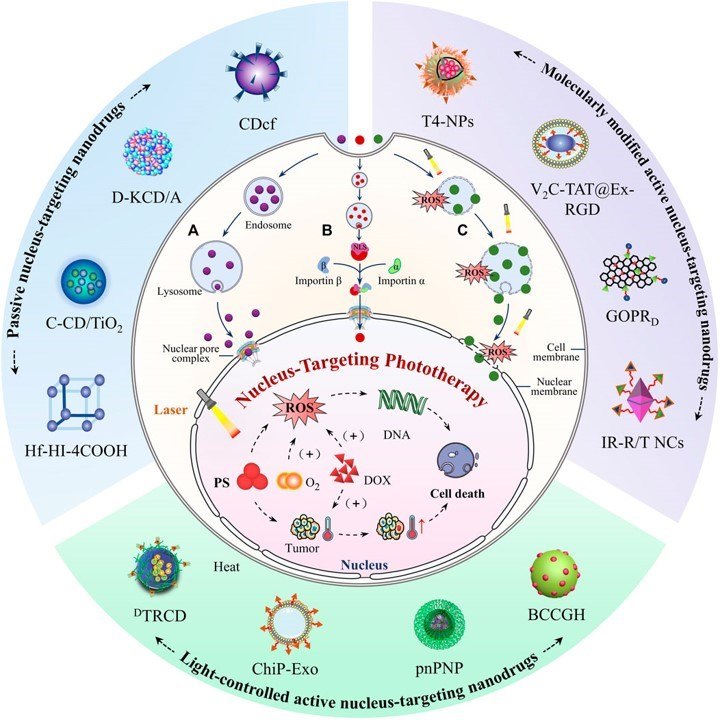 Fig 1. Schematic illustration of nucleus-targeting nanodrugs.1,3
Fig 1. Schematic illustration of nucleus-targeting nanodrugs.1,3
Nuclear Targeting Strategy
The nuclear localization signal (NLS) demonstrates strong binding to nuclear pore structures, enabling traversal of bipartite nuclear membranes. Subnuclear targeting strategies are critical for therapeutic interventions, with NLS frequently employed for biomacromolecule complexation (proteins, nucleic acids). Engineered cell-penetrating peptide derivatives enable organelle-specific delivery to this compartment, where NLS integration into conjugates remains an established methodology. Novel nucleolin-targeting peptides (NBPs) exhibit in vivo efficacy in ocular models, transporting therapeutic proteins, imaging agents, and genetic payloads to nuclei. PEG-modified NBP nanostructures enhance intranuclear transport efficiency and transgene expression profiles, positioning these systems as promising vectors for ophthalmic therapeutic applications.
- Viral and non-viral vectors for nuclear delivery
Viral-derived peptides exhibiting nuclear trafficking capabilities—such as the SV40 T-antigen-derived KKKRKV sequence—are employed to facilitate DNA transport into nuclei. To bypass constraints of viral delivery platforms, engineered non-viral carriers mimicking pathogenic mechanisms have been developed for polynucleotide transport. These systems primarily utilize lipid-derived nanostructures (lipoplexes) for nucleic acid encapsulation or cationic polymer-based assemblies (polyplexes) employing macromolecules such as PEI. Diverging from lipidosome approaches, polyplexes employ hyperbranched or multiamine structural configurations. Cellular uptake occurs via endocytosis, with endosomolytic compounds enhancing endosomal escape. Strategic integration of nuclear localization signals—through covalent linkage or lipid formulation co-engineering—optimizes intranuclear payload deposition. Additionally, chromatin-associated proteins rich in cationic residues (histones, protamine) demonstrate utility in nucleic acid compaction and delivery.
- Delivery using nanoparticles
Synthetic nanoscale architectures function as modular transport platforms, surpassing legacy delivery methods like liposomal carriers. Nanomedicine—an advancing field—showcases translational capacity for bioactive payload conveyance, with multiple systems reaching clinical translation. Bioactive payloads are integrated into nanocarrier frameworks, where structural precision optimizes stability and controlled release dynamics. Surface engineering with targeting ligands enables membrane traversal precision and subcellular addressing. While sub-200 nm constructs undergo endocytic uptake, larger micron-scale systems may follow phagocytic pathways to phagosomal compartments. A critical challenge remains cytosolic payload liberation—addressed through stimuli-responsive polymeric architectures that exploit pH gradients between endosomes and cytoplasm to trigger controlled release.
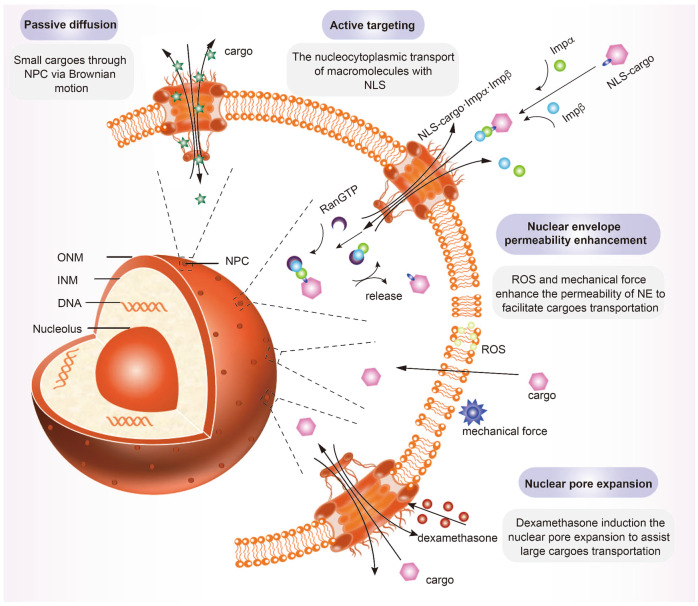 Fig 2. Design guidelines of nuclear-targeted nanosystems.2,3
Fig 2. Design guidelines of nuclear-targeted nanosystems.2,3
- Nuclear delivery through peptoids
Peptoids, synthetic biomimetic oligomers, exhibit cell-penetrating architectures mediated by glycine-rich (5–6 mer) backbone structures. Engineered through side chain diversification, two variants emerge: amino-functionalized and guanidinium-modified peptoids. Despite shared cationic properties, their intracellular sorting diverges—aminopeptoids accumulate cytosolically, while guanidinium derivatives localize to nuclei. This demonstrates how side chain chemistry governs intracellular sorting kinetics and subcellular destination, enabling rational design of compartment-specific pharmaceuticals.
What We can Offer?
Creative Biolabs has a complete module delivery system and an experienced team of scientists. We offer:
- Individual targeting modules
- Different types of module-payload/carrier complexes for specific subcellular organelles
- A wide range of corresponding products
- In vitro and in vivo validation of targeting module efficacy and specificity
- Consultation and support throughout the project lifecycle
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner for nucleus targeting module development. We offer a unique combination of expertise, technology, and customer focus to ensure the success of your research and development projects. Our commitment to quality and innovation sets us apart.
- Deep Expertise: Our team comprises leading experts in nucleus targeting, with extensive experience in designing and developing novel drug delivery systems.
- State-of-the-Art Technology: Our nuclear-targeted vectors employ pioneering technological frameworks to ensure uncompromised precision in subcellular delivery systems. Core capabilities span molecular synthesis platforms, super-resolution microscopy, and validated multi-scale models encompassing cellular assays through preclinical biodistribution studies.
- Customized Solutions: Our customized platforms are engineered to address unique client requirements and strategic goals. Through a partnership model, we maintain continuous alignment across all project phases with dedicated iterative consultation.
- Proven Success: Creative Biolabs has a strong track record of success in developing nucleus targeting modules for a variety of therapeutic applications. Our clients experience significant improvements in drug efficacy and reductions in off-target effects.
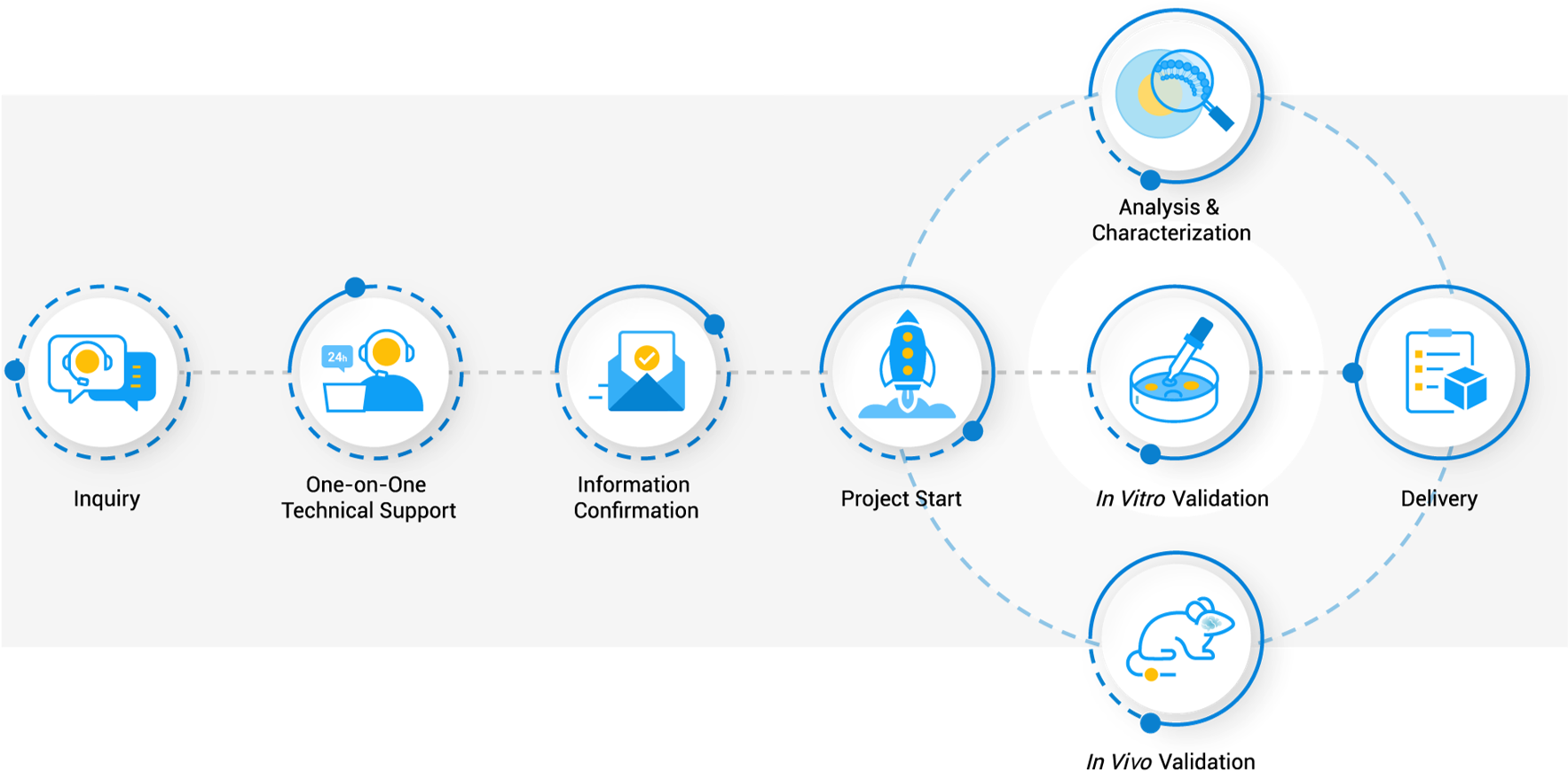
Workflow
FAQs
What methodologies guarantee precision in Creative Biolabs' nuclear targeting platforms?
Our methodology combines systematic engineering of nuclear localization signals (NLS) with refined biomolecular recognition for karyopherin-mediated transport pathways. Cross-platform evaluations spanning computational modeling through live-animal validation verify targeting fidelity while eliminating non-nuclear accumulation.
Does Creative Biolabs engineer nuclear-targeting systems for macromolecular therapeutics?
Affirmative. We deploy advanced transport engineering, leveraging TAT peptide-mediated nuclear entry pathways to accommodate bulky payloads. Our nanocarrier technology circumvents nuclear membrane steric restrictions through size-optimized vector architectures.
What are the advantages of using nucleus-targeted drug delivery compared to traditional methods?
Nucleus-targeted drug delivery offers several advantages, including increased drug efficacy, reduced off-target effects, and the potential to overcome multidrug resistance. By delivering therapeutic agents directly to the nucleus, we can maximize their interaction with their target and minimize their exposure to other cellular compartments.
What types of therapeutic agents can be delivered using Creative Biolabs' nucleus targeting modules?
Our technology is versatile and can be adapted to deliver a wide range of therapeutic agents, including small molecules, proteins, nucleic acids, and gene therapy vectors. We can customize our modules to meet the specific requirements of your therapeutic agent.
Creative Biolabs provides tailored targeted delivery solutions addressing unique research and therapeutic requirements. To explore these capabilities, contact our technical team for protocol specifications and collaborative development pathways.
References
- Long, Xingyu, et al. "Nucleus-targeting phototherapy nanodrugs for high-effective anti-cancer treatment." Frontiers in Pharmacology 13 (2022): 905375.
- Yang, Jingjing, et al. "Organelle-targeted therapies: a comprehensive review on system design for enabling precision oncology." Signal transduction and targeted therapy 7.1 (2022): 379.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



