Micelle based Delivery System Development Service
In modern drug development, therapeutic impact hinges on precise delivery. Systemic toxicity and poor bioavailability of advanced modalities like nucleic acids and protein degraders are major roadblocks. Creative Biolabs' micelles-based delivery system development service provides the critical engineering required to overcome these challenges. We design highly stable, targeted polymeric nanocarriers that dramatically enhance drug concentration at the site of action, improving efficacy and safety.
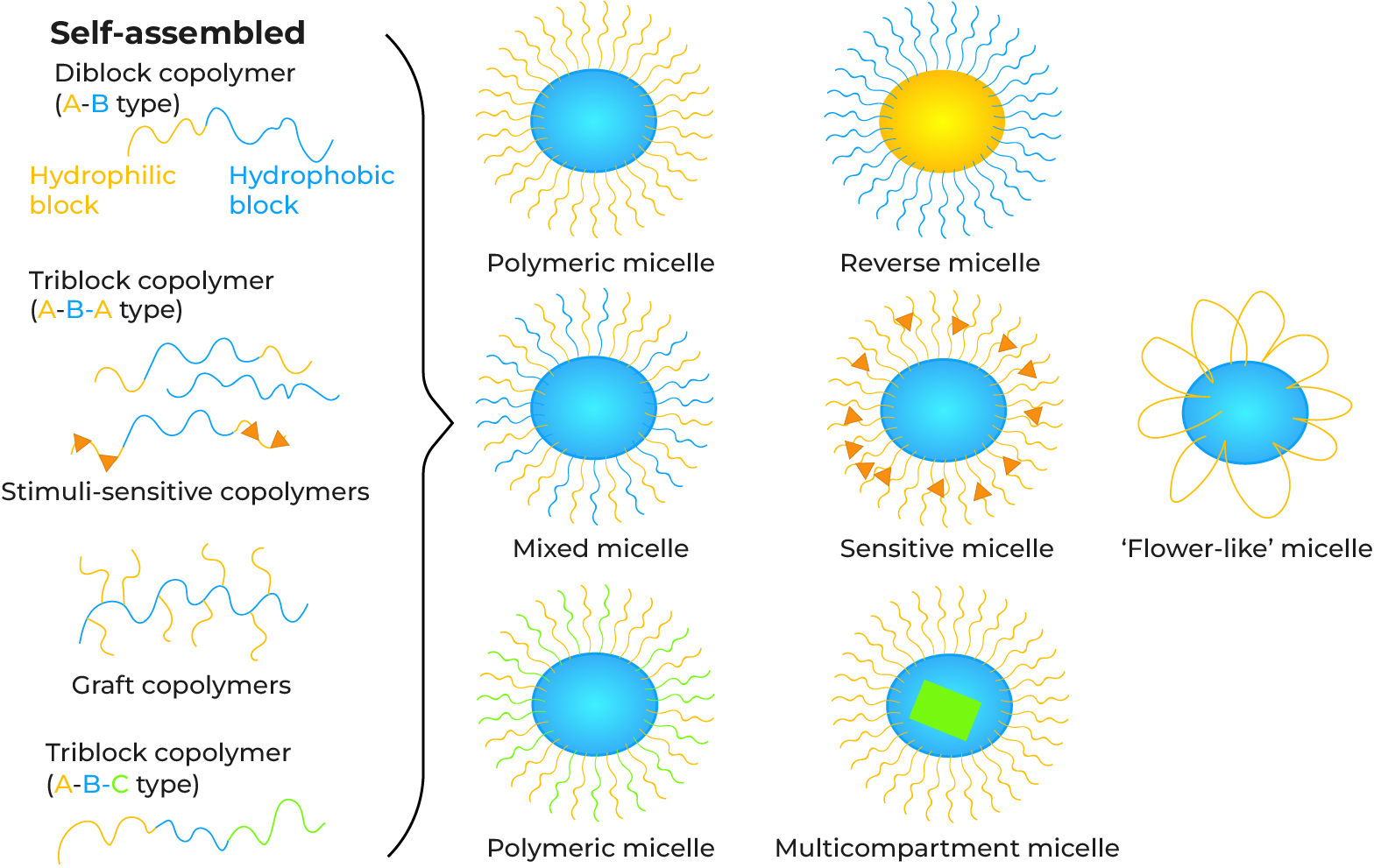
What Are Polymeric Micelles?
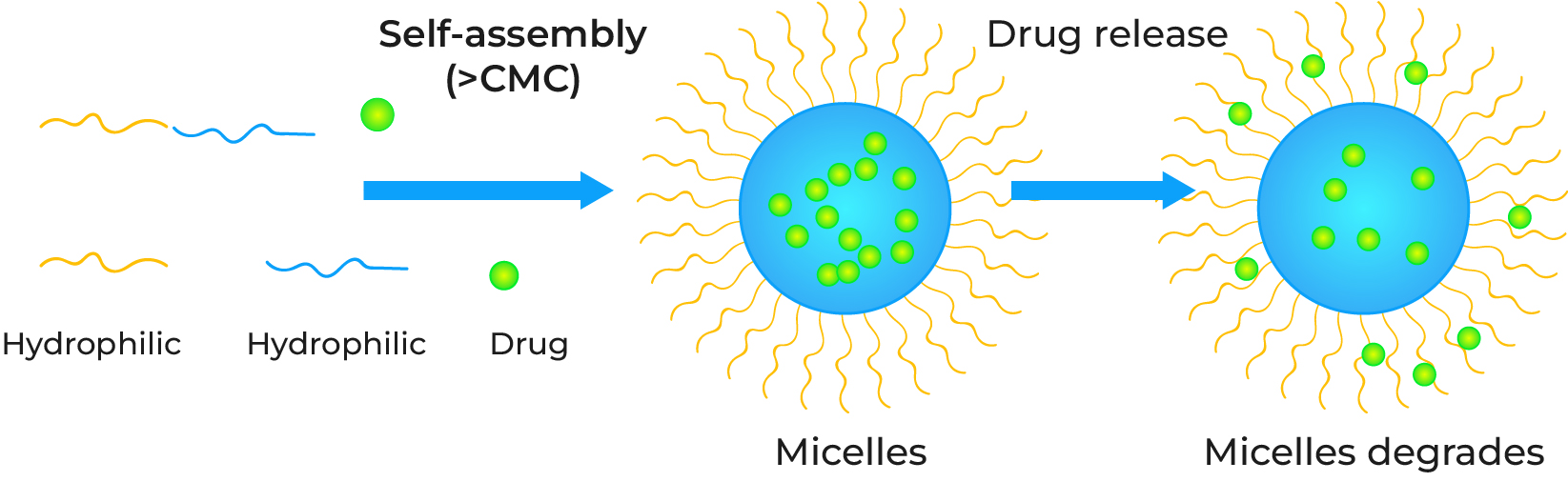
Polymeric micelles are nanosized (typically 10–100 nm) core-shell structures formed by the self-assembly of amphiphilic block copolymers in aqueous solution. The polymer consists of a hydrophilic block (e.g., PEG) that forms the outer shell, and a hydrophobic block (e.g., PCL) that forms the inner core. This architecture allows the hydrophobic core to encapsulate water-insoluble therapeutics, while the hydrophilic shell provides "stealth" properties, minimizing non-specific binding, immune recognition, and prolonging systemic circulation.
Essential Polymer Components for Micelle Construction
Selecting the appropriate block copolymer is the foundation of a successful micelle system. We utilize an extensive library of materials, each offering unique pharmacokinetic and payload-retention characteristics.
Hydrophilic Polymers
| Polymer | Structure | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEG |
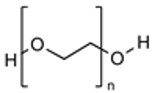
|
Clinically Proven Stealth Properties Extended Circulation Reduced RES Uptake Enhanced EPR Effect |
Unpredictable Pharmacokinetics Non-Biodegradable |
| Polysaccharides |
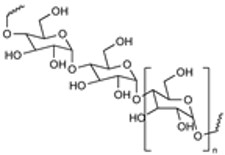
|
Excellent Biocompatibility Inherent Stealth Mucoadhesive Targeting Capabilities Anti-inflammatory Highly Modifiable |
Processing Sensitivity Purity-Dependent Toxicity |
| pHPMA |
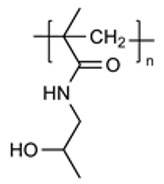
|
Favorable Safety Profile Engineerable |
Limited Clinical Translation Complex Synthesis Preclinical-Clinical Discrepancy |
| Poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) |
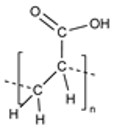
|
Stimuli-Responsive Mucoadhesive Biocompatible & Biodegradable |
Poor Mechanical Strength |
| Poly(glutamic acid) (PGA) |
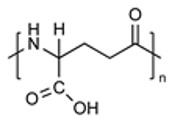
|
Stimuli-Responsive Biocompatible & Biodegradable Easily Modified |
MW Limitations High Production Cost |
| Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) |
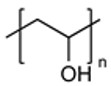
|
Versatile Building Block Excellent Biocompatibility |
Hydrolytic Instability |
| Poly(N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) (PVP) |
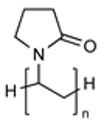
|
Functionalizable |
Non-Biodegradable Hygroscopic |
| Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) (PNIAAm) |
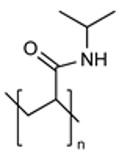
|
Thermo-Responsive | Lack of In Vivo Data |
| Poly(ethylene imine) (PEI) |
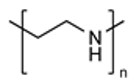
|
Superior Cellular Uptake Endosomal Escape |
Significant Cytotoxicity Payload Entrapment |
Hydrophobic Polymers
| Polymer | Structure | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(histidine) (PHIS) |
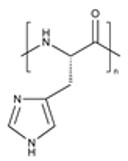
|
pH-Responsive Biocompatible & Biodegradable Endosomal Escape |
Stability Concerns Performance Variability |
| Polyethers |
|
Widely Available & Cost-Effective Thermo-Responsive |
Low Drug Affinity |
|
Polyesters (e.g., PLGA, PCL, PGA, PLCA) |
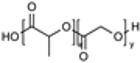
|
Industry Standard Biocompatible & Biodegradable Tunable Release Stimuli-Responsive |
Hydrophobicity & Opsonization Degradation Byproducts Burst Release Degradation Rate Mismatch Cationic Toxicity |
The Critical Role of Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC)
The critical micelle concentration (CMC) is a fundamental parameter defining micelle stability. It is the minimum concentration required for the block copolymers to form micelles. For in vivo applications, the micelles must maintain structural integrity when diluted in the bloodstream. Creative Biolabs engineers systems with ultra-low CMC values (often in the nanomolar range) to prevent premature payload release, guaranteeing the therapeutic reaches its intended site intact.
How Micelles Achieve Precision Targeting
Micelles enable superior biodistribution through a combination of passive and active strategies:
Passive Targeting: The small size of the micelle allows it to preferentially accumulate at tumor sites or inflamed tissues with leaky vasculature via the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect.
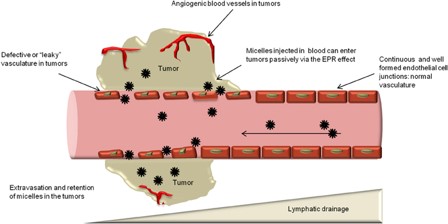 Fig. 1 EPR effect and passive targeting. 1,3
Fig. 1 EPR effect and passive targeting. 1,3
The Power of Stimuli-Responsive Micelles
Stimuli-responsive micelles, often called "smart" nanocarriers, represent a major advancement in targeted delivery. These systems are engineered to remain stable during systemic circulation but rapidly change their physicochemical properties (e.g., size, charge, or solubility) only when they encounter a specific biological cue or external stimulus. This environmental sensing capability ensures that the therapeutic payload is released precisely at the disease site or within the correct cellular compartment, maximizing efficacy and minimizing off-target effects.
| Stimuli | Micelle Mechanism | Biological Trigger |
|---|---|---|
| pH | Protonation or deprotonation of polymer side chains (e.g., poly(β-amino ester)) causes rapid micelle swelling or disassembly. | Low pH environment in endosomes, lysosomes, or acidic tumor tissue (pH 5.0−6.5) |
| Redox | Cleavage of disulfide (S–S) bonds in the polymer backbone or cross-links by high concentrations of reducing agents. | High concentration of intracellular reducing agents, such as glutathione (GSH), promoting cytosolic release. |
| Temperature | Polymers undergo a sharp phase transition at a specific critical solution temperature (LCST/UCST). | Localized hyperthermia treatment (mild temperature increases), causing micelle disruption and rapid drug release. |
| Enzyme | Specific peptide sequences or ester bonds in the polymer are selectively cleaved by catalytic action. | Overexpressed enzymes (e.g., Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs), phospholipases) in the disease microenvironment. |
| Hypoxia | Utilizes nitroaromatic or similar chemical groups that undergo rapid degradation under reducing conditions. | Low oxygen tension characteristic of solid tumor cores and ischemic tissues. |
| Magnetic | Incorporates magnetic nanoparticles for enhanced field-guided accumulation and potential remote-triggered release. | Application of an external magnetic field to the desired site of action. |
Creative Biolabs' Integrated Micelle Development Services
Creative Biolabs combines proprietary polymer synthesis with advanced formulation expertise to design and produce micellar systems tailored to your specific therapeutic and biological challenge. We don't offer off-the-shelf guesswork; we provide customized, precision nanocarriers.
Custom Polymer Synthesis
We engineer the foundation of your delivery system with personalized block copolymer customization service, focusing on precise control over physicochemical properties.
Polymer Composition
Customization of polymer type (PEG, PLGA, PCL) and structure (diblock AB, triblock ABA or ABC) to optimize micelle stability and degradation.
Molecular Weight & Proportion
Control of molecular weight (1k-200k DA) and block ratios to fine-tune micelle size, CMC, and drug loading capacity.
Functional Groups
Incorporation of key functional groups (carboxyl, amino, thiol, maleimide, azide, alkyne, fluorophores) for subsequent bioconjugation or imaging probe development.
Advanced Polymerization Methods
Utilizing state-of-the-art techniques, including click chemistry and enzymatic catalytic polymerization, for synthesizing complex, high-purity copolymers.
High-Efficiency Payload Encapsulation

Our optimized methodologies maximize the therapeutic concentration delivered per nanocarrier.
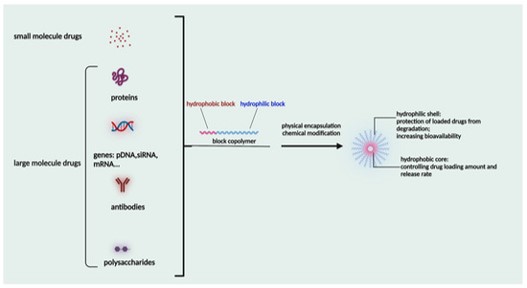
Tailored Loading Techniques
Utilization of specialized methods (e.g., film hydration, solvent evaporation, dialysis) selected based on the payload's physicochemical properties.
Complex Payload Expertise
Specialized capability in encapsulating challenging therapeutics, including Nucleic Acids, Protein Degraders, and BCS Class II/IV small molecules.
High Encapsulation Efficiency
Guaranteed exceptional encapsulation efficiency and high drug loading capacity, essential for maximizing the active payload delivered per carrier mass for optimal scientific research.
Advanced Active Targeting Strategy
We design highly selective delivery systems through sophisticated surface modifications:
Covalent Ligand Conjugation
Secure attachment of specific Targeted Modules (peptides, aptamers, antibodies) to the micelle's hydrophilic shell via robust chemical linkers.
Receptor-Mediated Selectivity
Strategy focused on designing systems for receptor-mediated uptake, dramatically improving targeted delivery and the therapeutic index against diseased cells.
Responsive Trigger Integration
Development of pH-, thermal-, or redox-responsive modules to facilitate on-demand release and enhance endosomal escape at the subcellular level.
Physicochemical Characterization Service

Our meticulous characterization services ensure exceptional batch-to-batch consistency and provide the comprehensive, verifiable data essential for validating your micelle system's performance.
Workflow
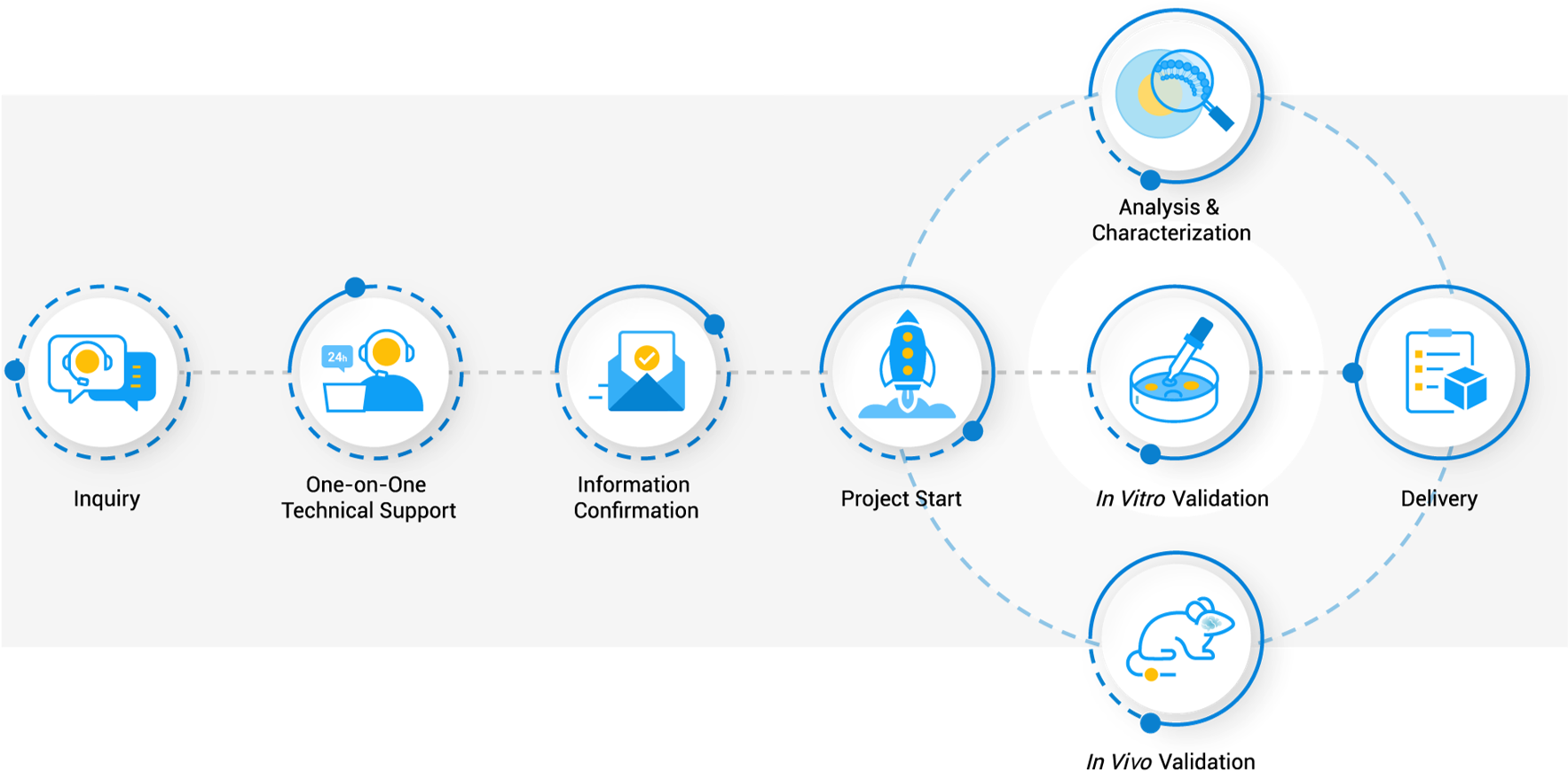
Applications of Micelles in Modern Research
Our advanced micelle delivery systems are engineered to solve delivery challenges across critical therapeutic domains, helping researchers envision the potential of precision nanocarriers in their work:
- Nucleic Acid Delivery (Gene Therapy & Silencing): Micelles protect siRNA/mRNA from degradation and utilize responsive polymers to achieve efficient endosomal escape and cytoplasmic release for gene therapy applications.
- Oncology and Disease Targeting: We target solid tumors using the EPR effect for passive accumulation, combined with active ligand functionalization to enhance specific cellular uptake and reduce systemic toxicity.
- Protein & Peptide Delivery: The protective hydrophobic core stabilizes complex Proteins, Peptides, and novel modalities like Protein Degraders, ensuring structural integrity and activity until target release.
- Specialized Tissue Delivery: We engineer functionalized micelles capable of crossing biological barriers like the blood-brain barrier (BBB), enabling delivery for CNS and ophthalmic disease treatments.
- Tissue Engineering & Biodegradable Scaffolds: Polymer-based micelle technology can be adapted to develop biocompatible and biodegradable hydrogels or scaffolds, enabling localized drug release for regenerative medicine.
- Stimuli-Responsive Systems: Engineering micelles with pH-, thermal-, or redox-responsive polymers that trigger payload release precisely upon encountering specific disease biomarkers or environmental cues.
Why Choose Creative Biolabs for Micelles Development?
With over 20 years of experience in sophisticated drug delivery, Creative Biolabs is more than a vendor—we are your scientific partner in navigating the complexities of nanomedicine formulation.
Expertise in Complex Payloads
We specialize in formulating nucleic acids and advanced therapeutics that challenge traditional delivery systems.
Modular Approach
We integrate our micelle systems with various targeted modules (peptides, aptamers) and other module delivery systems (Liposomes, LNPs) for truly customized, hybrid solutions.
Accelerated R&D
Our proven methodologies and deep scientific knowledge empower your researchers to accelerate your research from concept to preclinical validation with confidence.
20+ Years of Nanomedicine Expertise
Leverage two decades of scientific knowledge and formulation success in overcoming biological and chemical barriers in drug delivery.
Ready to transform your therapeutic candidate into a highly effective nanomedicine? Let Creative Biolabs' expertise in precision micelle engineering solve your most demanding delivery challenge. Contact our experts today to accelerate your critical R&D project.
Related Services
FAQs
What is the minimum stability requirement for my micelle formulation to proceed to in vivo testing?
We highly recommend formulations with a CMC in the low nanomolar (nM) range or below. This ultra-low CMC ensures the micelle remains intact and stable when exposed to high dilution rates in the systemic circulation.
Can you customize the micelle size for a specific tumor type or tissue?
Yes. Micelle size is highly dependent on the polymer block length ratios and formulation method. We can precisely control the final diameter, typically between 10 nm and 100 nm, to optimize for tumor penetration or clearance kinetics based on your specific target.
Which polymer is best suited for my novel hydrophobic small molecule drug?
This depends on the drug's log P value, molecular weight, and any inherent ionic characteristics. We initiate the project with a polymer screening phase, testing systems like PEG-PCL, PEG-PLA, or novel hydrotropic polymers to optimize drug loading and core compatibility.
What is the primary difference between passive and active targeting in your micelle systems?
Passive targeting relies on the micelle's size to accumulate in leaky tissues (EPR effect). Active targeting involves attaching a specific ligand (Targeted Module) to the surface for receptor-mediated internalization by the target cell.
What characterization data is included in the final deliverable?
We provide fundamental physicochemical data, including particle size (DLS), zeta potential, and drug loading/encapsulation efficiency. Advanced characterization services, such as morphology (TEM/AFM), CMC determination, and detailed in vitro release kinetics, are available as customizable options.
Can you work with my novel or proprietary block copolymer structure?
Yes, we are technology agnostic and can optimize the formulation process for almost any novel amphiphilic block copolymer provided by the client, ensuring the resulting micelle system meets all performance requirements.
References
- Jhaveri, Aditi M., and Vladimir P. Torchilin. "Multifunctional polymeric micelles for delivery of drugs and siRNA." Frontiers in pharmacology 5 (2014): 77. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2014.00077
- Wang, Qi, et al. "Exploring the application of micellar drug delivery systems in cancer nanomedicine." Pharmaceuticals 16.3 (2023): 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030433
- Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

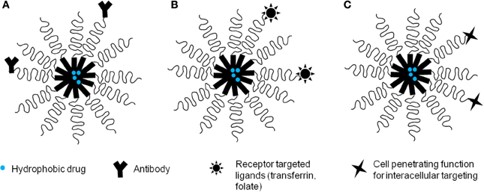 Fig. 2 Drug-loaded polymeric micelles with various targeting functions. 1,3
Fig. 2 Drug-loaded polymeric micelles with various targeting functions. 1,3