Our expertise in conjugation chemistry allows us to create stable and highly effective RDCs by attaching your chosen targeting ligand to various radionuclides. We optimize the linker and chelator to ensure maximum stability and targeted delivery.
Radionuclide Drug Conjugate (RDC) Development Service
Are you currently facing challenges such as long drug development cycles, limited treatment options for metastatic diseases, or significant off-target toxicity with traditional therapies? Creative Biolabs' advanced RDC services help you overcome these hurdles and accelerate your research by providing a complete suite of services from custom targeting module synthesis to pre-clinical validation.
Radionuclide Drug Conjugates (RDCs)
Radionuclide drug conjugates (RDCs) are a sophisticated class of targeted agents that represent a significant evolution in nuclear medicine. They are specifically engineered to deliver a lethal radioactive payload directly to a disease site, typically a tumor, while minimizing exposure to healthy tissue. An RDC is composed of three key components: a targeting molecule (such as a monoclonal antibody, a peptide, or a small molecule), a radioactive atom (radionuclide), and a linker or chelator that stably connects the two. The targeting molecule acts as a "homing beacon," recognizing a specific protein or receptor overexpressed on the surface of target cells. The radionuclide, upon arrival, emits high-energy radiation that induces DNA damage and localized cell death. This targeted approach forms the basis of theranostics, where the same targeting molecule can be labeled with a diagnostic radionuclide to locate the tumor, and then with a therapeutic radionuclide for treatment. This diagnostic-therapeutic pairing provides a powerful tool for personalized medicine. The study discussed in the Published Data section is a prime example of this technology in action, showcasing how an RDC can be designed to not only kill cancer cells directly but also to modulate the surrounding immune environment for a more comprehensive therapeutic effect.
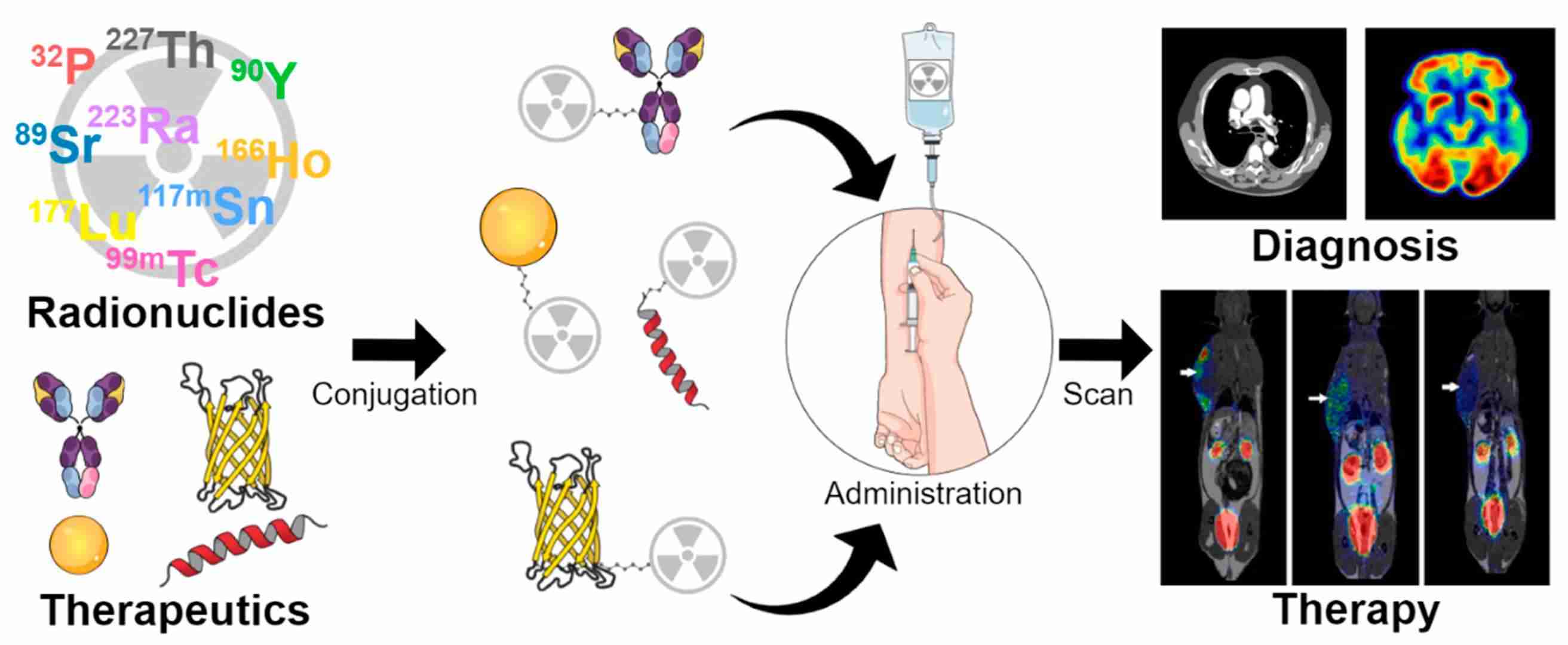 Fig.1 The use of radionuclides as theragnostics.1,3
Fig.1 The use of radionuclides as theragnostics.1,3
Our Radionuclide Drug Conjugates (RDCs) Solution
The versatility of RDCs lies in the ability to select and combine different components to create a tailored therapeutic agent. Our solutions are designed around this principle, offering a range of RDC types to fit your specific project needs. We categorize our RDCs based on the targeting molecule and the type of radionuclide used, allowing for a strategic approach to drug design:
- Antibody-Based RDCs (Radioimmunoconjugates): Utilizing monoclonal antibodies as the targeting moiety, these RDCs are ideal for targets with a slow clearance rate and a long circulation time. Their large size makes them well-suited for targeting extracellular antigens and for treating hematological malignancies.
- Peptide-Based RDCs: These RDCs use smaller peptide sequences as targeting ligands. Peptides offer faster tumor penetration and clearance from non-target organs, making them highly effective for solid tumors and for use with short-lived radionuclides.
- Small Molecule-based RDCs: The smallest of the targeting moieties, small molecules can rapidly and effectively penetrate solid tumors. These RDCs are often used to target intracellular or low-expression receptors and are excellent for diagnostic imaging and therapy of specific cancers like prostate cancer.
- Alpha-Emitter RDCs: These RDCs use alpha-emitting radionuclides that release high-energy particles with a very short range, causing highly localized and potent cell death. They are exceptionally effective at treating small tumors and individual cancer cells.
- Beta-Emitter RDCs: These RDCs utilize beta-emitting radionuclides, which have a longer range and lower energy than alpha emitters. This allows for a "crossfire" or bystander effect, where the radiation can kill nearby untargeted cancer cells, making them well-suited for larger tumors.
Application
The targeted nature of RDCs makes them a powerful tool across a wide range of therapeutic and diagnostic applications, particularly in oncology.
- Targeted Cancer Therapy: RDCs are used to treat various types of cancer by delivering a lethal dose of radiation directly to tumor cells. This is particularly effective for treating cancers that have spread throughout the body, such as metastatic prostate cancer and certain neuroendocrine tumors, which are often difficult to treat with localized external radiation therapy.
- Diagnostic Imaging: By labeling the same targeting molecule with a diagnostic radionuclide, RDCs can be used to precisely locate and stage tumors. This imaging capability provides critical information for guiding treatment decisions and monitoring a patient's response to therapy.
- Theranostics: The ultimate application of RDCs is the seamless integration of diagnosis and therapy. A diagnostic RDC can first identify patients whose tumors highly express a specific target, thereby predicting which patients are most likely to respond to the therapeutic RDC. This personalized approach to medicine ensures more effective treatment and improved patient outcomes.
Contact Us About Bioconjugation Services
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs is uniquely positioned at the forefront of targeted drug delivery innovation. Our team of expert scientists brings over two decades of collective experience in developing sophisticated RDC solutions. We offer a comprehensive suite of products and services designed to meet your project's needs:
Custom Conjugation Services
Targeting Module Development
We provide bespoke synthesis and optimization of targeting ligands, including custom peptides and small molecules, tailored to bind with high specificity to your unique disease biomarker.
Pre-clinical Validation
Our comprehensive in vitro and in vivo testing services assess targeting efficiency, cellular uptake, biodistribution, and therapeutic efficacy, providing you with the crucial data needed to advance your project.
Ready-to-Use Solutions
We offer a selection of pre-validated RDC constructs and components for a range of common targets, allowing you to quickly initiate your research and development efforts.
Scientific and Regulatory Support
Partner with us to leverage our deep scientific knowledge, state-of-the-art facilities, and rigorous quality control for your RDC projects. We provide support from experimental design to data analysis, helping you navigate the complexities of radiopharmaceutical development.
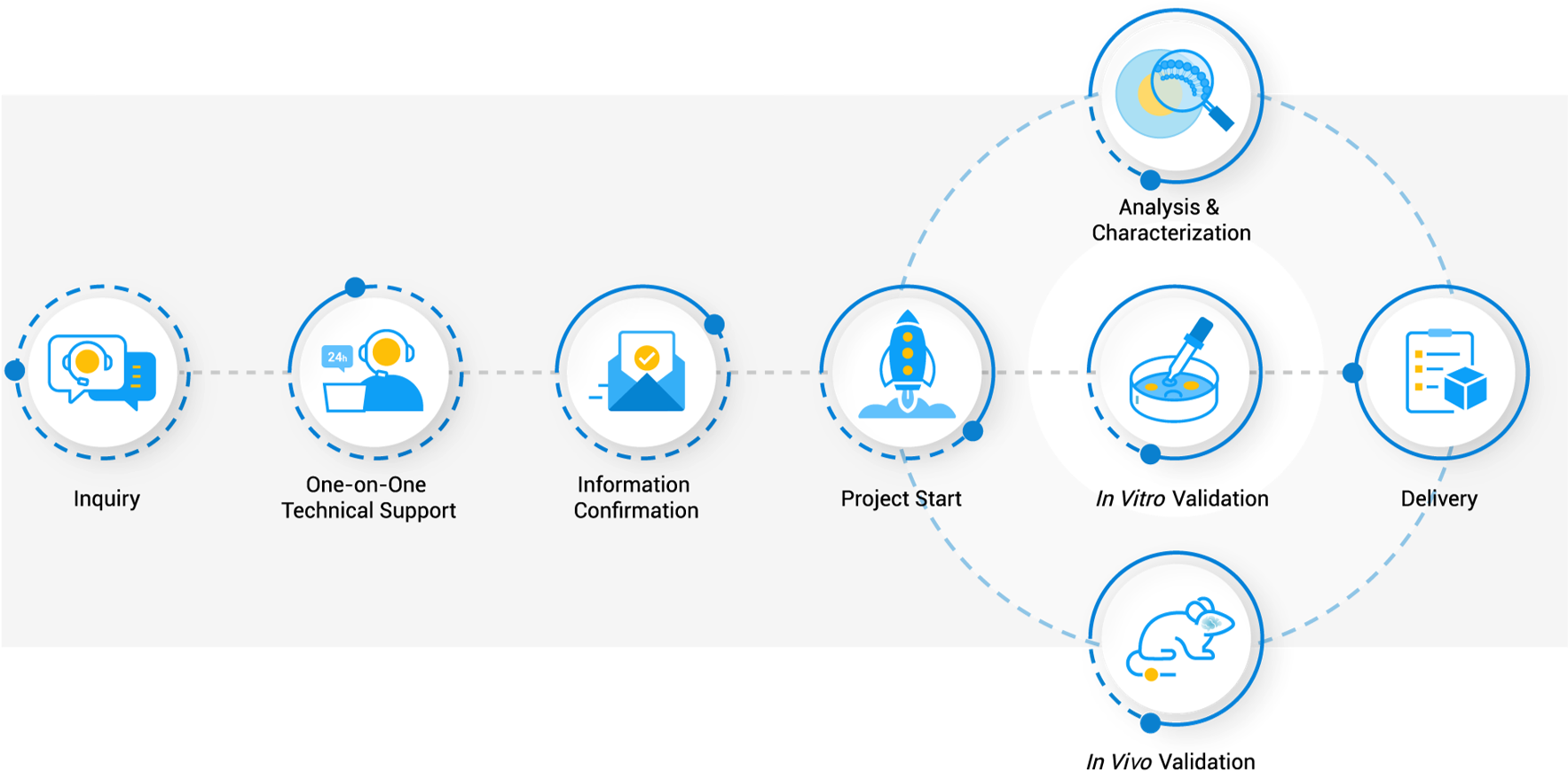
Workflow
Why Choose Us?
Partnering with Creative Biolabs means choosing a path to accelerated drug development, enhanced therapeutic efficacy, and a significant reduction in off-target effects. Our commitment to innovation and scientific excellence ensures that your therapeutic agents reach their intended targets with unprecedented precision, unlocking new possibilities for disease treatment.
Proven Expertise
Our highly specialized team of chemists and biologists possesses deep scientific knowledge in RDC design, synthesis, and characterization. We leverage this expertise to navigate the complex challenges of radiopharmaceutical development, ensuring your project's success.
Innovative Technology
We utilize state-of-the-art platforms and proprietary conjugation methodologies for module synthesis and characterization, ensuring the creation of stable, high-purity RDCs.
Tailored Customization & Flexibility
We offer completely customized RDC design and optimization for your specific therapeutic goals. Our flexible approach allows us to adapt to the unique requirements of your research, from proof-of-concept to lead optimization.
Rigorous Quality & Reliability
Our commitment to scientific rigor and meticulous quality control ensures reliable, reproducible, and high-quality results. Every RDC is thoroughly tested to guarantee its stability, specificity, and therapeutic potential.
Published Data
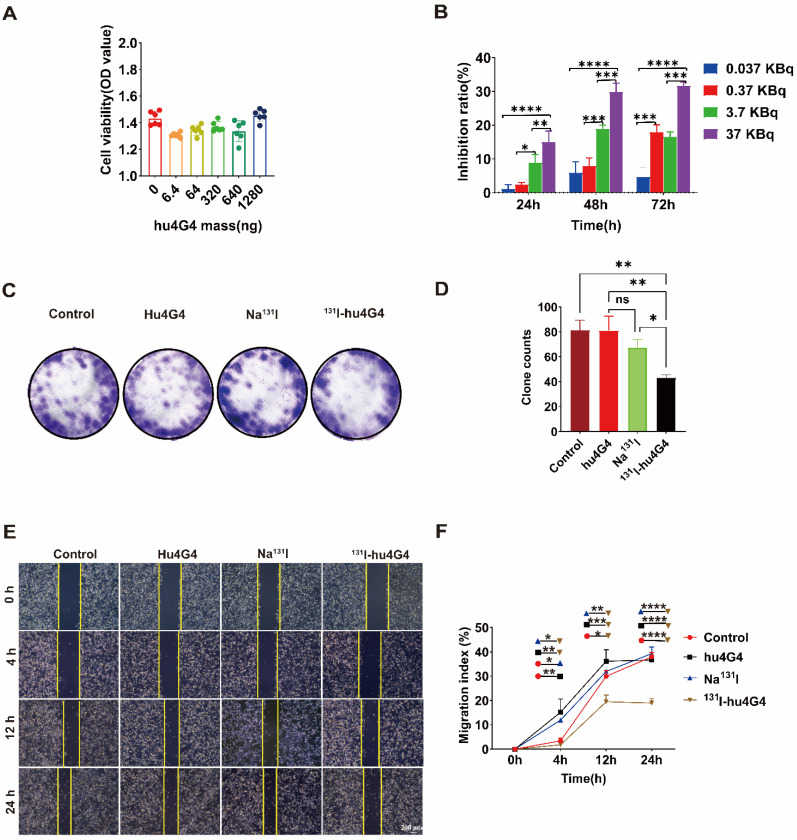 Fig.2 131I-hu4G4 inhibited the viability of U87 cells in vitro.2,3
Fig.2 131I-hu4G4 inhibited the viability of U87 cells in vitro.2,3
In their experiments, the researchers first prepared the 131I-hu4G4 RDC and confirmed its strong ability to bind to its target protein, B7-H3, on cancer cells. In vitro tests on glioblastoma cells demonstrated that the drug effectively inhibited their growth. For the main study, they used a mouse model where glioblastoma tumors were grown in the brains of the mice. The mice were split into four groups: a control group given a placebo, and three groups that received different treatments. The most significant results came from the group treated with 131I-hu4G4, which showed remarkable antitumor activity. The survival rate in this group was 80%, a notable improvement over the 40-60% survival rates seen in the control groups. Further analysis revealed that the drug did more than just kill cancer cells; it also remodeled the tumor's environment. The treatment increased the presence of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, which are crucial immune cells, and shifted the function of macrophages from a pro-tumor (M2) to an anti-tumor (M1) state. The study also concluded that the drug induces immunogenic cell death (ICD), a process that alerts the immune system to the presence of cancer, by changing certain protein expressions on the cancer cells. These results highlight the drug's dual action: directly targeting and killing cancer cells while also boosting the body's immune response against the tumor.
FAQs
Q: How do these conjugates kill cancer cells without harming healthy tissue?
A: The key is the targeting molecule. It acts like a precision-guided missile, specifically designed to bind to a marker that is highly expressed on the surface of cancer cells but is rare on healthy cells. Once bound, the radioactive payload delivers its energy over a very short distance, destroying the cancer cell while leaving the surrounding healthy tissue largely unaffected.
Q: What is the main advantage of this technology over traditional chemotherapy?
A: Unlike chemotherapy, which often kills fast-dividing cells indiscriminately, this technology is highly selective. By directly targeting the cancer cells, it significantly reduces the systemic toxicity and side effects often associated with conventional treatments, leading to a much more favorable therapeutic window and better quality of life for the patient.
Q: How long does it take to develop a new conjugate?
A: The development timeline can vary depending on the complexity of the project. However, our streamlined process, proven platforms, and extensive experience are designed to optimize every stage from initial design to pre-clinical validation, helping you to accelerate your discovery and development timeline.
Q: How do you ensure the conjugate is stable and won't release the radioactive payload prematurely?
A: We utilize advanced conjugation chemistry and state-of-the-art chelators that form extremely stable bonds with the radionuclide. Our rigorous quality control and in vitro stability assays are designed to test the integrity of the conjugate in a simulated biological environment, ensuring that the payload is delivered safely and effectively to its intended target.
Q: Can this technology be applied to other diseases besides cancer?
A: While oncology is the most prominent application, the principles of targeted delivery can be applied to other diseases as well. Any condition that involves a unique cell surface marker could potentially be a candidate for this technology. We encourage you to reach out to our team to discuss your specific research ideas and explore the possibilities.
Creative Biolabs offers unparalleled expertise and comprehensive services for the development of Radionuclide Drug Conjugates. Our integrated platform, from custom targeting module synthesis to pre-clinical validation, is built to accelerate your drug discovery journey with precision and confidence. We provide the tools and scientific support needed to create highly effective, targeted therapeutic agents that will transform the future of medicine.
Connect with our experts for project-specific consultation and detailed insights.
References
- Chakraborty, Kushal et al. "Advances in Radionuclides and Radiolabelled Peptides for Cancer Therapeutics." Pharmaceutics vol. 15,3 971. 17 Mar. 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030971
- Zheng, Meng et al. "Radioimmunotherapy Targeting B7-H3 in situ glioma models enhanced antitumor efficacy by Reconstructing the tumor microenvironment." International journal of biological sciences vol. 19,13 4278-4290. 15 Aug. 2023, https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.87763
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



