Access a comprehensive catalog of pre-validated Module Delivery Systems, including liposomes, exosomes, LNPs, and polymeric nanoparticles. We also offer a selection of validated Targeted Modules such as aptamers, peptides, functionalized lipids, targeted polymers, and responsive materials, all prepared for your immediate research and development needs.
Polymer based Conjugation Service
Are you currently facing challenges in achieving targeted delivery, overcoming limited therapeutic windows, or minimizing off-target effects in your therapeutic development? Our Polymer-Delivery System Conjugation Services at Creative Biolabs help you enhance therapeutic efficacy, improve drug safety, and unlock new treatment possibilities through advanced polymer chemistry and innovative delivery system design.
Polymer-Based Conjugation Solution
Polymer-drug conjugates (PDCs) are advanced nanomedicines that integrate therapeutic agents within polymeric molecules for targeted delivery. This approach transforms cancer treatment by addressing issues like poor drug solubility, rapid clearance, and non-specific distribution. PDCs enhance drug effectiveness through precise delivery to biological targets, minimizing off-target effects and toxicity. Engineered for biocompatibility and specific in vivo behavior, these polymers often cross biological barriers. PDCs are critically activated by physiological cues, such as enzymatic activity or pH changes in diseased tissues, enabling selective therapeutic intervention.
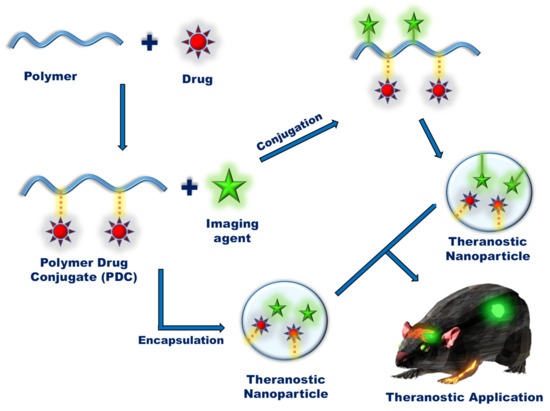 Fig.1 A general overview of the preparation of polymer-drug conjugate-based theranostic nanoparticles.1,4
Fig.1 A general overview of the preparation of polymer-drug conjugate-based theranostic nanoparticles.1,4
Polymer-based conjugation effectively enhances therapeutic agents, serving as versatile carriers that improve solubility, stability, and pharmacokinetic profiles. These systems are engineered into various forms, including nanoparticles, micelles, dendrimers, and linear conjugates.
- Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG): A widely used synthetic polymer, PEG offers excellent biocompatibility, low immunogenicity, and prolongs therapeutic circulation. PEGylation reduces protein aggregation and enzymatic degradation, a cornerstone in drug delivery.
- N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA) copolymers: Versatile, biocompatible, and biodegradable synthetic polymers. HPMA copolymers are easily functionalized for therapeutic agents and targeting ligands, with some conjugates in clinical trials due to favorable safety and controlled release.
- Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA): A biodegradable, biocompatible synthetic polymer widely used for sustained release and nanoparticle platforms. PLGA degrades into naturally cleared lactic and glycolic acids, making it a safe option.
- Hyaluronic Acid (HA): A natural, biodegradable, biocompatible, non-toxic, and non-immunogenic polysaccharide. HA's specific binding to the CD44 receptor (overexpressed on cancer cells) makes it an excellent targeting moiety for tumor-specific delivery.
- Dextran: An intricately branched polysaccharide exhibiting biocompatibility and biodegradability. Dextran conjugates are explored for drug delivery and imaging due to their water solubility and stable conjugate formation.
Polymer selection is critical, dictating the conjugate's biocompatibility, biodegradability, and in vivo behavior.
Couplings Methods
A key aspect of polymer-based conjugation is the use of intelligent linkers, designed for controlled release. These linkers ensure the active agent is liberated precisely where needed, minimizing off-target effects and maximizing therapeutic impact. We utilize various polymer-related couplings, including:
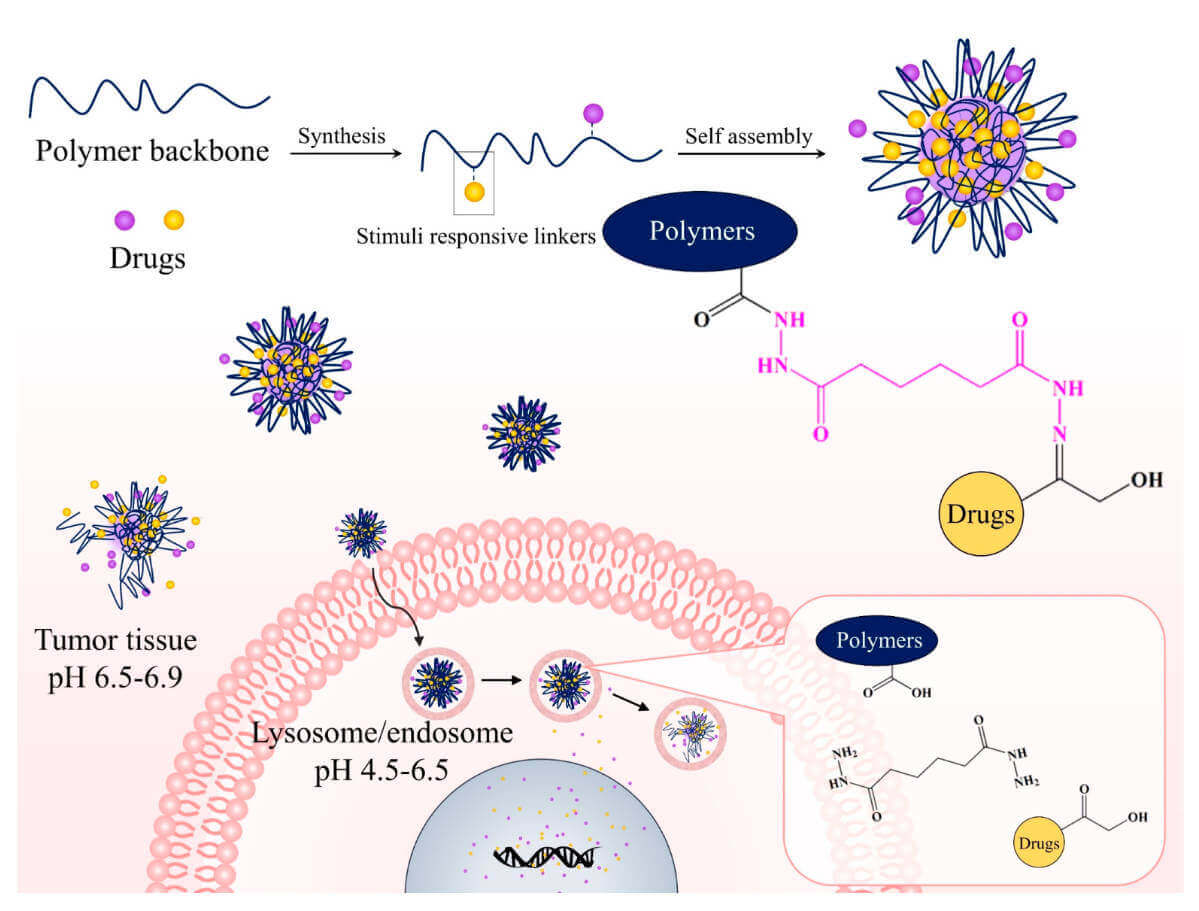 Fig.2 PDCs transported into cancer cells and their release using pH-sensitive linkers.2,4
Fig.2 PDCs transported into cancer cells and their release using pH-sensitive linkers.2,4
- pH-Sensitive Couplings: Linkers engineered to be stable in systemic circulation but cleavable under acidic conditions, such as the lower pH found in tumor microenvironments or inflammatory tissues. This allows for targeted drug release upon reaching the acidic target site.
- Enzyme-Sensitive Couplings: Linkers designed to be stable in the bloodstream but specifically broken down by enzymes prevalent at disease sites (e.g., proteases overexpressed in cancer). This mechanism ensures the active agent is released only when the relevant enzyme is present.
- Redox-Sensitive Couplings: Linkers that respond to differences in redox potential between healthy and diseased tissues (e.g., higher glutathione concentrations inside cancer cells). Disulfide bonds are a common example, cleaving under reductive conditions to release the drug intracellularly.
- Temperature-Sensitive Couplings: Polymers or linkers designed to undergo a phase transition or change in permeability in response to localized temperature increases (e.g., hyperthermia induced at tumor sites). This allows for controlled drug release in response to thermal stimuli.
- Light-Sensitive Couplings: Photo-cleavable linkers that enable drug release upon exposure to specific wavelengths of light. This offers precise spatiotemporal control over drug delivery, particularly useful for superficial tumors or localized therapies.
By customizing the polymer architecture and linker chemistry, we create highly optimized polymer conjugates tailored for specific therapeutic applications, including the conjugation of small molecules, peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Application
Polymer-based delivery systems offer diverse applications in therapeutics and diagnostics:
- Targeted Drug Delivery: A primary application, especially in oncology. Systems precisely deliver agents to cancer cells via the Enhanced Permeability and Retention (EPR) effect or targeting ligands, reducing systemic toxicity and aiding in treating inflammatory diseases and infections.
- Enhanced Bioavailability and Pharmacokinetics: For rapidly cleared agents, polymer conjugation extends circulation half-life and improves bioavailability, allowing less frequent dosing and sustained therapeutic levels.
- Gene Therapy and Nucleic Acid Delivery: Polymers facilitate intracellular uptake and endosomal escape of nucleic acids (e.g., siRNA, mRNA), enabling efficient gene silencing or expression.
- Diagnostic Imaging: Functionalized polymers conjugated to imaging agents (e.g., fluorescent dyes) enable precise localization and visualization of diseased tissues, supporting theranostic applications.
- Vaccine Development: Polymeric carriers enhance antigen immunogenicity and presentation, leading to robust, long-lasting immune responses for vaccines.
- Overcoming Biological Barriers: Engineered polymer systems can cross challenging barriers like the blood-brain barrier, delivering therapeutics to previously inaccessible sites.
Contact Us About Bioconjugation Services
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs is uniquely positioned at the forefront of targeted drug delivery innovation. Our team of expert biologists, chemists, and engineers brings over two decades of collective experience in developing sophisticated delivery solutions. We remain committed to advancing your initiatives through:
Ready-to-Use Solutions
Tailored Development Services
Leverage our bespoke service to develop customized delivery systems and novel targeted modules from concept through validation. We precisely meet your project's unique specifications, offering custom polymer synthesis and conjugation, alongside optimization of delivery system characteristics for specific cell types or disease contexts.
Expert Conjugation Services
Benefit from our specialized expertise in conjugating selected ligands or therapeutic agents to various advanced polymer-based delivery platforms, including nanoparticles, liposomes, and other polymer constructs. Our exacting molecular tethering methods guarantee superior yield and structural integrity.
Rigorous Pre-Clinical Testing
Utilize our robust in vitro and in vivo testing capabilities to thoroughly assess the targeting efficiency, cellular uptake, biodistribution, and therapeutic efficacy of your conjugated polymer systems.
Comprehensive Scientific Partnership
Partner with Creative Biolabs to harness our deep scientific knowledge, access state-of-the-art facilities, and rely on our rigorous quality control for your targeted delivery projects, from initial experimental design to meticulous data analysis.
Workflow
Why Choose Us?
Partnering with Creative Biolabs means choosing a path to accelerated drug development, enhanced therapeutic efficacy, and a significant reduction in off-target effects. Our commitment to innovation and scientific excellence ensures that your therapeutic agents reach their targets with unprecedented precision, unlocking new possibilities for disease treatment.
Unparalleled Expertise
Our team of highly specialized biologists, chemists, and engineers possesses deep scientific knowledge and over two decades of experience in designing and optimizing polymer-based drug delivery systems and targeting module development.
Cutting-Edge Technology
We leverage state-of-the-art platforms for polymer synthesis, precise conjugation, and comprehensive characterization, ensuring the highest quality and performance of your polymer-delivery systems.
Unrivaled Customization & Flexibility
We offer highly customized polymer design and delivery system optimization tailored precisely for your therapeutic goals and specific cellular or tissue targets.
Commitment to Quality & Reliability
Our dedication to scientific rigor and stringent quality control processes guarantees reliable, reproducible, and high-quality results for your most critical and complex projects.
Published Data
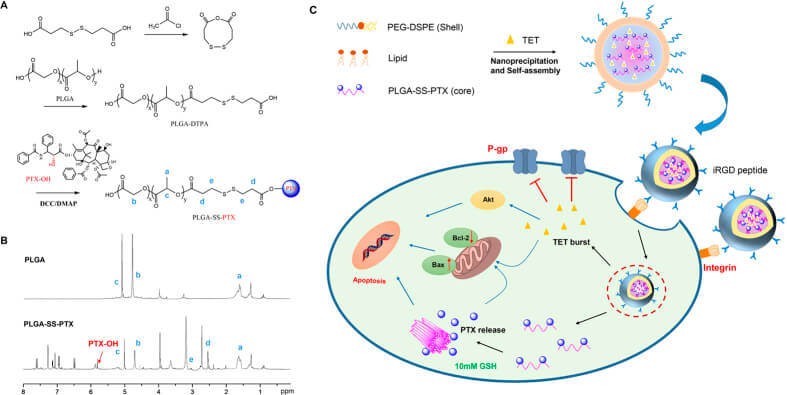 Fig.3 MDR reversal by PTX and TET co-delivery in iRGD peptide conjugated NPs.3,4
Fig.3 MDR reversal by PTX and TET co-delivery in iRGD peptide conjugated NPs.3,4
In a study focused on overcoming multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer, researchers successfully developed an innovative co-delivery system utilizing iRGD peptide-conjugated lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPNs). The principal aim sought to augment the therapeutic performance of paclitaxel (PTX) against ovarian carcinoma, a condition often plagued by MDR from P-glycoprotein (P-gp) overexpression. The experimental design involved covalently linking PTX to a poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) polymeric core via a redox-sensitive disulfide bond. Simultaneously, tetrandrine (TET), a known P-gp inhibitor, was physically encapsulated within the LPNs to achieve early P-gp suppression.
The results of the study demonstrated that the PTX+TET/iRGD LPNs significantly increased the intracellular accumulation of PTX within resistant cancer cells. This enhanced uptake was critical for overcoming the efflux pump activity of P-gp. Furthermore, the co-delivery system promoted the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which is a key mechanism for inducing cellular damage and apoptosis. The study observed a notable enhancement in apoptosis and cell cycle arrests in MDR cancer cells treated with the PTX+TET/iRGD LPNs, indicating improved cytotoxicity compared to free drugs or non-targeted formulations. These results highlight the therapeutic promise of iRGD peptide-mediated LPNs as an effective methodology for managing multidrug-resistant malignancies, demonstrating the efficacy of precision co-delivery systems against formidable treatment barriers.
FAQs
Q: What types of therapeutic agents can be conjugated with polymer delivery systems?
A: A wide range of agents can be conjugated, including small molecule drugs, peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids (like siRNA or mRNA). The specific agent dictates the optimal polymer and conjugation chemistry required for effective delivery.
Q: How do polymer-delivery systems improve drug efficacy and safety?
A: These systems enhance efficacy by increasing drug accumulation at target sites and prolonging circulation, while improving safety by reducing systemic exposure and minimizing off-target effects. This leads to a more concentrated therapeutic action where it's needed most.
Q: Are polymer-delivery systems suitable for both in vitro and in vivo applications?
A: Yes, polymer-delivery systems are designed for both in vitro studies to assess cellular interactions and in vivo applications for preclinical and clinical evaluation, demonstrating their versatility across the drug development pipeline.
Q: Can these systems be customized for specific disease targets or cell types?
A: Absolutely. A key advantage is their high customizability. Polymers can be functionalized with specific targeting ligands (e.g., antibodies, peptides) to ensure precise delivery to particular disease targets or cell populations, enhancing therapeutic specificity.
Q: How do polymer-delivery systems address challenges like drug solubility and stability?
A: Polymers can encapsulate or covalently link hydrophobic drugs, significantly improving their aqueous solubility. They also provide a protective environment, shielding drugs from enzymatic degradation and premature clearance, thereby enhancing their stability and extending their therapeutic half-life.
Creative Biolabs' Polymer-Delivery System Conjugation Services are your strategic partner in advancing next-generation therapeutics. We offer comprehensive solutions—from custom polymer synthesis and delivery system design to expert conjugation, preclinical validation, and scientific support—ensuring your therapeutic agents reach their full potential through precision, quality, and accelerated development.
Connect with our experts for project-specific consultation and detailed insights.
References
- Manandhar, Sajana, et al. "Polymer-drug conjugates as nanotheranostic agents." Journal of Nanotheranostics 2.1 (2021): 63-81, DOI: 10.3390/jnt2010005.
- Junyaprasert, Varaporn Buraphacheep, and Parichart Thummarati. "Innovative Design of Targeted Nanoparticles: Polymer-Drug Conjugates for Enhanced Cancer Therapy." Pharmaceutics vol. 15,9 2216. 27 Aug. 2023, DOI:10.3390/pharmaceutics15092216.
- Zhang, Jinming et al. "Co-delivery of paclitaxel and tetrandrine via iRGD peptide conjugated lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles overcome multidrug resistance in cancer cells." Scientific reports vol. 7 46057. 4 May. 2017, DOI:10.1038/srep46057.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



