In Vitro Expression Validation Service for Synthetic Circular RNA (circRNA)
Introduction
Our In Vitro Expression Validation for Synthetic Circular RNAs service addresses challenges in validating circRNA expression. With a robust workflow and advanced methods like divergent primer design and optimized RNase R treatment, it streamlines validation and delivers reliable data. Tailored end-to-end, it handles synthetic constructs, providing clear results to support gene therapy and functional genomics projects.
Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation
In Vitro Expression Validation for Synthetic Circular RNAs
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a fascinating class of non-coding RNAs with a unique covalently closed loop structure. This gives them exceptional stability, resisting enzymes like RNase R. As key gene regulators, they act as miRNA sponges, transcriptional regulators, and protein scaffolds, making them attractive for novel therapeutics, especially gene therapy.
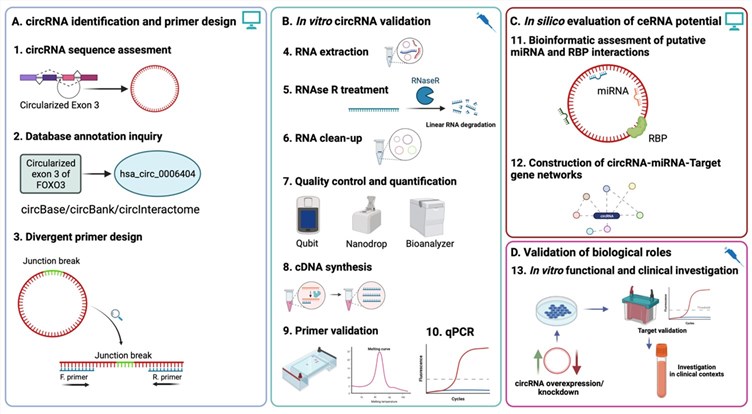 Fig.1 Experimental workflow and downstream functional studies of circRNA evaluation using qRT-PCR.1
Fig.1 Experimental workflow and downstream functional studies of circRNA evaluation using qRT-PCR.1
The core purpose of in vitro expression validation is to confirm that a synthetic circRNA construct is correctly transcribed and present at detectable levels within a cellular system. This is a crucial step before proceeding to functional studies. The key verification steps involve distinguishing the circular RNA from linear transcripts, quantifying its expression, and ensuring the specificity of the detection method.
Key precautions include:
- Divergent Primer Specificity: It is essential to use primers that are designed to target the back-splicing junction, as this is the only way to differentiate the circular molecule from its linear isoform.
- Linear RNA Depletion: RNAse R treatment is a critical step to remove linear RNA contamination, which can lead to false-positive signals and inaccurate quantification.
- Positive and Negative Controls: Including linear cDNA and RNA controls, as well as no-template controls, is vital for confirming the validity of the results and the absence of contamination.
Tab.1 A commonly used method for in vitro validation of circular RNAs.
| Category | Experimental Method | Experimental Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verification steps | Quality verification of synthetic circRNA | Ensure that the input materials are qualified and eliminate impurities and structural abnormalities |
1. Purity testing: Nanodrop tests OD260/280 (1.8-2.0); 2. Concentration quantification 3. Preliminary structural screening: Agarose gel electrophoresis distinguishes ring-shaped from linear |
| Verification of cell delivery and expression levels | Detect the intracellular delivery efficiency, expression level, and stability |
1. Delivery: Liposome transfection/electroporation, fluorescently labeled to observe efficiency; 2. Quantification: RT-qPCR at different time points; 3. Stability: Residual amount compared with linear RNA |
|
| Verification of the integrity of ring structures | Confirm that the circular structure has not been damaged | RNase R treatment experiment: Observation of circRNA retention and linear RNA degradation | |
| Preliminary verification of potential functional associations | Quickly assess the potential of the function |
Downstream target detection: RT-qPCR/Western blot; Cell phenotype observation: CCK-8 / flow cytometry |
|
| Common verification methods | RT-qPCR | Quantitative expression level and stability | Amplify the target sequence through specific primers. |
| RNase R resistance assay | Verify the integrity of the ring structure | The specific degradation of linear RNA by enzymes was utilized to compare the treatment group with the control group. | |
| Northern blot | Visually detect size and integrity | After electrophoresis, hybridization color development is carried out, and the position of the bands is observed to distinguish between ring-shaped and linear. | |
| circRNA-seq | Confirm sequence correctness and rule out mutations | High-throughput sequencing was used to analyze the full-length sequences of circRNAs. | |
| FISH | Observe intracellular localization | The signal position was observed under a microscope after fluorescence probe hybridization. |
Workflow
Required Starting Materials: To initiate the service, we require:
- Synthetic CircRNA constructs: Purified plasmid DNA or RNA templates.
- Target Gene Information: The full sequence of the gene or region of interest, including exon-intron boundaries.
- Cell Line/Model System: The specific cellular environment where the circRNA will be expressed.
-
Step 1: Bioin Key Steps Involved:
-
formatic Assessment & Primer Design
Our team uses advanced bioinformatics tools to analyze your circRNA sequence and design divergent primers. These primers span the back-splicing junction, ensuring only circular forms are amplified and avoiding false positives from linear transcripts.
-
formatic Assessment & Primer Design
-
Step 2: Linear RNA Depletion (RNAse R Treatment)
We treat samples with RNAse R—an exoribonuclease that specifically digests linear RNA—to enrich stable circRNAs, minimizing background noise for a cleaner signal. -
Step 3: cDNA Synthesis
Enriched circRNA templates are reverse transcribed into cDNA, providing the substrate for quantitative PCR analysis. -
Step 4: qRT-PCR Validation
Using optimized divergent primers and prepared cDNA, we perform qRT-PCR to quantify synthetic circRNA expression, ensuring precise, reliable measurement. -
Step 5: Product Validation
Post-qRT-PCR, we validate products via agarose gel electrophoresis and melting curve analysis to confirm correct size, expected melting profile, and reaction specificity.
Final Deliverables: Upon completion, you will receive a comprehensive report that includes:
- Quantitative Expression Data: Detailed charts and graphs showing the expression levels of your synthetic circRNA.
- Methodology Report: A full description of the protocols, reagents, and instruments used for complete transparency and replicability.
- Data Analysis: Interpretive insights and conclusions from our expert team.
Estimated Timeframe: The typical timeframe for this service ranges from 4 to 6 weeks, depending on the complexity of the project and the number of constructs to be validated.
What we can offer
Our In Vitro Expression Validation for Synthetic Circular RNAs service provides a unique and powerful combination of expertise, cutting-edge technology, and customization to meet your specific research needs. We are not just a service provider; we are your partner in scientific discovery.
Precision and Specificity
We ensure target circRNA-specific detection via rigorous RNase R-mediated linear RNA depletion and highly specific divergent primer design.
Customized Solutions
Our scientists develop tailored validation plans, optimizing primers for complex back-splicing junctions and selecting suitable assays per your needs.
Methodological Excellence
We use qRT-PCR (gold standard for circRNA quantification) and offer alternatives like digital gene expression and luciferase reporter assays for accurate data.
Seamless Project Flow
We guide you from consultation and sample prep to data analysis and reporting, providing a streamlined one-stop service.
Unparalleled Expertise
With extensive RNA biology experience, our team offers insightful consultation and technical support for troubleshooting and experiment design.
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
Case Study
| Longer-term Expression of EGFP | |
|---|---|
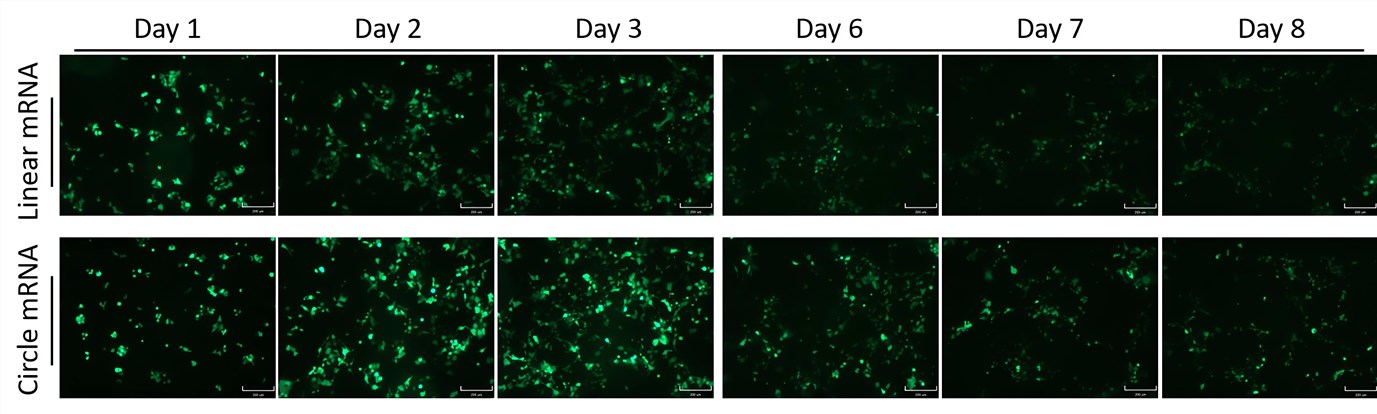
|
|
| Fig.2 The circular mRNA of EGFP shows more persistent expression than linear. | |
| Western Blot | EGFP Relative Level |
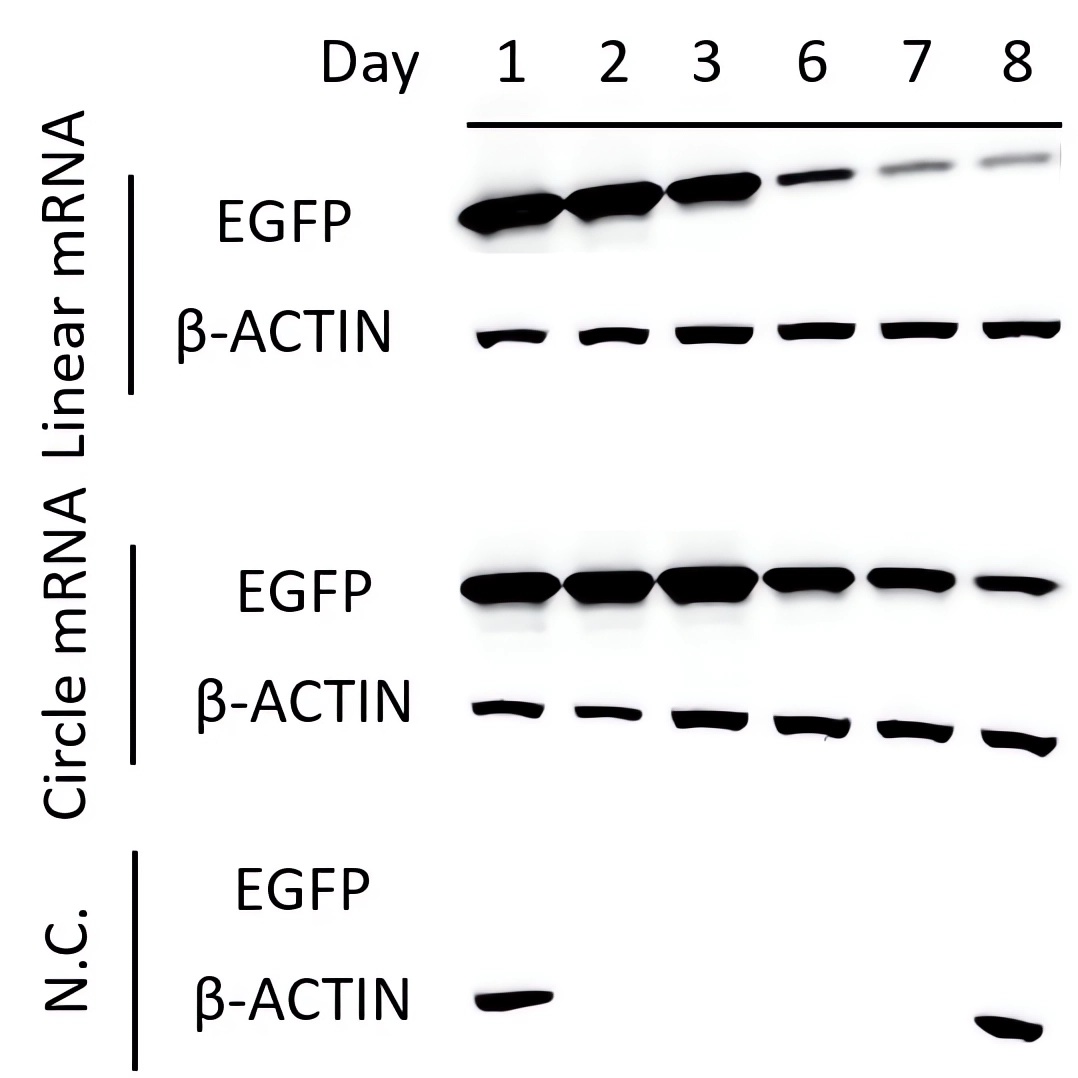
|
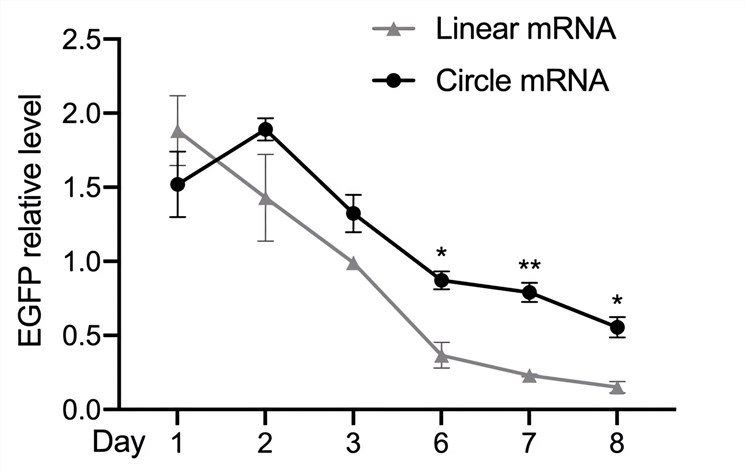
|
| Fig.3 The level of EGFP protein was detected by Western Blot assay. | Fig.4 The expression levels of EGFP translated from circular and linear mRNAs were statistically analyzed. |
Customer Reviews

FAQs
Why do I need to validate my synthetic circRNA if I've already confirmed the plasmid sequence?
While your plasmid sequence may be correct, in vitro expression validation confirms that the circRNA is being properly transcribed and back-spliced into its circular form within the cell. This is not guaranteed by the plasmid sequence alone and is a crucial step to prove that your construct is functional.
How do you ensure you are detecting the circRNA and not the linear RNA?
We employ a two-pronged approach: first, we treat the RNA sample with RNase R to digest linear transcripts. Second, we use divergent primers that are specifically designed to amplify the unique back-splicing junction of the circRNA, which is not present in the linear transcript.
What if my circRNA is very low in abundance? Can your service still detect it?
Yes, our methodologies are optimized for sensitivity. The combination of RNAse R enrichment and highly specific primer design allows for the detection and accurate quantification of even low-abundance circRNAs.
At Creative Biolabs, our In Vitro Expression Validation for Synthetic Circular RNAs service provides a critical and reliable solution for researchers in gene therapy and functional genomics. We deliver high-quality data, supported by a rigorous and transparent workflow, to accelerate your discovery process and build confidence in your research findings.
Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project
Reference
- Drula, Rares et al. "Investigating Circular RNAs Using qRT-PCR; Roundup of Optimization and Processing Steps." International journal of molecular sciences vol. 24,6 5721. 16 Mar. 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065721. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
