DNA/2'-O-Methyl RNA Chimera
Incorporating 2'-O-methylRNA bases into antisense oligonucleotides or miRNAs can enhance their stability, prevent them from being degraded by nucleases, and increase their affinity for target mRNA by increasing Tm. With years of experience in custom oligonucleotide modification, Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive range of oligonucleotide modification services, including 2'-O-methyl ester modification. Our scientists are proficient in the preparation of DNA/2'-O-Methyl RNA chimera with high purity and high quality to promote clients' meaningful research.
Core Composition and Modification of DNA/2'-O-Methyl RNA Chimera
-
DNA Unit
composed of deoxyribonucleotides, with a deoxyribose backbone, consistent with the structure of natural DNA, and binds to target nucleic acids (such as mRNA and DNA) through complementary base pairing. -
2'-O-MethylRNA Unit
The 2'-hydroxyl group of RNA nucleotides is methylated (i.e. 2'-O-Me RNA). This modification does not alter the base pairing ability, but significantly enhances the stability of the molecule - resisting degradation by nucleases such as RNase and reducing its likelihood of being recognized by the human immune system as an "exogenous nucleic acid". -
Chimera
The two are connected by a phosphodiester bond. A common design is the "DNA core region+2'-O-methylRNA end region" (e.g., modified RNA at both ends and DNA in the middle) to balance binding specificity and in vivo stability.
Introduction of 2'-O-Methyl RNA
2'-O-methylation is a common nucleoside modification of RNA, in which a methyl group is added to the 2' hydroxyl of the ribose moiety of a nucleoside to produce a methoxy group. 2'-O-Methyl RNA is a naturally occurring modification of RNA found in tRNA and small RNAs. It represents one of the earliest sugar modifications employed in antisense medicinal chemistry and is widely used to improve the nuclease stability of siRNA or antisense oligonucleotides. A number of studies have revealed that the oligonucleotides modified with 2'-O-Methyl RNA showed higher nuclease resistance and affinity to target mRNA compared to unmodified oligonucleotides. Especially, the combination of 2'-O-Methyl RNA with phosphorothioate linkages is recommended to be introduced in the process of oligos synthesis in order to further increase the nuclease resistance.
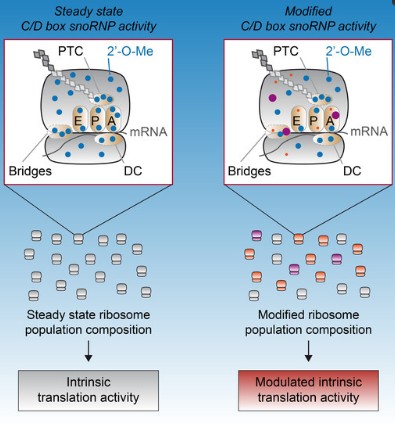 Figure 1 Model of 2′-O-methylation (2′-O-Me) profile modulation and its consequence on the intrinsic translational activity of ribosomes.1
Figure 1 Model of 2′-O-methylation (2′-O-Me) profile modulation and its consequence on the intrinsic translational activity of ribosomes.1
How to Create an RNA Chimera?
The synthesis of DNA/2'-O-methylRNA chimeras is a complex process based on mature solid-phase synthesis protocols. This process requires highly skilled chemists and specialized equipment.
The basic steps are as follows:
- Solid Support Attachment: covalently attach the first nucleotide to a solid phase carrier, such as controlled pore size glass (CPG).
- Deprotection: Deprotech the 5 '- hydroxyl group of the first nucleotide for the next step of conjugation.
- Coupling: Activate the phosphoramide structural unit (DNA or 2'-O-methylRNA phosphoramide) and couple it with the deprotected 5'-hydroxyl group. Form a triphosphate bond.
- Oxidation: Oxidation of triphosphate esters to more stable triphosphate esters.
- Capping: Capping any unreacted 5'-hydroxyl groups to prevent the formation of truncated sequences in subsequent cycles.
- Cutting and Deprotection: After adding the last nucleotide, the oligonucleotide is cut from the solid carrier and undergoes overall deprotection, removing all protective groups on the base and phosphate backbone.
Key Advantages
- High stability: 2'-O-methyl modification makes RNA less easily degraded by RNase in vivo, and compared to natural nucleic acid molecules, the half-life in vivo can be extended several times to tens of times.
- Strong specificity: The base pairing of DNA units is rigorous and can accurately identify target sequences (such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)), reducing binding to non target nucleic acids.
- Low immunogenicity: Modified RNA fragments are not easily recognized by immune molecules such as Toll like receptors (TLRs) in the body, reducing inflammatory reactions and other immune side effects, making them more suitable for in vivo applications.
Breakthrough in Preparation and Purification Technology
Preparation
The preparation of DNA/2'-O-Methyl RNA chimeras faces two key challenges: sequence accuracy and purity control. During the synthesis phase, to address the low coupling efficiency caused by the significant steric hindrance of the 2'-O-Methyl RNA monomer, an activator optimization strategy was employed, replacing traditional reagents with bis(diisopropylamino)phosphoryloxy)ferrocene (ferrocene). This increased coupling efficiency from 95% to over 98%, significantly reducing truncated sequences caused by incomplete coupling.
Purification
During the purification phase, a two-step HPLC purification method was developed to take advantage of the chimeras' differing charge and hydrophobicity.
- The first step utilizes IE-HPLC with triethylamine bicarbonate (TEAB) as the mobile phase, separating oligonucleotides of varying lengths via gradient elution to remove incompletely synthesized short-chain impurities.
- The second step utilizes RP-HPLC with acetonitrile-water (containing trifluoroacetic acid) as the mobile phase to precisely remove hydrophobic impurities such as protecting group degradation products and unactivated monomers generated during the synthesis process. For challenging long-chain chimeras (>30 nt), reversed-phase ion-pair chromatography (IP-RP-HPLC) is additionally employed, enhancing separation efficiency through the addition of ion-pairing reagents such as tetrabutylammonium salt. Ultimately, the product maintains a stable purity exceeding 95%, meeting the stringent requirements of preclinical research.
Core Services at Creative Biolabs
Equipped with rich expertise in oligonucleotide production and chemical modifications, Creative Biolabs is confident in offering unbeatable synthesis services of RNA and DNA chimeric oligos with 2'-O-Methyl modification for global clients. Our advanced oligonucleotide synthesis platform is composed of nucleic acid synthesizers, nucleic acid purification systems, and nucleic acid analysis instruments, allowing delivery of micrograms or even hundreds of grams oligos in a short time. Besides, we also provide a variety of strategies to improve properties of chimeric oligos, for example, by adding 2'-O-Methyl RNA and phosphorothioate linkages into oligos to further improve their nuclease resistance, by retaining an RNase H activating domain in 2'-O-Methyl RNA chimeric oligos to enable them possess the activity of RNase H cleavage.
Features of Our Services
- An experienced expert team providing real-time technical guidance
- Advanced technical platform feasible for different production scales and purification strategies
- Highly stable oligonucleotide product amenable to different downstream applications and research purposes
- Best after-sale service
Purification Methods for 2'-O-Methyl RNA Bases
The success of any oligonucleotide therapy depends on the purity of the final product. Pollutants, truncated sequences, and adverse byproducts can all affect the effectiveness and safety of candidate drugs. At Creative Biolabs, we use state-of-the-art purification techniques to ensure the highest quality of our 2'-O-methylRNA chimeras. Our main purification method is high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), which is the gold standard for separating complex mixtures. HPLC is applied in two key stages:
Reverse Phase High Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
This technique separates oligonucleotides based on their hydrophobicity. It can efficiently remove triphenylmethyl and other synthesis related impurities.
Ion Exchange High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (IE-HPLC)
This method separates oligonucleotides based on their charge, which is directly related to the length of the oligonucleotide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the main advantages of 2'-O-methylRNA modification?
A: The main advantage is significantly improving nuclease resistance, thereby prolonging the half-life of oligonucleotides in the body and enhancing their binding affinity with target RNA, thereby enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
Q: Can you synthesize oligonucleotides with both 2'-O-methyl and thiophosphate modifications?
A: Yes, we specialize in synthesizing complex oligonucleotides with various modifications, including 2'-O-methyl bases and thiophosphate backbone, to achieve the characteristics required for your application.
Q: What is the difference between DNA/2'-O-methylRNA chimera and complete 2'-O-methylRNA modification (ON)?
A: Complete 2'-O-methylRNA modification (ON) has high stability, but weak DNA targeting binding (Δ G is about 10% lower than DNA). Chimera combines the stability of 2'-O-Me RNA with the strong target affinity of DNA, making it more suitable for DNA/RNA hybridization targets (such as viral DNA).
Q: How can I choose different chimeric designs based on my specific application?
A: The optimal chimeric design depends on multiple factors, including the expected mechanism of action, delivery mode, target tissue, and desired duration of action. Our technical team can provide personalized design consultation based on your specific needs. Typically, antisense applications benefit from gap design, while gene regulatory applications may require alternative modification modes that support RISC activity.
Customer Review
"Our team has long been dedicated to research on regulating hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene expression. Previously, our experiments targeting viral mRNA interference were repeatedly hindered by the fact that conventional oligonucleotides were easily degraded by nucleases in vitro, yet triggered a significant immune response upon in vivo administration. The overall experience, from initial communication to product delivery, exceeded expectations: Creative Biolabs' technical team not only optimized the base length and modification ratio of the chimera based on the target sequence we provided, but also predicted the Tm value and nuclease resistance through simulation experiments, providing invaluable design advice. The chimera we received was accompanied by a detailed quality control report, demonstrating a purity of 97% as determined by HPLC, and the MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry results fully matched the predicted molecular weight."
— Dr. Elena Marquez, Director of Antiviral Research at a Leading Biopharmaceutical Company
Don't Hesitate, Contact Us!
Creative Biolabs has organized an expert team with extensive experience in the field of custom oligonucleotide synthesis and modification. We are committed to providing end-to-end custom oligo modification services from consultation, oligo design, production, and purification, to oligo quality control and delivery. Please don't hesitate to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Monaco P L, Marcel V, Diaz J J, et al. 2′-O-methylation of ribosomal RNA: towards an epitranscriptomic control of translation? Biomolecules, 2018, 8(4): 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom8040106 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
