Custom siRNA Synthesis Service
Introduction
Creative Biolabs' Custom siRNA Synthesis Service accelerates gene discovery and therapeutic development via rational design, advanced modifications, and cutting-edge platforms. Tailored for functional genomics and drug discovery, we deliver high-purity, sequence-specific siRNAs with optimized stability and minimal off-target effects for in vitro/in vivo studies, ensuring reliable gene knockdown and streamlined target validation.
[Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation]
Custom siRNA Synthesis
RNA interference (RNAi) represents a revolutionary biological mechanism for sequence-specific gene silencing, offering unprecedented opportunities in both fundamental research and therapeutic development. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) molecules, central to this pathway, have evolved from powerful laboratory tools for gene function studies into refined drug candidates. The ability of siRNAs to precisely target and degrade specific messenger RNA (mRNA) transcripts at the post-transcriptional level positions them as a highly promising modality for treating a wide array of diseases.
Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are double-stranded RNA molecules, usually 19-23 base pairs long, that serve a vital function in the RNA interference pathway.
Upon entering a cell, siRNAs are incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which disassembles the siRNA duplex. The antisense strand of the siRNA directs RISC to a complementary mRNA target, resulting in the cleavage and degradation of that mRNA. This highly specific process efficiently "knock down" target gene expression, rendering siRNAs essential for investigating gene function, validating drug targets, and creating innovative therapeutics.
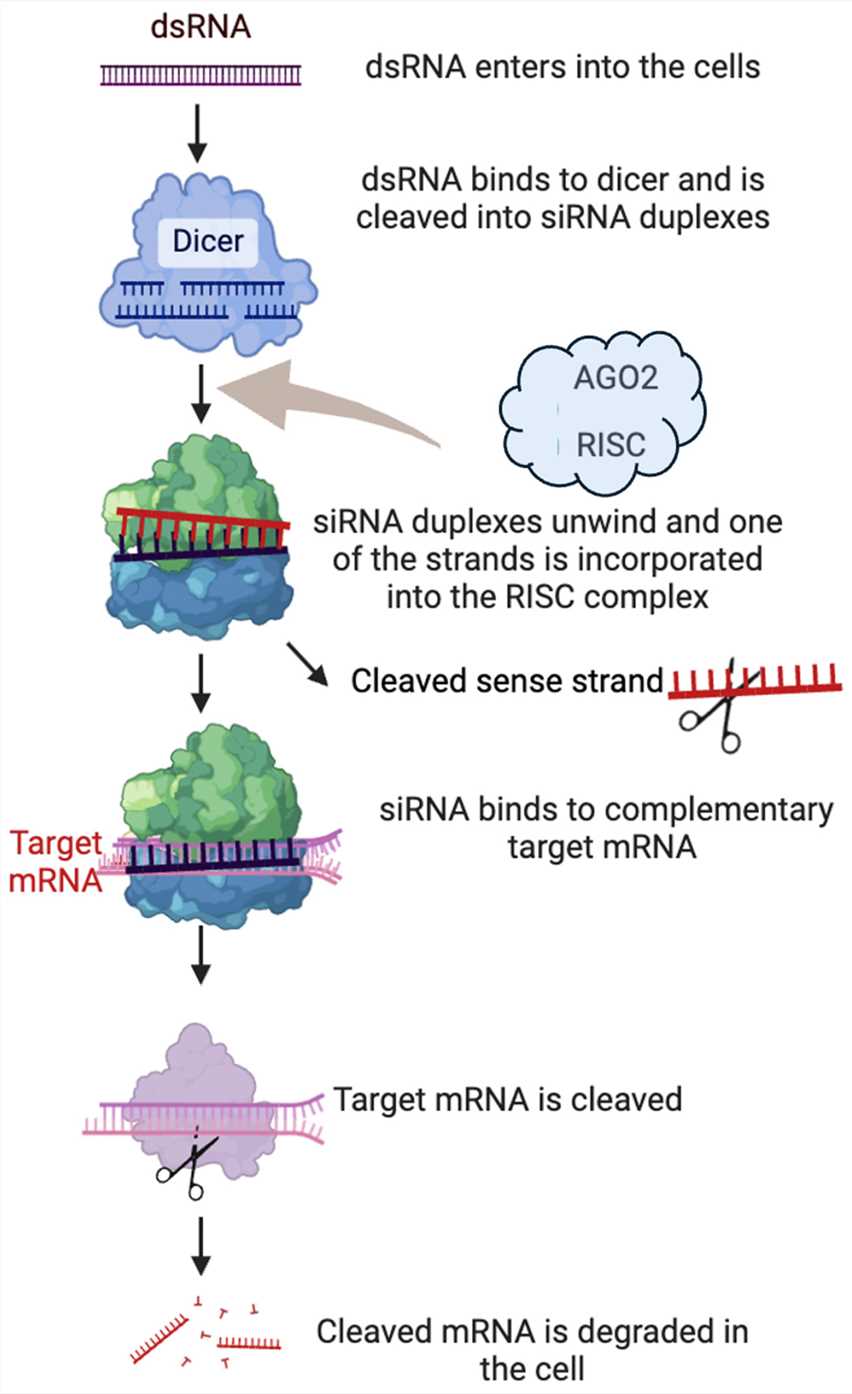 Fig.1 Dicer-generated siRNA is loaded into RISC, where AGO2 mediates the separation of the passenger strand from the guide strand. The complex then targets mRNA via the guide strand, inducing cleavage through sequence-specific complementarity between siRNA and target mRNA.1,3
Fig.1 Dicer-generated siRNA is loaded into RISC, where AGO2 mediates the separation of the passenger strand from the guide strand. The complex then targets mRNA via the guide strand, inducing cleavage through sequence-specific complementarity between siRNA and target mRNA.1,3
Workflow
| Target Information | Modification | Purification and QC | Quantities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identify sense sequence (5'→3') |
2'-O-Methyl (2'-OMe) and 2'-O-Methoxyethyl (2'-MOE) Enhance nuclease resistance, improve affinity with target miRNA, and avoid degradation. |
Analytical HPLC Provides a quantitative assessment of purity, ensuring that the final product is predominantly the desired full-length siRNA duplex. |
Identify required quantities, such as 50 nmol, 100 nmol, or 200 nmol. |
| Identify antisense sequence (Optional, 5'→3') |
Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) The thermal stability and binding affinity to the target miRNA were improved, and the specificity was also improved. |
Mass Spectrometry Used to confirm the exact molecular weight of each strand, thereby verifying the correct sequence and incorporation of modifications. |
|
|
Endotoxin Testing For siRNAs designated as "in vivo ready," rigorous endotoxin testing is performed to ensure the product is safe for animal administration, meeting stringent regulatory requirements. |
|||
|
Functional Testing (Optional) Upon request, we can also perform functional validation to confirm the gene silencing efficiency of the synthesized siRNA in relevant cell lines. |
|||
|
Phosphorothioate (PS) Backbone Increases resistance to nuclease degradation and prolongs the half-life of the inhibitor in vivo. |
Gel Electrophoresis Used to confirm the successful annealing of the sense and antisense strands into a stable duplex and to assess the overall integrity of the siRNA. |
||
| Click for a full list of available modifications | |||
| Final Deliverables |
|
||
| Estimated Timeframe | The typical timeframe for custom siRNA synthesis ranges from 2 to 4 weeks, depending on the complexity of modifications, scale of synthesis, and specific quality control requirements. Our team will provide a precise timeline after reviewing your project specifications. | ||
| Shipping | The high-quality siRNA duplexes are then formulated as lyophilized pellets to ensure maximum stability and safety during shipment. For specific applications, such as in vivo studies, siRNAs can be provided with specialized processing for direct use. | ||
Furthermore, in the design of siRNA configuration, the following points need to be followed:
Sequence design of siRNA
Focus on maximizing gene silencing efficiency and specificity while minimizing off-target effects. Antisense strand pairing with target mRNA is critical, whereas sense strand activity must be suppressed to avoid non-specific silencing. Control sequence length (≤21 nt) and structure to prevent Toll-like receptor activation and immune responses2,3.
The design of chemical modification patterns for siRNA
The design of siRNA chemical modification patterns requires combining phosphate backbone, ribose, and base modifications, achieving a balance between stability, activity, and safety through combinatorial configurations. Common patterns are as follows:
- Standard Template Chemistry: When the sense and antisense strands are 21nt and 23nt in length, respectively, the antisense strand has two phosphorothioate (PS) linkages at its 3' end; the sense strand has consecutive 2'-F modifications at positions 9, 10, and 11 of its 5' end; and the antisense strand has consecutive 2'-OMe modifications at positions 11, 12, and 13 of its 5' end. 2'-OMe and 2'-F are used alternately at other positions to enhance stability and affinity without impairing RNAi activity.
- Enhanced Stabilization Chemistry: Optimized from the standard chemistry, it increases the number of PS linkages at the 5' end of the antisense strand and the 3' end of the sense strand, reduces 2'-F substitutions, enhances siRNA efficacy and duration, and supports lower doses and less frequent administration.
- Advanced Design: It retains 6 PS linkages at the strand termini, further reduces the proportion of 2'-F, increases liver exposure and RISC loading efficiency, and strengthens gene-silencing effects.
These modification patterns, through the overall configuration of different modification types, not only enhance siRNA stability, extend its half-life, and improve targeted delivery efficiency but also reduce immunogenicity and off-target effects, laying the foundation for its clinical application.
What We Can Offer
At Creative Biolabs, our Custom siRNA Synthesis service is meticulously designed to empower your research with precision and efficiency. We are committed to delivering tailored solutions that directly address your unique scientific challenges.
Comprehensive Customization
Fully tailored siRNA design, modifications, and purification to meet specific research needs.
Rational Design Expertise
Bioinformatics tools and algorithms for high-efficiency siRNA sequences with minimal off-target effects.
Advanced Modifications
2'-O-Methyl, phosphorothioate, fluorescent labels to enhance stability, uptake, and function.
Multi-Scale Synthesis
Nanomole to preclinical-scale production via state-of-the-art platforms.
In Vivo Ready siRNAs
Sterile, low-endotoxin formulations with counter-ion exchange for direct animal use.
Dedicated Technical Support
Expert guidance from design to troubleshooting by biology specialists.
[Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today]
Customer Reviews

Custom siRNA Synthesis Service FAQs
How to solve the problem of poor gene silencing effect caused by low double-stranded unwinding efficiency of siRNA?
We optimize the unspinning efficiency through thermodynamic asymmetric design:
The 2'-O-methyl modification was introduced at the 3' end of the sense chain (to lower the unspinning temperature), while the phosphate group was retained at the 5' end of the antisense chain (to enhance RISC binding). The adoption of the 3 bp dTdT protruding end instead of the traditional 2 bp design has increased the efficiency of AgO2-mediated chain selection by 2.3 times. For the GC-enriched region, two uracil (UU) promoter sequences are inserted at the 5' end of the antisense chain to promote helicase recognition.
What special considerations are there in the design of siRNA for non-model organisms (such as flies and zebrafish)?
Our cross-species optimization strategy includes:
- Conserved sequence targeting: Use the professional database to identify conserved regions of homologous genes to avoid the influence of species-specific SNPS;
- Codon bias adjustment: Optimize the wobble base pairing of the siRNA antisense strand based on the codon usage frequency of the target species.
- Endogenous siRNA pathway adaptation: 21 nt siRNA (instead of 23 nt in mammals) was used in zebrafish to match its Ago1-mediated silencing pathway.
What are the key technical difficulties and solutions in the design of siRNA for long non-coding RNA (lncRNA)?
The particularity of lncRNA targeting siRNA lies in:
- Transcript structure complexity: Predict the secondary structure of lncRNA through RNA structure, and select single-stranded open regions (such as the ring regions of stem-loop structures) as targets.
- Subcellular localization adaptation: For nuclear localization lncRNAs, nuclear localization signal peptides (NLS) are added to the 5' end of the antisense chain of siRNA to enhance the intracellular delivery efficiency.
- Domain-specific targeting: By integrating CHIP-seq data, target the functional domains where lncRNA binds to proteins (such as the PRC2 binding domain of HOTAIR), avoiding interference from non-functional regions.
Creative Biolabs is your premier partner for Custom siRNA Synthesis, leveraging advanced technology and expertise to deliver high-purity, precisely engineered siRNAs. Our comprehensive solutions, from rational design and synthesis to strict QC and in vivo ready options, accelerate gene silencing research and therapeutic development.
[Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project]
Related Sections
References
- Ebenezer, Oluwakemi, et al. "Recent update on siRNA therapeutics." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26.8 (2025): 3456. DOI: 10.3390/ijms26083456.
- Hu, Bo et al. "Therapeutic siRNA: state of the art." Signal transduction and targeted therapy vol. 5,1 101. 19 Jun. 2020. DOI:10.1038/s41392-020-0207-x.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
