Inducible Vector Systems Design Service for Lentiviral Vector
Lentiviral vectors have emerged as safe and effective delivery vehicles for clinical gene therapy, particularly for monogenic recessive disorders. As a world-class biotechnology company, Creative Biolabs provides all-encompassing technologies to meet the diverse needs of our clients. With our professional experience and advanced lentiviral vector design platform, we are therefore confident in offering the best service for the treatment of a range of diseases.
What Is a Lentiviral Vector?
Lentiviral vectors are a powerful class of gene delivery tools derived from lentiviruses—a subclass of retroviruses characterized by their ability to infect both dividing and non-dividing cells. These vectors undergo extensive genetic engineering to serve as safe and efficient vectors for stable gene transfer in a variety of mammalian cell types. The basic structure of lentiviral vectors retains key viral elements required for packaging, integration, and transduction while removing pathogenic components. By systematically deleting virulence genes and isolating viral functions onto multiple plasmids during production, modern lentiviral vector systems can achieve highly efficient gene delivery while minimizing the risks associated with replicating viruses.
Table 1. Comparison of Viral Vector Systems for Gene Delivery
| Vector Type | Integration | Target Cell Range | Expression Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lentiviral | Integrating | Dividing & non-dividing cells | Long-term stable |
| Adenoviral | Non-integrating | Dividing & non-dividing cells | Transient |
| Retroviral | Integrating | Dividing cells only | Long-term stable |
| AAV | Mostly non-integrating | Dividing & non-dividing cells | Prolonged transient |
Inducible Vector Systems Design for LV introduction
While LVs offer significant advantages in providing stable integration, sustained high levels of therapeutic gene expression can be detrimental, leading to off-target toxicity, dose-limiting side effects, or immune responses. Inducible vector systems address this issue through precise external control of transgene expression.
An inducible system is a gene switch that allows transgene expression to be turned on or off, or quantitatively regulated, by a specific, non-toxic, and bioavailable external stimulus (inducer). An ideal inducible lentiviral vector system should possess the following characteristics:
- Precise regulation: In the off state, basal expression (leakage) is close to zero.
- High dynamic range: In the on state, expression levels are stable and high.
- Rapid kinetics: The system can be rapidly activated and inactivated after inducer administration/withdrawal.
- Biocompatibility: The inducer must be pharmacologically non-toxic to the host and widely distributed in the target tissue.
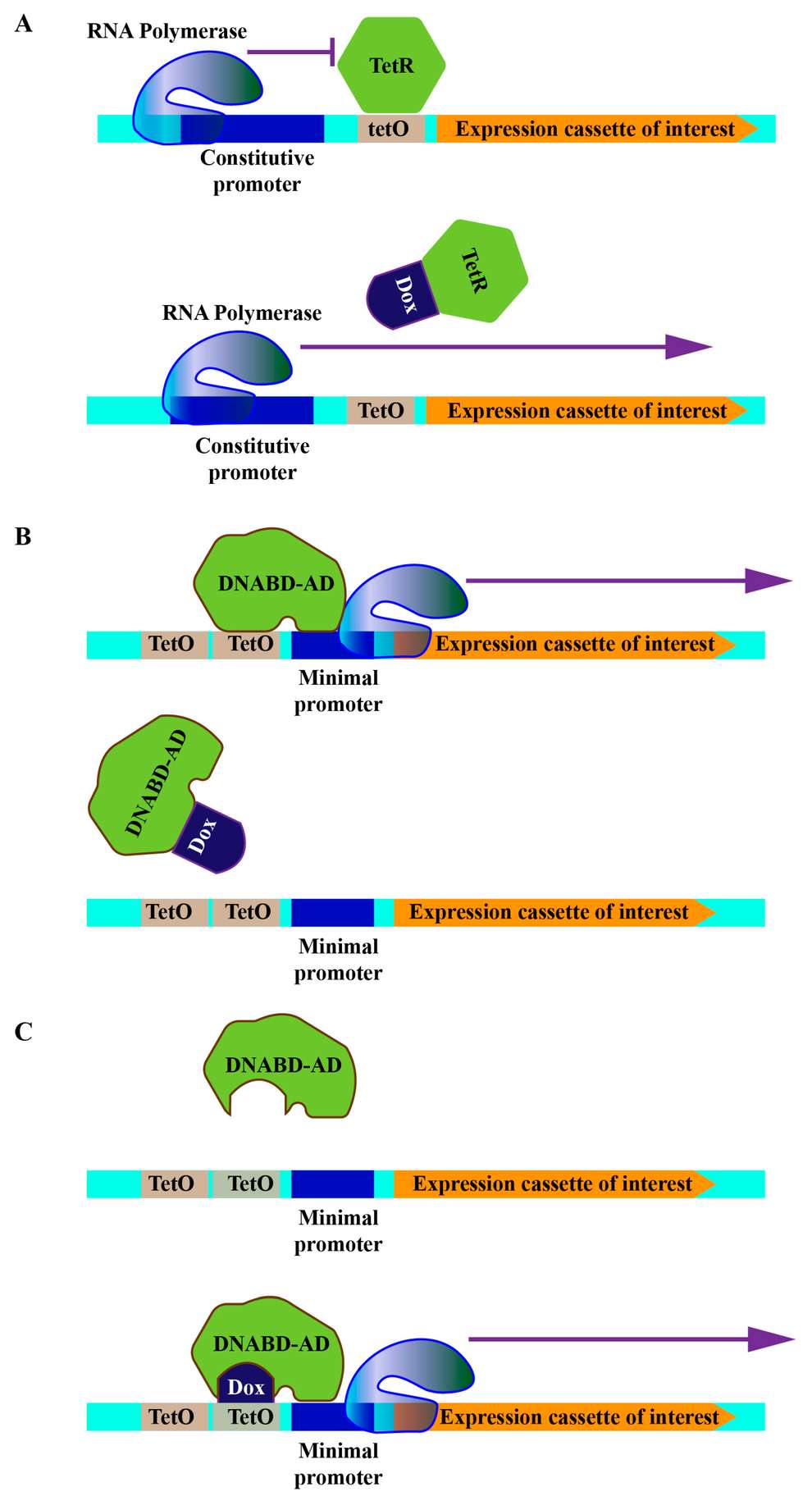 Figure 1. Schematic representations of tetracycline-controled operator systems. (A) Repression based configuration. (B) Tet-off configuration. (C) Tet-on configuration. DNABD: DNA binding domain, AD: activating domain, TetO: tetracycline operator, Dox: doxycycline, TetR: tet repressor.1
Figure 1. Schematic representations of tetracycline-controled operator systems. (A) Repression based configuration. (B) Tet-off configuration. (C) Tet-on configuration. DNABD: DNA binding domain, AD: activating domain, TetO: tetracycline operator, Dox: doxycycline, TetR: tet repressor.1
Design and Engineering Challenges of Inducible Systems in LV
01 Transcriptional Leakage (Basic Expression)
The main challenge lies in maintaining transcriptional silencing in the absence of inducers. Even extremely low basal expression (leakage) of highly toxic transgenes can lead to cell death or systemic adverse reactions. This often stems from interactions between minimal promoter elements and endogenous cellular transcription factors.
02 Dynamic Range and Kinetics
Simultaneously achieving high expression levels (high dynamic range) and rapid switch responses is extremely challenging. High dynamic range requires optimizing the binding affinity of the regulatory protein to its target sequence, while rapid kinetics depends on the short half-life of the regulatory protein and the transgene mRNA/protein.
03 Immunogenicity
Regulatory proteins (e.g., rtTA, VP16 domains, or novel synthetic activators) are often heterologous (derived from non-human sources) and may trigger unwanted immune responses in clinical settings, leading to rejection of transduced cells. The solution lies in constructing fully humanized or highly codon-optimized regulatory elements to minimize T-cell epitope presentation.
04 Limitations of Vector Genomes
Lentiviral (LV) genomes have limited packaging capacity (typically less than 10 kb). Inducible systems require the integration of multiple elements—transgenic components, regulatory cassettes, and inducible promoter elements—into a single vector, which limits the size of the therapeutic payload.
Innovative Directions in Inducible Vector Systems Design for LV
Transcription Activator-Free System Architecture
In recent years, innovations in the design of inducible vector systems have primarily focused on eliminating the need for heterologous transcription activators, thereby overcoming key limitations of traditional methods. State-of-the-art novel systems have achieved integrated, transcription activator-free, doxycycline-sensitive lentiviral vectors that regulate gene expression without the introduction of bacterial-derived regulatory proteins.
Safety-Optimized Design for Applications
Modern vector engineering increasingly emphasizes safety-optimized design to reduce the risks associated with random integration and uncontrolled transgene expression. The introduction of insulation strategies is a significant innovation in this area. For example, inserting specific insulating elements such as Is2 into the long terminal repeat sequences of lentiviral vectors has been shown to effectively reduce positional effects leading to expression variation and epigenetic silencing.
Comparison of Inducible System
| System Type | Key Components | Induction Ratio | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Tet-On | rtTA, TRE, tTS | 10-100 fold | Standard cell lines, in vitro studies |
| All-in-One Tet System | rtTA2S-M2, tTSKid, TRE | >100 fold | Hematopoietic cells, long-term expression |
| LOP Transactivator-Free | Optimized TRE, insulator | >100 fold | Primary T cells, ATMPs |
| JEx System | Crystal violet responsive | High (4-fold > Tet) | Microbial systems, metabolic engineering |
Our Services
Progress in gene therapy has allowed the development of several strategies against human diseases. Inducible lentiviral vectors are excellent tools to transfer genes into cells. Creative Biolabs offers end-to-end solutions for Inducible Lentiviral Vector Systems, tailored for cutting-edge research. Our services span the entire lifecycle, from concept and in silico design to validated, high-titer vector production. To date, we have successfully developed a variety of inducible lentiviral vector systems, including tetracycline-inducible systems, doxycycline-inducible systems, and oxidative stress-inducible systems.
Design Strategies for Optimal Inducible LV Performance
Our design philosophy is holistic, focusing on optimizing each component of the vector cassette for optimal performance and application readiness.
-
Promoter Engineering
- Operon Tandemization
- Insulating Element Introduction
-
Codon Optimization and Fusion Tag
The synthesized regulatory proteins undergo systematic codon optimization to match a transfer RNA library targeting human cells, thereby maximizing protein expression yield and stability.
Why Choose Our Services?
Creative Biolabs is more than just a vector supplier; we are your strategic partner in gene therapy development.
Synthetic Biology Expertise
We have PhD-level scientists specializing in designing orthogonal switches and next-generation switches, ensuring your systems are industry-leading and effectively avoid cross-reactivity.
Performance Guarantee
We have complete confidence in our vectors, guaranteeing minimal dynamic range and maximum leakage rate—a commitment unmatched by other companies.
Scalability and Compliance
Our manufacturing facilities and processes are designed for a seamless transition from research-grade to preclinical vector production.
Intellectual Property Freedom
We recommend the best non-proprietary or licensed induction systems, ensuring your product development is not hindered by intellectual property rights.
Optimized Pseudotyping for Enhanced Tropism
We engineer the LV capsule with targeted ligands or novel pseudotypes to achieve highly specific transduction of the desired cell population.
PK/PD Informed System Tuning
Our design process takes into account the half-life and bioavailability of the selected inducer, ensuring perfect alignment with the planned dosing regimen.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do you ensure the "tightness" (low leakage) of your inducible systems?
A: We use highly sensitive detection methods, such as droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) and highly sensitive luminescence, to quantify basal expression at a detection limit below 0.01% of the maximum expression level. Furthermore, we employ optimized minimal promoters and introduce robust insulating elements, such as cHS4, to epigenetically protect the promoter from transcriptional elongation.
Q: Can you design a system that is activated only under specific in vivo conditions (e.g., hypoxia or inflammation)?
A: Absolutely. We focus on designing tissue-specific and internally responsive systems. This involves replacing the minimal inducible promoter with sequences responsive to endogenous factors, such as using a hypoxia-responsive element (HRE) in response to oxygen (O₂) deficiency or an NF-κB-responsive element in response to inflammation, thereby achieving true local in vivo control without the need for exogenous drug administration.
Q: What is the typical fold induction achievable with your inducible lentiviral vector systems?
A: The specific fold induction will vary depending on the target cell type, the nature of the transgene, and the specific vector configuration. We will comprehensively characterize each custom vector to determine its performance parameters in the relevant cell models and provide you with validated data to guide your experimental design. For some highly challenging applications, even minimal basal expression can cause problems; we can implement additional inhibition strategies to further reduce background activity while maintaining robust inducibility.
Q: How long does it typically take to develop a custom inducible lentiviral vector system?
A: The time required to develop a custom inducible lentiviral vector system depends on the complexity of the system and the level of optimization required. Simple configurations using established components may be delivered in a shorter time, while more complex systems requiring extensive optimization or validation in primary cells may take longer. We provide a detailed project timeline during the initial planning phase and provide regular progress updates throughout the project to ensure transparency and manage expectations. For time-sensitive projects, we can implement an expedited process—please discuss your time requirements with our team during the initial consultation.
Connect with Us Anytime!
Creative Biolabs has long-term devoted to the design methods of lentiviral vector. With years of experience, our scientists have developed several lentiviral vector design platforms to boost our global customers' research and project goals. We are pleased to use our extensive experience and advanced platform to offer the best service and the most qualified products to satisfy the diverse needs from our customers. If you are interested in our services, please contact us or send us an inquiry.
Reference
- Kallunki T, Barisic M, Jäättelä M, et al. How to choose the right inducible gene expression system for mammalian studies?. Cells, 2019, 8(8): 796. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080796 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
