Radiation-induced Adenovirus Vector Construction Service
Adenovirus-mediated gene therapy combined with radiation is expected to be an attractive approach to treat cancer. Creative Biolabs is a leading expert in adenovirus vector construction for gene delivery and gene therapy applications. Equipped with powerful viral vector construction technologies and experienced expert team, we provide excellent adenovirus vector construction service to meet your various needs.
Background of Radiation-induced Adenoviral Vectors
Several strategies of gene therapy of tumors are currently under investigation, including the transfer of genes that regulate growth and induce an antitumor immune response. Adenoviral vectors have been chosen as effective delivery vehicles for therapeutic genes. However, they have limited effectiveness due to the poor level of tumor cell transduction and potential toxicity. Previous reports have found that radiation can increase the antitumor effect of replication-defective adenoviruses by enhancing adenoviral transgene expression both in vitro and in vivo. Radiation-induced enhancement of adenoviral transgene expression is mediated through DNA damage, specifically double-strand DNA break. The radiation-induced DNA damage response results in increased production of RNA and proteins, including adenoviral transgene products. In addition, some studies have reported that ionizing radiation induces adenoviral uptake by increased Dynamin 2 (a large GTPase) function to improve the selectivity of adenovirus targeting tumors. Lonizing radiation improves both transduction efficiency and duration of transgene expression. This may lead to the development of new protocols combining radiation and gene therapy in treating human malignancy.
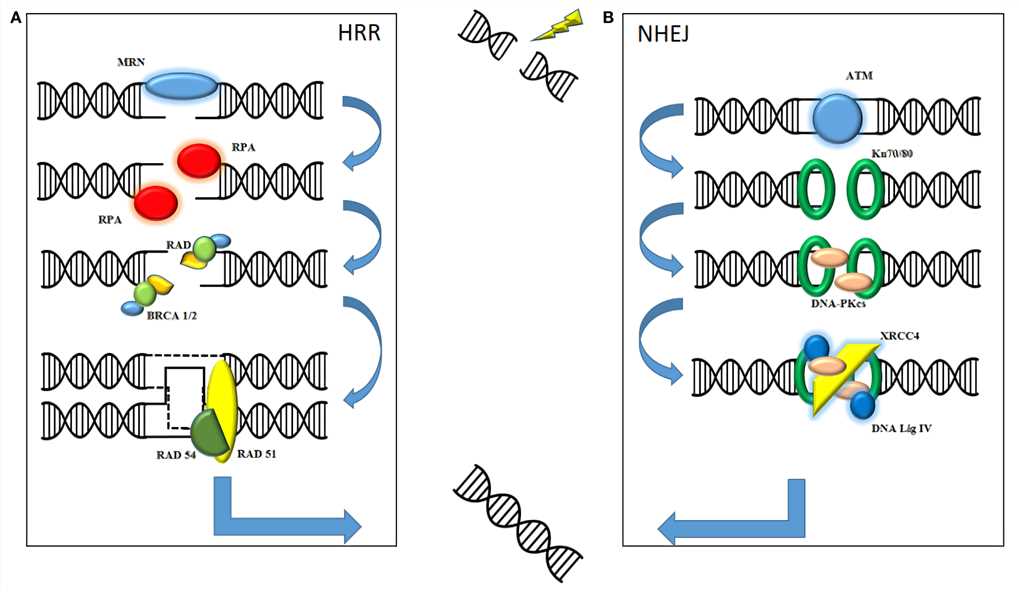 Figure 1. Radiation causes a fatal double-strand break. DNA damage repair is mediated by two major pathways: homologous recombination repair (HRR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). (O'Cathail, 2017)
Figure 1. Radiation causes a fatal double-strand break. DNA damage repair is mediated by two major pathways: homologous recombination repair (HRR) and non-homologous end joining (NHEJ). (O'Cathail, 2017)
Radiation-induced Adenoviral Vectors in Gene Therapy
Radiotherapy is an important method for the clinical treatment of many cancers, but its therapeutic effect is often affected by damage to the surrounding normal tissues and tumor radiation tolerance. Therefore, radiotherapy alone has certain limitations. Gene-radiotherapy, as a new therapy combining gene therapy and radiation therapy, has aroused great interest and has broad application prospects. The basic principle of gene-radiotherapy is to use the radiation-induced characteristics of early growth response-1 (Egr-1) to increase the expression of a target gene following radiation and thereby enhance the treatment effect. Since their first use in gene therapy, adenoviral vectors have made significant progress and are currently undergoing clinical trials in several gene therapies and anti-cancer studies. The efficient expression of radiation-inducible therapeutic genes in cancer cells is crucial in gene-radiotherapy. The combination of adenoviral cancer gene therapy and radiotherapy is a promising approach that exhibits several advantages:
- This combination could lead to increased tumor control without an increase in toxicity owing to a nonoverlapping side effect profile.
- This combination increases the level of transgene expression in cancer cells and shows better therapeutic effects.
Service
Radiation can enhance adenoviral vector-mediated gene therapy by increasing the expression of the transgene. This effect can be achieved by using a radiation-inducible promoter/enhancer, as it opens up the possibility of placing gene expression under the spatial and temporal control of radiation. The feasibility of this new method has been confirmed in different tumor models. Based on this, Creative Biolabs has provided a wide variety of radiation-inducible adenoviral vectors for customers around the world through the use of suitable promoters and other elements. Compared to traditional vectors, our radiation-induced adenoviral vectors have higher gene transduction efficiency and very low toxicity, and show broader prospects in gene delivery and gene therapy applications.
Creative Biolabs offers a broad range of adenovirus vector construction service at a reasonable cost and with quick turnaround time. Our highly experienced scientists are on hand to solve any difficulties in your adenoviral vector construction projects. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
Reference
- O'Cathail Sean, M.; et al. (2017). Combining Oncolytic Adenovirus with Radiation-A Paradigm for the Future of Radiosensitization. Frontiers in Oncology. 7:153. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
