Hydrogel-Based Delivery Strategies: A Simple, Science-Backed Guide
Hydrogel-based delivery strategies are becoming one of the most versatile and reliable tools in modern drug delivery, offering a simple way to control how and where medicines are released. These soft, water-rich materials can protect sensitive drugs, improve patient comfort, and support long-lasting therapeutic effects. Because they work across wound care, injectable systems, vaccines, and regenerative medicine, hydrogels are gaining strong attention in both research and industry. In this article, Creative Biolabs will break down the science in clear terms so readers can quickly understand why hydrogels matter and how they shape the future of targeted delivery.
Introduction: What Are Hydrogels in Drug Delivery?
Hydrogels are three-dimensional networks of polymers that can absorb and hold a huge amount of water. Think of them as soft, jelly-like materials that do not dissolve but stay stable while swollen. Because they are mostly water, they feel "tissue-like" and are usually friendly to cells and tissues.
In drug delivery, hydrogels can be built from:
- Natural polymers such as gelatin, collagen, alginate, or hyaluronic acid
- Synthetic polymers such as PEG (polyethylene glycol), PVA, or polyacrylamide
- Hybrid systems that mix natural and synthetic components for extra control
The cross-links between polymer chains create a mesh. The size of this mesh controls how easily molecules can move in or out. By adjusting polymer type, cross-link density, and water content, scientists can tune mechanical strength, swelling behavior, and drug release rate. Because hydrogels are soft, wet, and tunable, they are ideal for hydrogel-based delivery strategies in many medical and research settings.
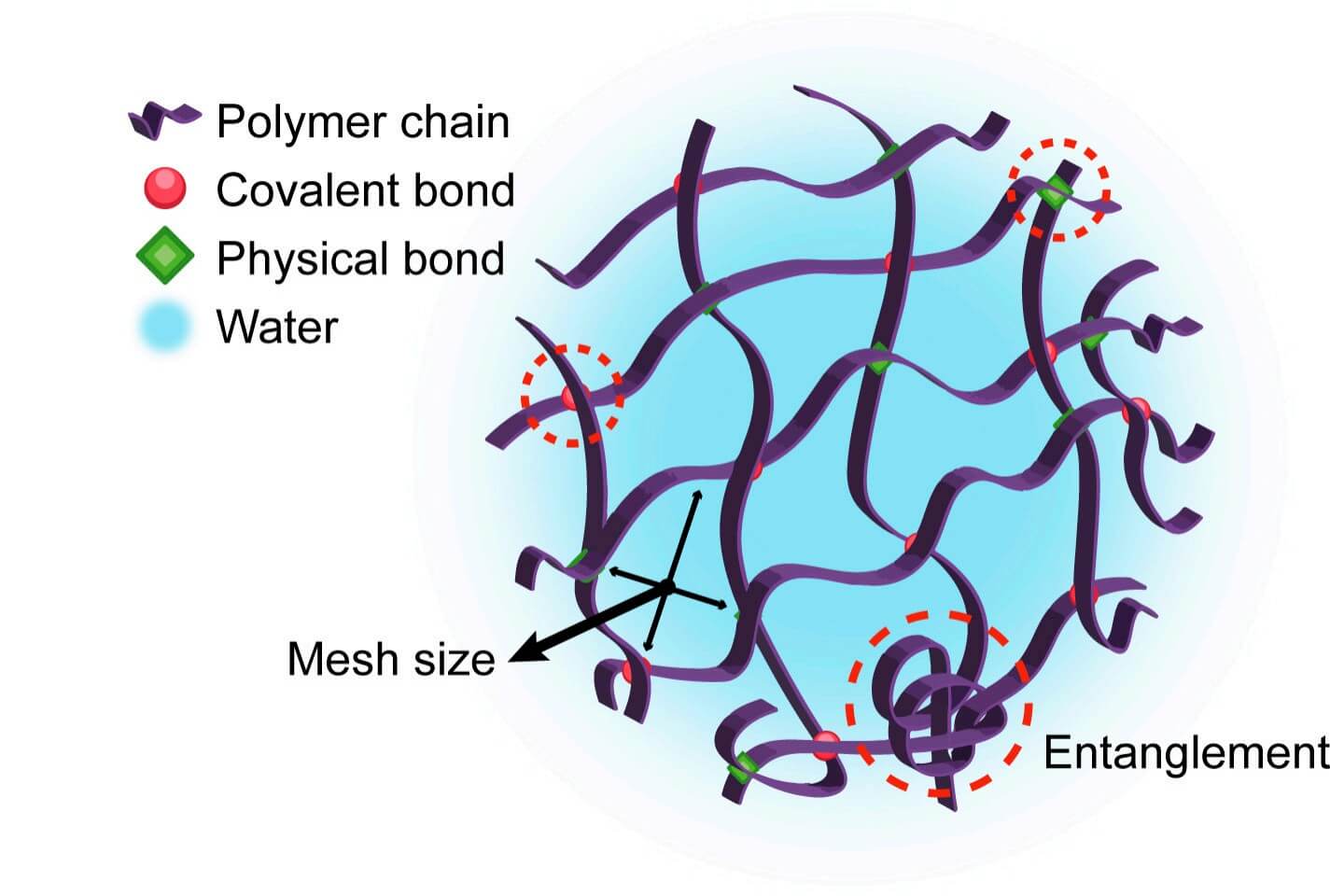 Fig.1
The general structure of a hydrogel.1
Fig.1
The general structure of a hydrogel.1
How Hydrogel-Based Delivery Strategies Work
Hydrogel-based drug delivery systems mainly work through a few core mechanisms. Understanding these mechanisms helps you see why hydrogels can be so powerful and flexible.
1. Diffusion-Controlled Release
Many hydrogels hold drug molecules inside their water-filled pores. Over time, the drug diffuses out into the surrounding tissue or fluid.
- Small molecules usually move faster.
- Large molecules or proteins move more slowly through the mesh.
- The mesh size and swelling level will strongly affect the release rate.
2. Swelling-Controlled Release
Some hydrogels swell when exposed to certain conditions, such as a change in pH or temperature (Figure 2). When they swell, the mesh opens, and drugs can move out more easily. This allows for "on-demand" or gradual release, which is helpful when you want extended dosing with fewer injections.
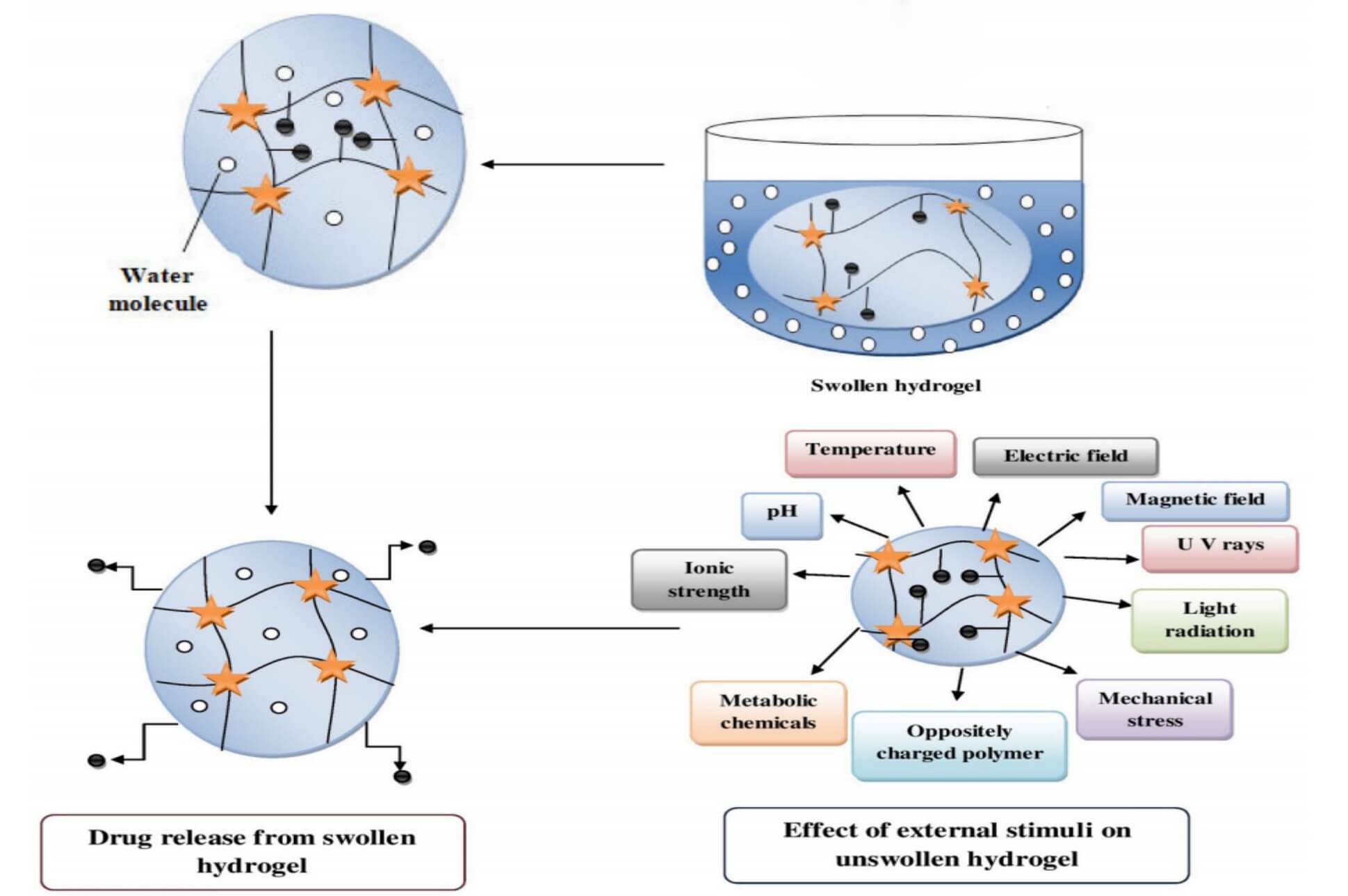 Fig.2
The mechanism of swelling-controlled release.3
Fig.2
The mechanism of swelling-controlled release.3
3. Degradation-Controlled Release
Biodegradable hydrogels slowly break down inside the body. As the network degrades, the drug is released from the structure.
- Useful for single-use depots that do not need surgical removal
- Common in tissue engineering and localized cancer therapy
4. Stimuli-Responsive and Smart Hydrogels
Advanced hydrogel-based delivery strategies use smart hydrogels that respond to specific cues, such as:
- pH changes in inflamed or tumor tissues
- Temperature near the body or skin
- Enzymes present in certain organs
- Glucose levels or other biomarkers
These systems can deliver drugs only when needed or at specific sites, improving precision and safety.
Advantages of Hydrogel-Based Drug Delivery vs. Traditional Systems
Hydrogel-based delivery strategies offer several important advantages over simple pills, solutions, or conventional injections.
High Biocompatibility
Because hydrogels are mostly water, and many are built from biological or bio-friendly polymers, they generally show good compatibility with tissues. This helps reduce irritation and inflammation.
Controlled and Extended Release
Hydrogels can be engineered to release drugs over hours, days, or weeks. This controlled release:
- Improves patient convenience
- Reduces dosing frequency
- Stabilizes drug levels in the body
Localized Delivery
By placing the hydrogel at or near the target site, scientists can deliver high local concentrations while reducing systemic side effects. This is especially valuable in oncology, ophthalmology, and wound care.
Protection of Fragile Molecules
Many modern therapies, such as proteins, peptides, antibodies, or nucleic acids, are very sensitive. Hydrogels can protect these molecules from:
- Enzymatic degradation
- pH extremes
- Mechanical stress
This protection increases the chance that the active drug reaches the target in a functional form.
Design Flexibility
Hydrogels can be customized in many ways:
- Composition (natural, synthetic, or hybrid)
- Cross-linking strength
- Degradation rate
- Shape (films, beads, lenses, injectable depots)
This flexibility allows hydrogel-based delivery strategies to be tailored for specific routes, targets, and payloads.
Looking to leverage hydrogel's unique advantages for your drug product?
Share your payload type, target site, and release timeline goals with our Hydrogel Delivery Experts. We will craft a tailored solution—including optimized hydrogel composition, cross-linking strategy, and localized delivery design—aligned with your product's needs.
Key Applications of Hydrogel Drug Delivery
Hydrogel-based delivery strategies are already widely used in clinics and research labs. Below are some of the most important application areas.
Wound Dressings and Skin Care
Hydrogel dressings keep wounds moist but not flooded, which supports healing and reduces pain. They can:
- Hold antibiotics, growth factors, or anti-inflammatory drugs
- Conform to irregular wound shapes
- Cool and soothe sensitive skin
This makes them highly valuable for the treatment of burns, chronic wounds, and surgical sites.
Ophthalmic (Eye) Drug Delivery
The eye is very sensitive, and many drops drain away quickly. Hydrogels can:
- Form soft lenses or in-situ gels that slowly release drugs
- Improve contact time with the eye surface
- Support long-term treatment for glaucoma, infections, or inflammation
Injectable Depots for Local Drug Release
Injectable hydrogels can be delivered as a liquid that gels inside the body. They are especially useful for:
- Local cancer therapy near tumors
- Long-acting pain management
- Delivery of proteins, antibodies, or cells
Because the hydrogel stays at the injection site, it can provide high local drug levels with lower systemic exposure.
Vaccine and Immunotherapy Platforms
Hydrogels can act as depots or scaffolds for antigens and adjuvants. They support:
- Slow and controlled antigen release
- Local immune cell recruitment
- New vaccine delivery strategies, including combination with nanoparticles
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
In regenerative medicine, hydrogels serve as "artificial ECM" (extracellular matrix). They:
- Provide structural support for cells
- Allow diffusion of nutrients and waste
- Can be loaded with growth factors or genetic material
This combination of structure and delivery makes hydrogels central to future organ repair, cartilage repair, and neural regeneration strategies.
Innovations: Smart, Injectable, and Biodegradable Hydrogels
The most exciting hydrogel-based delivery strategies today go far beyond simple passive gel systems.
Smart and Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels
These hydrogels respond to internal or external stimuli, such as:
- pH changes in tumors or inflamed tissue
- Temperature close to body heat
- Enzymes specific to certain organs
- Electric or magnetic fields
They can change swelling, cross-linking, or degradation in response, allowing precise control of release.
Self-Healing Hydrogels
Self-healing hydrogels can repair their own structure after being damaged or cut. This behavior:
- Extends functional lifetime
- Supports flexible or moving tissues
- Helps maintain controlled delivery even under stress
Biodegradable and Bioresorbable Hydrogels
Instead of staying in the body permanently, these systems slowly break down into safe by-products. They:
- Remove the need for surgical removal
- Reduce long-term foreign material burden
- Are well-suited for single-use depots and tissue scaffolds
3D-Bioprinted and Hybrid Hydrogel Systems
Combining hydrogels with nanoparticles, liposomes, or fibers creates hybrid platforms. These can:
- Provide multi-stage or multi-drug release
- Improve mechanical strength
- Support complex tissue structures through 3D bioprinting
These innovations open new paths for personalized medicine, combination therapies, and complex targeted delivery strategies.
Ready to harness cutting-edge hydrogel innovations for your product?
Share your target stimuli (pH, temperature, enzymes), delivery route, and product lifecycle goals with our Advanced Hydrogel Innovation team. We will recommend the ideal next-gen solution—whether smart stimuli-responsive, self-healing, biodegradable, or 3D-bioprinted hybrid hydrogels—tailored to your precise needs.
Challenges and Limitations in Hydrogel Drug Delivery
Despite many benefits, hydrogel-based drug delivery is not perfect. There are some real scientific and industrial challenges.
1. Burst Release
Sometimes, a large fraction of the drug leaves the hydrogel very quickly after administration. This "burst release" can lead to:
- Temporary overdosing at the local site
- Shorter effective duration
- Wasted drug
Careful design of polymer composition, cross-linking, and loading method is needed to control this.
2. Stability of Large or Fragile Molecules
Proteins, peptides, and nucleic acids can be unstable during:
- Hydrogel formation
- Sterilization
- Storage
To maintain the integrity of large molecule complexes, formulators must select gentle conditions and consider options like lyophilization, cryoprotectants, or stabilizing excipients.
3. Sterilization and Manufacturing
Medical products must be sterile and consistent. However:
- Some hydrogels degrade under heat or radiation.
- Large-scale casting, injection, or 3D printing of hydrogels can be complex.
This requires smart process engineering and careful selection of sterilization methods, such as filtration, gamma, or e-beam, depending on the system.
4. Regulatory and Quality Requirements
Hydrogels used in drug delivery face strict requirements on:
- Biocompatibility
- Extractables and leachables
- Degradation products
- Performance consistency
Regulatory pathways can be more complex when hydrogels act as both device and drug carrier.
How Creative Biolabs Supports Hydrogel-Based Delivery Strategies
At Creative Biolabs, we focus on advanced targeted delivery solutions that can work hand-in-hand with hydrogel-based strategies. Through our Targeted Delivery Platforms, we help clients:
- Design and optimize carrier systems for complex payloads
- Combine hydrogels with nanocarriers and biologics
- Evaluate release profiles and targeting performance in relevant models
- Translate early hydrogel concepts into robust, scalable solutions
If you are exploring hydrogel-based delivery strategies for your next project, our experts are ready to discuss tailored solutions and help move your ideas from concept to preclinical reality.
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Related Services You May Be Interested in
FAQs
What is a hydrogel in drug delivery?
A hydrogel in drug delivery is a soft, water-rich polymer network that can hold drugs and release them in a controlled way at or near the target site.
How do hydrogels release drugs?
Hydrogels release drugs mainly through diffusion, swelling, or degradation. In many designs, environmental changes such as pH or temperature help control the release rate.
What are hydrogel-based delivery systems used for?
They are used in advanced wound dressings, eye drug delivery, cancer depots, injectable systems, vaccines, and tissue engineering scaffolds that also provide therapeutic release.
Are hydrogels safe for medical use?
Many hydrogel systems are designed to be biocompatible and have been used in approved medical products for years, but each new system still needs careful safety and regulatory evaluation.
What are the main benefits of hydrogel drug delivery?
Protection of fragile biologics such as proteins and nucleic acids.
What are the biggest challenges in hydrogel-based delivery strategies?
The main challenges are burst release, stability of sensitive drugs, sterilization, scalable manufacturing, and navigating complex regulatory pathways for new hydrogel products.
Conclusion: Why Hydrogels Matter for the Future of Drug Delivery
Hydrogel-based delivery strategies provide a unique mix of softness, water content, and tunable structure. They can protect fragile drugs and release them in a controlled way. While there are challenges in manufacturing and regulation, ongoing innovation in smart, self-healing, and biodegradable hydrogels is expanding what is possible in modern drug delivery. For researchers, developers, and formulation teams, hydrogels are now a core platform, not just a niche material.
For Research Use Only. Not for Clinical Use.
References
- Delgado-Pujol, E. J. et al. "Hydrogels and Nanogels: Pioneering the Future of Advanced Drug Delivery Systems." Pharmaceutics 17, 215 (2025). https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/17/2/215. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Raeisi, A. & Farjadian, F. "Commercial hydrogel product for drug delivery based on route of administration." Front. Chem. 12, 1336717 (2024). https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2024.1336717/full.
- Raina, N. et al. "Drug Delivery Strategies and Biomedical Significance of Hydrogels: Translational Considerations." Pharmaceutics 14, 574 (2022). https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/14/3/574. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Thang, N. H., Chien, T. B. & Cuong, D. X. "Polymer-Based Hydrogels Applied in Drug Delivery: An Overview." Gels 9, 523 (2023). https://www.mdpi.com/2310-2861/9/7/523.



