Dendrimer-Based Delivery Strategies: A Clear Guide for Modern Drug Delivery
Dendrimer-based delivery strategies are gaining attention because they offer a precise and flexible way to transport drugs, genes, and imaging agents in modern research. Their tree-like structure allows researchers to load cargo efficiently, improve solubility, and guide molecules toward specific targets. As demand grows for smarter and more controlled delivery systems, dendrimers are becoming a valuable platform in advanced drug delivery development. Creative Biolabs supports this progress by helping researchers design and evaluate dendrimer-based systems with clarity and confidence.
Introduction to Dendrimers
What Are Dendrimers?
Dendrimers are nano-sized, perfectly branched polymers that look like tiny trees when you imagine their shape. They start from a central core, then grow outwards in layers called "generations" (Figure 1). With each new generation, the number of branches and surface groups increases.
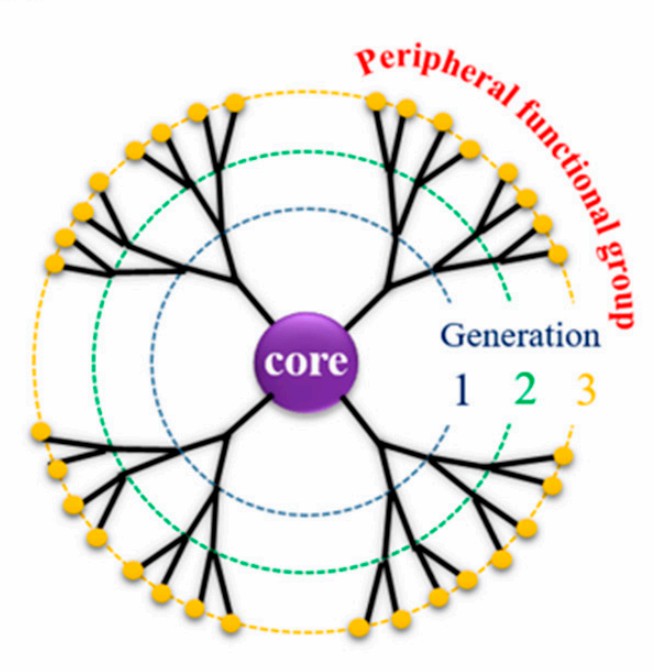 Fig.1
The diagram of the dendrimer structure.3
Fig.1
The diagram of the dendrimer structure.3
Because of this highly ordered structure, dendrimers have:
- A well-defined size, often in the range of a few nanometers
- Internal cavities that can hold small molecules
- Many surface groups that can be chemically modified
In practice, this means scientists can:
- Load drugs or other cargo inside the dendrimer
- Attach targeting ligands, imaging labels, or solubility enhancers on the outside
In simple terms, a dendrimer is like a tiny, customizable cargo ship: the inside can carry the load, and the outside can be decorated with "addresses" that guide where it goes.
Why Dendrimers Matter in Drug Delivery Science
Current Problems:
1. Modern research needs delivery systems that can carry complex molecules safely and precisely.
2. Many small molecules, nucleic acids, and biologics face problems such as:
- Poor water solubility
- Fast breakdown in the body
- Low uptake by target cells
- Unwanted distribution to non-target tissues
Solutions:
Dendrimer-based delivery systems offer tools to solve several of these issues at the same time. Because their structure is tunable, dendrimers can:
- Improve solubility for hydrophobic molecules
- Shield sensitive cargo from early breakdown
- Help guide cargo to specific cells or microenvironments
- Support controlled or sustained release profiles
For research teams working on advanced delivery, dendrimers are therefore not just another carrier. Instead, they are a flexible design platform that can be adapted to many project needs.
Need a tailored dendrimer delivery platform for your research?
Partner with our drug delivery experts to design a custom dendrimer system aligned with your cargo type, target cells, and release requirements.
Types of Dendrimer
Not all dendrimers are the same. Their structural differences—from core to surface groups—dictate their suitability for drug delivery. Below is a detailed breakdown of the most common types in delivery research, paired with key structural and functional insights
PAMAM dendrimers
Core & Structure: Featuring an ethylenediamine core and repetitive amide/amine branching units, they form well-defined globular architectures (Figure 2).
Key Trait: Rich in terminal amine groups, which enable electrostatic binding to nucleic acids (DNA/siRNA) for dendriplex formation and facile surface modification (e.g., PEGylation, ligand conjugation like lactoferrin for BBB targeting).
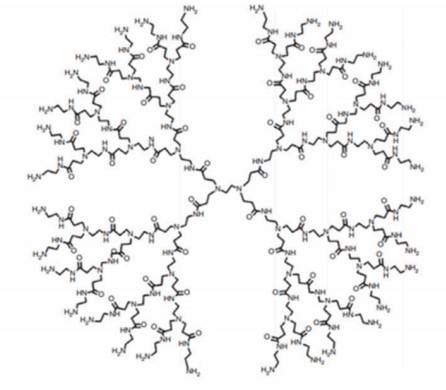 Fig.2
The structure of PAMAM dendrimers.3
Fig.2
The structure of PAMAM dendrimers.3
PPI dendrimers
Core & Structure: Highly branched cationic dendrimers with a diaminobutane (DAB) core and propyleneimine repeat units (Figure 3). Their internal cavity is more hydrophobic than PAMAM, as validated via solvatochromic probes.
Key Trait: Terminal amino groups enhance water solubility but cause cell membrane destabilization (lysis) without modification. Acetylation or PEGylation can mitigate toxicity and improve drug complex stability.
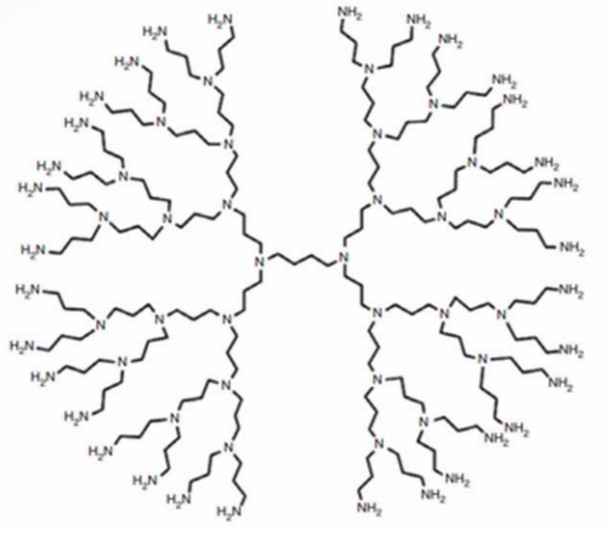 Fig.3
The structure of PPI dendrimers.3
Fig.3
The structure of PPI dendrimers.3
Carbosilane dendrimers
Core & Structure: Possess silicon-containing backbones (C-Si bonds) with hydrophobic scaffolds and high thermal stability. Reactive groups (Si-H, Si-Cl) enable surface functionalization (Figure 4).
Key Trait: Hydrophobic cores encapsulate lipophilic drugs; surface modification with polar moieties (e.g., hydroxyl groups) converts them to hydrophilic carriers, improving biocompatibility.
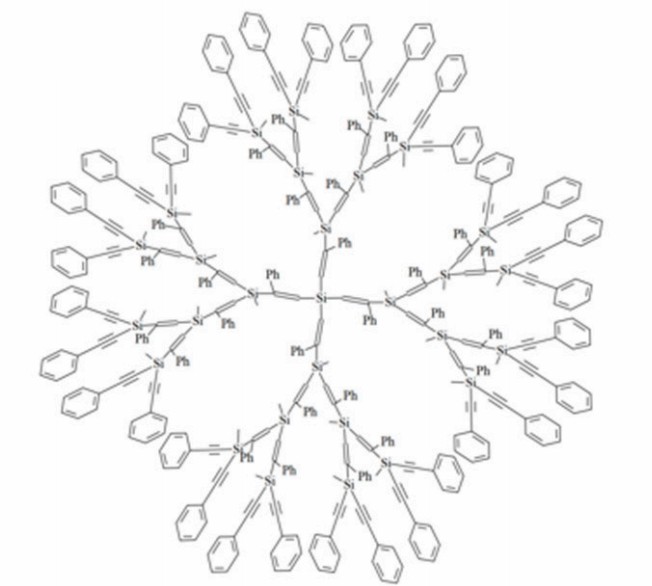 Fig.4
The structure of carbosilane dendrimers.3
Fig.4
The structure of carbosilane dendrimers.3
Polyester dendrimers
Core & Structure: Linked by ester bonds, with bis-MPA (2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)propanoic acid) as the most common building block. Neutral surface hydroxyl groups reduce toxicity.
Key Trait: Superior biodegradability (ester bonds hydrolyze safely) and low cytotoxicity, making them ideal for delivery to sensitive tissues such as the brain. Their uniform size (~10-20 nm) aids BBB penetration.
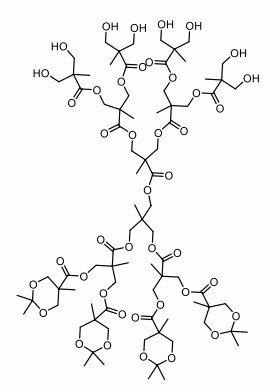 Fig.5
The structure of polyester dendrimers.6
Fig.5
The structure of polyester dendrimers.6
From a regulatory point of view, only a limited number of dendrimer-based systems have reached advanced development stages. Most work remains at the research or early clinical investigation level, mainly because:
- Safety and toxicity must be studied very carefully
- Manufacturing and quality control are complex
- Regulatory agencies require robust long-term data
Therefore, dendrimers are currently more common in preclinical and early-stage research than in widely approved products.
Need help selecting the right dendrimer type for your delivery system?
Collaborate with our team of nanomedicine experts to match dendrimer structure (core, branches, surface groups) to your research goals—from BBB targeting to nucleic acid delivery.
Advantages of Dendrimer-Based Delivery Systems
Dendrimer-based delivery systems have emerged as a game-changer in modern drug delivery, addressing key bottlenecks that plague traditional carriers. Their unique hyper-branched, globular structure and tunable surface chemistry unlock unparalleled advantages—from solving solubility issues to enabling precise, targeted transport—making them a cornerstone of preclinical research for complex diseases. Whether enhancing bioavailability, boosting targeting efficiency, or enabling controlled release, these nanocarriers redefine how therapeutic agents reach and act on their targets.
Better Solubility and Bioavailability
Many promising molecules fail because they do not dissolve well in water. Dendrimers can host these molecules:
- Inside their internal cavities
Or
- through interactions with their surface groups
As a result, they can increase the solubility and help the active compounds reach the desired environment in research models.
Precise Targeting Through Surface Functionalization
One of the strongest advantages of dendrimers is their multivalent surface. Researchers can attach:
- Antibodies or antibody fragments
- Peptides or small targeting ligands
- Sugars, vitamins, or other recognition motifs
Because many copies of a ligand can be displayed at once, the dendrimer can show enhanced binding to specific cell types or receptors, which is key for targeted delivery strategies.
High Loading Capacity Due to Branched Architecture
The dense, branched architecture of dendrimers allows them to:
- Trap small molecules inside
- Bind nucleic acids through charge interactions
- Carry multiple functional groups at the surface
This means a single dendrimer-based delivery system can carry more than one type of payload, such as a drug plus an imaging agent, or multiple drugs together.
Controlled Release and Improved Stability
By tuning the chemistry of the branches and linkers, researchers can design dendrimers that:
- Release cargo slowly over time
- Respond to pH, enzymes, or other triggers
- Protect fragile molecules, such as nucleic acids, from early degradation
This control is extremely attractive for building smart, responsive delivery systems in preclinical research.
Key Applications of Dendrimer-Based Delivery
Dendrimer-based delivery strategies are being explored across several application areas.
Drug Delivery
Dendrimers can:
- Improve the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs
- Enhance penetration across biological barriers
- Support sustained or controlled release in model systems
These features are especially useful in targeted delivery research, where efficient transport to specific sites is essential.
Gene and Nucleic Acid Delivery
Because many dendrimers carry positive charges, they can form complexes with negatively charged nucleic acids, such as:
- DNA
- siRNA
- mRNA
- Oligonucleotides
These complexes can help protect genetic cargo and support cellular uptake, making dendrimers a key platform in gene delivery and genome engineering research.
Imaging and Diagnostics
Dendrimers can be loaded or decorated with:
- Fluorescent dyes
- MRI contrast agents
- Radionuclides
This multi-label approach allows researchers to design multimodal imaging probes that help track the distribution, uptake, and retention of delivery systems.
Transdermal and Mucosal Delivery
Because of their small size and tunable surface chemistry, dendrimers are also being studied for:
- Transdermal delivery through the skin
- Delivery across mucosal barriers, such as the nasal or oral routes
They can help improve permeation and local retention in these models.
Biosensing and Combination Approaches
Dendrimers can host sensing elements or respond to environmental cues, which makes them valuable for:
- Biosensor platforms
- Co-delivery of diagnostic and active agents
- Emerging "sense-and-respond" delivery concepts
New Innovations in Dendrimer-Based Delivery
Despite these challenges, innovation in dendrimer-based delivery strategies is very active.
Key directions include:
- Biodegradable dendrimers to reduce long-term accumulation
- Stimuli-responsive systems that react to pH, enzymes, or redox conditions
- Multimodal platforms that combine delivery, imaging, and sensing in one structure
- Integration with gene editing tools for precise genome engineering
- AI-assisted design, where computational tools help predict optimal structures, surface chemistries, and payload combinations
These innovations aim to retain the strong benefits of dendrimers while reducing risks and simplifying translation.
The future of dendrimer-based delivery lies in smarter, safer, and more integrated systems that can support truly precision-focused research.
Looking to leverage cutting-edge dendrimer innovations for your research?
Collaborate with Creative Biolabs to develop tailored solutions—whether biodegradable carriers, stimuli-responsive systems, or multimodal platforms aligned with your precision-focused goals.
Current Challenges in Applying Dendrimer-Based Delivery
While dendrimers offer many advantages, several challenges still limit their broad adoption.
Safety and Toxicity Concerns
Some dendrimers, especially highly cationic structures, can:
- Interact strongly with cell membranes
- Cause membrane disruption at high doses
- Trigger unwanted immune or inflammatory responses
As a result, researchers must carefully optimize:
- Generation number
- Surface charge and functional groups
- Dosing strategies
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Dendrimers are highly ordered molecules that often require multi-step synthesis and strict quality control. This can lead to:
- Higher production costs
- Longer development timelines
- Scale-up challenges for larger batches
Regulatory and Translational Barriers
Because dendrimers are relatively new compared with traditional excipients, regulators need:
- Detailed data on safety
- Clear understanding of manufacturing consistency
- Well-designed preclinical and clinical studies
These requirements can slow the path from lab to real-world use. However, they also push the field towards better-designed and better-characterized dendrimer systems.
How Creative Biolabs Supports Dendrimer-Based Delivery Research
Creative Biolabs provides a broad targeted delivery portfolio that can support research using dendrimer-based delivery strategies. By combining deep expertise in delivery system design with advanced analytical and characterization platforms, Creative Biolabs can help teams:
- Design and optimize custom dendrimer-based delivery systems
- Evaluate loading, release, and targeting performance in relevant models
- Characterize physicochemical properties, including size, charge, and stability
- Explore combination strategies, such as dendrimer-based co-delivery or multimodal imaging constructs
For researchers interested in integrating dendrimers into their next delivery project, Creative Biolabs offers flexible, project-driven support under a research-use-only framework.
Related Services You May Be Interested in
FAQs
What are dendrimers used for in drug delivery?
Dendrimers are used to improve solubility, protect sensitive cargo, and guide active molecules or nucleic acids to specific cells or tissues in research models.
How do dendrimers target specific cells?
Dendrimers can be decorated with targeting ligands, such as antibodies or peptides, on their surface. These ligands help the dendrimer bind to receptors that are more common on certain cell types.
Why are dendrimers not widely approved yet?
Because dendrimers are complex nano-structures, regulators need extensive safety, toxicity, and quality data. Many systems are still in research or early development, so broad approvals remain limited.
What types of dendrimers are most common in delivery research?
PAMAM and PPI dendrimers are the most widely studied families. Other types, such as carbosilane and polyester dendrimers, are also gaining interest for their potential biocompatibility advantages.
What is the growth potential for dendrimer-based delivery?
Market studies suggest steady growth with strong demand in drug delivery and diagnostics research. This reflects rising interest from pharma, biotech, and academic teams in advanced delivery platforms.
Conclusion: The Future of Dendrimer-Based Delivery Strategies
Dendrimer-based delivery strategies bring together precise structure, high loading capacity, and flexible surface chemistry. These features make dendrimers powerful tools for improving solubility, stability, and targeting in modern delivery research. Although safety, manufacturing, and regulatory questions remain, ongoing innovation is pushing the field towards safer, smarter, and more versatile systems.
Creative Biolabs is ready to collaborate with research teams who want to explore or advance dendrimer-based delivery strategies, helping turn complex ideas into well-designed, data-driven delivery solutions.
For Research Use Only. Not for Clinical Use.
References
- Alamos-Musre, S. et al. "From Structure to Function: The Promise of PAMAM Dendrimers in Biomedical Applications." Pharmaceutics 17, 927 (2025). https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/17/7/927.
- Ordonio, M. B., Zaki, R. M. & Elkordy, A. A. "Dendrimers-Based Drug Delivery System: A Novel Approach in Addressing Parkinson's Disease." Future Pharmacology 2, 415–430 (2022). https://www.mdpi.com/2673-9879/2/4/27.
- Zhu, Y., Liu, C. & Pang, Z. "Dendrimer-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Brain Targeting." Biomolecules 9, 790 (2019). https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/9/12/790. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Abbasi, E. et al. "Dendrimers: synthesis, applications, and properties." Nanoscale Res Lett 9, 247 (2014). https://link.springer.com/10.1186/1556-276X-9-247.
- Pérez-Ferreiro, M., M. Abelairas, A., Criado, A., Gómez, I. J. & Mosquera, J. "Dendrimers: Exploring Their Wide Structural Variety and Applications." Polymers 15, 4369 (2023). https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4360/15/22/4369.
- Wang, J., Li, B., Qiu, L., Qiao, X. & Yang, H. "Dendrimer-based drug delivery systems: history, challenges, and latest developments." J Biol Eng 16, 18 (2022). https://jbioleng.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13036-022-00298-5. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.



