AAV Vector Design Service for Parkinson's Disease (PD)
Introduction
Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, mainly marked by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to classic motor symptoms (resting tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement). Existing treatments like L-DOPA ease symptoms but don't stop progression and may cause side effects. Gene therapy, especially with AAV vectors, offers a promising targeted, long-lasting solution to address PD's root cause. Research confirms AAVs' potential for safe, effective CNS gene delivery.
Parkinson's Disease
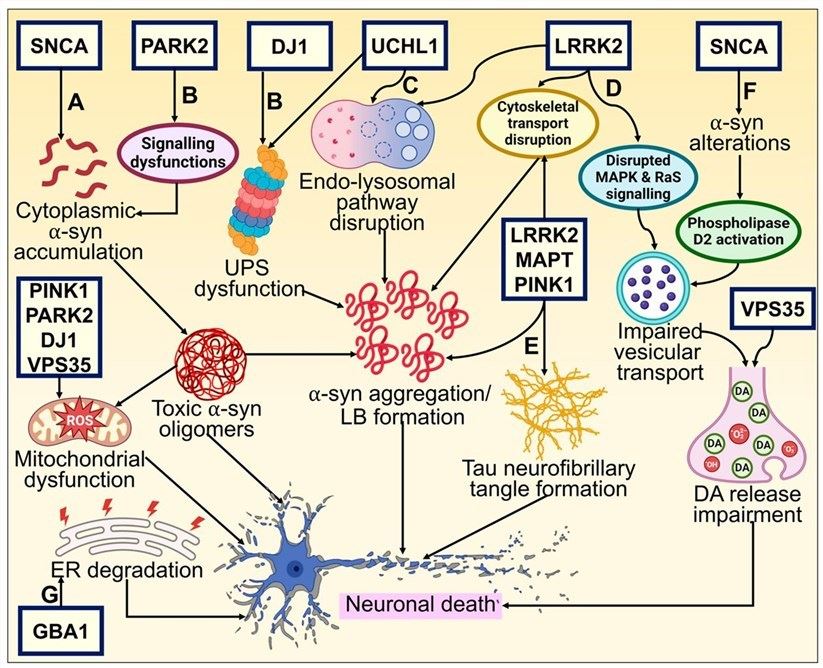 Fig.1 The pathogenic mechanism of Parkinson's disease.1
Fig.1 The pathogenic mechanism of Parkinson's disease.1
Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized primarily by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, presenting with motor symptoms such as resting tremor and muscle rigidity. Its pathogenic mechanisms involve multiple abnormalities at the genetic, cellular, and molecular levels, which can be elaborated on as follows.
Genetic Basis: Pathogenesis Driven by Key Gene Mutations
PD has significant genetic heterogeneity, with core genes (SNCA, LRRK2, PINK1/Parkin, DJ-1, VPS35, GBA1) whose mutations disrupt protein function, mitochondrial activity, or lysosomal processes, leading to α-syn aggregation and dopaminergic (DAergic) neuron death.
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms:
Neurodegeneration Induced by Synergistic Multi-Pathways
- Protein Misfolding and Aggregation
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress
- Calcium Homeostasis Imbalance
- Dopamine (DA) Metabolic Toxicity
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction
- Oxidative and Nitrosative Stress
- Neuroinflammation and Immune Dysregulation
- Non-Dopaminergic and Non-Motor Pathology
Therapeutic Targets
Key therapeutic targets for gene therapy in PD include:
- Neurotrophic Factors: Delivering genes for proteins like GDNF (Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor) and Neurturin, which can protect dopamine neurons from degeneration and promote their survival.
- Enzyme Supplementation: Providing the gene for Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC) to enhance the conversion of L-DOPA to dopamine in the brain, improving the efficacy of symptomatic therapies.
- Gene Silencing: Using techniques like RNA interference to reduce the production of neurotoxic proteins, such as alpha-synuclein, which is implicated in the pathology of PD.
AAV vectors are the preferred tool for these treatments due to their high safety profile and ability to transduce non-dividing neurons in the brain, providing stable, long-term expression. They can be engineered to target specific cell types and can be delivered via various routes, including directly into the brain or through the spinal fluid, to bypass the blood-brain barrier.
Workflow
- Project Consultation & Planning: This initial phase involves a detailed discussion to understand your research goals, specific target genes (e.g., GDNF, AADC, or alpha-synuclein), and the desired expression profile. We will also discuss the optimal AAV serotype and promoter for your application.
- Vector Design & Construction: Our team designs/constructs custom rAAV vectors—selecting optimal serotypes, designing robust promoters/regulatory elements, and cloning target genes into backbones—to optimize efficient, targeted expression.
- Virus Packaging & Purification: Package designed vectors into high-titer AAV particles in advanced facilities; purify rigorously to remove impurities for a pure, potent final product.
- Quality Control & Validation: Conduct comprehensive QC on each batch (qPCR for titer, SDS-PAGE for purity, cell culture tests for expression) to ensure reliable, consistent products.
- Final Deliverables: Purified rAAV vector, Certificate of Analysis (CoA) with quality control data, and a final project report.
- Estimated Timeframe: The typical timeframe for this service ranges from 8 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the vector design and the number of serotypes requested.
Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation
What We Can Offer
As a leader in gene therapy vector services, we are committed to providing the highest quality products and personalized support to accelerate your research. Our offerings are meticulously designed to meet the unique needs of your project.
Our Advantage
One-stop Vector Design and Production
Offer integrated service from consultation/sequence design to viral packaging/purification, simplifying workflow and cutting turnaround time.
Customized rAAV Design and Engineering
Provide custom AAV serotype engineering and promoter selection for specific, efficient CNS neuronal gene delivery.
Precision and Quality
Guarantee high-titer, high-purity vectors meeting strict QC standards for reliable, reproducible research materials.
Comprehensive Project Support
Deliver expert consultation/technical support across the project (experimental design to data interpretation) as an extension of your lab.
Unmatched Scalability
Cover production from small research batches to large preclinical/clinical-grade vectors, supporting project growth without limits.
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today
Customer Reviews

FAQs
How can AAV gene therapy specifically target the right brain cells for Parkinson's research?
Vectors can be engineered with specific serotypes and promoters that allow them to selectively transduce certain cell types, like dopamine neurons. We can help you choose the ideal combination for your project to ensure precise and efficient gene delivery.
What are the potential safety concerns with AAV vectors?
The AAV virus is considered very safe as it is non-replicating and has a low rate of integration into the host genome. We further enhance safety through rigorous purification protocols and optimized vector design to minimize the risk of an immune response or off-target effects.
How does AAV gene therapy compare to traditional drug-based treatments?
Unlike traditional oral medications, which require systemic administration and have a short half-life, AAV gene therapy provides a one-time treatment that delivers the therapeutic gene directly to the target cells, offering continuous and localized expression and avoiding issues with patient compliance and side effects from fluctuating drug levels.
Can this service be used to create an animal model for Parkinson's Disease?
Yes, our services are ideal for creating robust animal models. We can provide custom vectors to overexpress pathogenic genes like alpha-synuclein or to deliver reporter genes, enabling you to study disease mechanisms or track therapeutic efficacy in a controlled environment.
Creative Biolabs offers specialized rAAV design and production services that provide a direct, reliable, and innovative approach to your Parkinson's Disease research. Our commitment to quality and scientific excellence ensures that you receive the highest-grade tools for your projects.
Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project
Reference
- Ratan, Yashumati, et al. "Advancements in genetic and biochemical insights: unraveling the etiopathogenesis of neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease." Biomolecules 14.1 (2024): 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom14010073. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
