Selenium Nanoparticle Delivery Strategies: A Simple Guide for Modern Drug Delivery
Selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies are becoming one of the most versatile and promising tools in modern drug delivery thanks to their strong biocompatibility, selective targeting, and built-in antioxidant activity. As researchers look for safer and more effective ways to transport drugs, nutrients, and therapeutic compounds, selenium nanoparticles offer a balanced blend of stability and precision. In this simple, clear guide, Creative Biolabs introduces how they work, why they matter, and where they are making the biggest impact in today's biomedical landscape.
Introduction: What Are Selenium Nanoparticles?
Selenium nanoparticles (often called SeNPs) are extremely small particles made from elemental selenium (Figure 1). Their size usually ranges from a few nanometers to a few hundred nanometers. At this tiny scale, selenium behaves very differently from bulk selenium.
In drug delivery, selenium nanoparticles act as tiny shuttles. They can carry drugs, protect them on the way to the target, and then release them in a controlled way. Because selenium is an essential trace element for humans and animals, properly designed SeNPs usually show good biocompatibility.
Key points to remember:
- Selenium is already part of many enzymes and antioxidants in the body.
- When turned into nanoparticles, selenium can carry drugs, modulate oxidative stress, and interact with cells in a more precise way.
- SeNPs can be tailored in size, surface charge, coating, and shape to match different delivery needs.
Why Selenium Nanoparticles Matter in Drug Delivery?
Selenium nanoparticles matter in drug delivery because they sit at the crossroads of efficacy and safety. Many classic drug delivery systems improve drug solubility or circulation time, but they may raise concerns about toxicity or long-term accumulation. SeNPs help address this gap.
Some of the most important reasons why selenium nanoparticles are gaining attention in drug delivery are:
Enhanced targeting of diseased cells
SeNPs often show selective toxicity toward cancer cells or pathogens while sparing healthy cells, especially when combined with targeting ligands or surface modifications.
Built-in antioxidant properties
Selenium is part of several antioxidant enzymes in the body. SeNPs can reduce oxidative stress, which plays a role in cancer, inflammation, and metabolic disorders.
Potentially lower toxicity than many metal nanoparticles
Compared with some inorganic nanoparticles (such as silver), selenium nanoparticles can show lower systemic toxicity when used at proper doses and with smart surface coatings.
Flexible platform for targeted delivery
SeNPs can be combined with antibodies, peptides, sugars, or polymers to reach tumors, inflamed tissues, or infected cells more precisely.
Because of these features, selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies are becoming a strong candidate for next-generation targeted and responsive drug delivery systems.
Selenium Nanoparticles vs. Other Nanoparticle Delivery Systems
SeNPs vs Gold Nanoparticles
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are well known for imaging and photothermal therapy. In comparison:
Gold nanoparticles
- Excellent for imaging and laser-triggered therapies.
- Inert core, often used as a scaffold for surface chemistry.
Selenium nanoparticles
- Add intrinsic biological activity (antioxidant, immunomodulatory).
- Often show lower cost and simpler raw material supply.
For pure imaging tasks, AuNPs may still lead. However, when you want a therapeutic nanocarrier with its own biological benefits, selenium nanoparticles become very attractive.
SeNPs vs Silver Nanoparticles
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are famous for broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects, but they also bring toxicity concerns.
Silver nanoparticles
- Vigorous, non-selective antimicrobial activity.
- Toxicity concerns for both host cells and the environment.
Selenium nanoparticles
- Strong antimicrobial effects but often with better selectivity.
- Potentially safer profile at therapeutic doses, especially with good surface design.
For long-term or systemic treatments, SeNPs may offer a more balanced approach between efficacy and safety.
SeNPs vs PLGA Nanocarriers
PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)) is a classic biodegradable polymer used for controlled release.
PLGA nanoparticles
- Excellent for sustained release.
- FDA-accepted polymer platform.
- Mostly "inert" carriers without additional therapeutic activity.
Selenium nanoparticles
- Combine carrier function with biological activity (antioxidant, cytotoxic to cancer cells, immune modulation).
- Can be hybridized with PLGA or other polymers to create core-shell systems that merge the best features of both platforms.
In many cases, selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies are explored alongside or on top of PLGA systems, rather than as a direct replacement.
Trying to choose between selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) and nanocarriers like AuNPs, AgNPs, or PLGA for your specific use case?
Share your core goal, payload type, safety thresholds, and regulatory targets with our Nanocarrier Selection Experts. We will break down tradeoffs—SeNPs' intrinsic antioxidant/anticancer activity for oncology, PLGA 's FDA-approved sustained release for chronic therapies, AgNPs' potent antimicrobial effects (with toxicity caveats)—and design a tailored solution (including hybrid core-shell systems) to maximize efficacy and align with your therapeutic needs.
Biomedical Applications of Selenium Nanoparticles
Selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) have emerged as versatile biomedical tools, leveraging their intrinsic biological activity (antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial) and carrier capabilities to drive innovations in cancer therapy, antimicrobial treatments, and nutritional metabolic support (Figure 1).
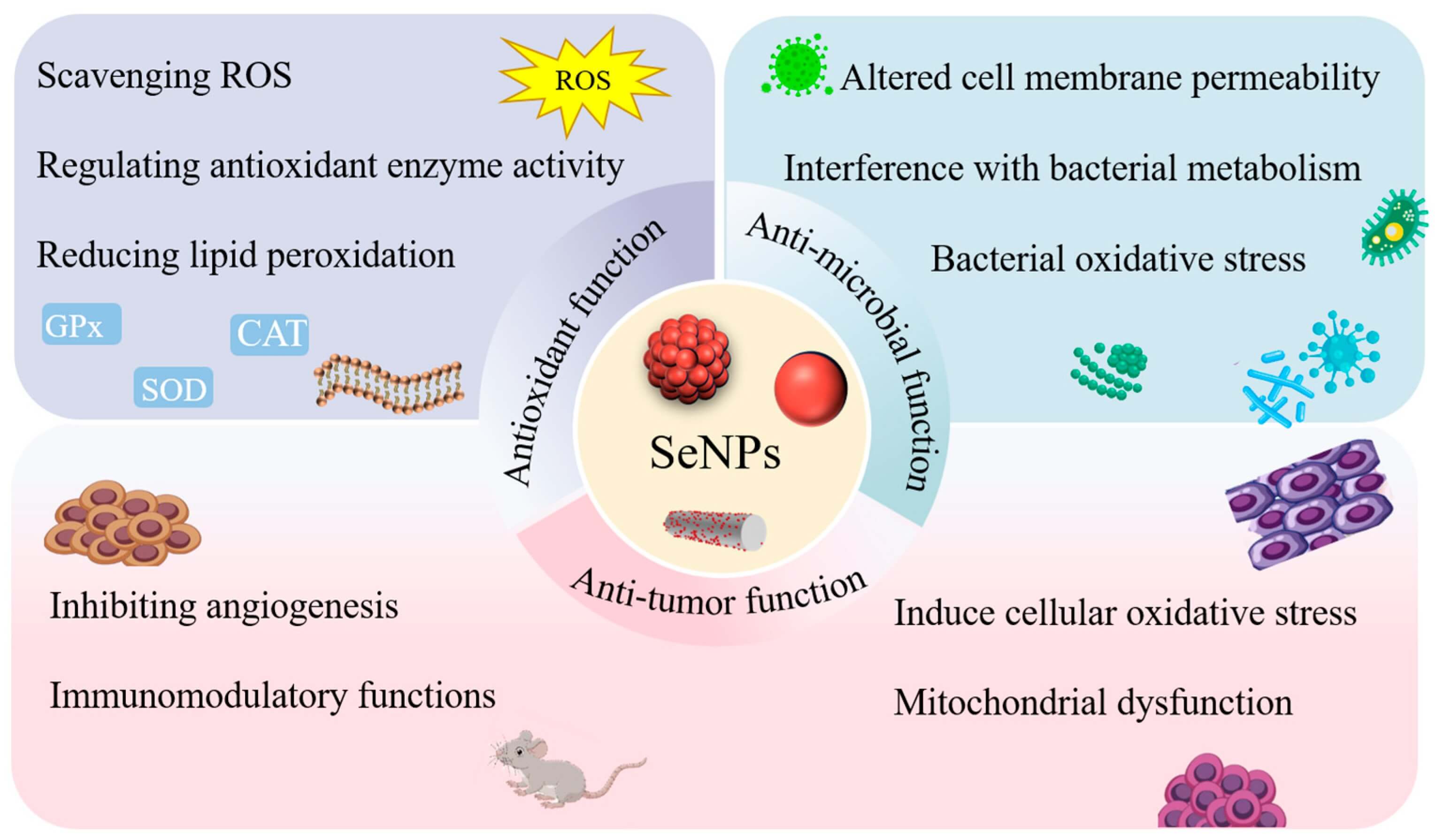 Fig.1
The antitumor, antibacterial, and antioxidant mechanisms of SeNPs.1
Fig.1
The antitumor, antibacterial, and antioxidant mechanisms of SeNPs.1
Selenium Nanoparticles in Cancer Drug Delivery
In oncology, selenium nanoparticles are used to:
- Carry chemotherapy drugs directly to tumors.
- Improve the local concentration of the drug while reducing exposure to healthy tissues.
- Exploit the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect, which helps nanoparticles accumulate in solid tumors.
Studies have shown that SeNPs can be used to deliver anticancer drugs, gene therapies, and immune modulators, often enhancing both tumour cell killing and chemosensitisation while reducing side effects.
Because selenium nanoparticles can also affect oxidative stress, they may help tip the balance inside cancer cells and make them more vulnerable to treatment.
Selenium Nanoparticles for Antimicrobial Applications
Selenium nanoparticles are also being developed as antimicrobial delivery systems. They can:
- Carry antibiotics or antifungal agents.
- Disrupt bacterial cell walls and biofilms.
- Support host immune responses against infections.
Research suggests that SeNPs can act both as direct antimicrobial agents and as smart drug carriers, improving the killing of resistant bacteria and intracellular pathogens.
This makes selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies very interesting for infections where standard antibiotics struggle, such as biofilm-associated infections or intracellular pathogens.
Selenium Nanoparticles for Nutritional & Metabolic Therapies
Selenium is an essential micronutrient, and SeNPs are being studied for:
- Nutritional supplementation with improved bioavailability.
- Stress modulation in metabolic and reproductive systems.
- Support in conditions linked to oxidative damage, such as some neurological or metabolic disorders.
By tuning particle size and surface chemistry, SeNPs can deliver selenium more gently and in a controlled way, which may reduce the risk of classic selenium toxicity while supporting key biological functions.
Recent Innovations in Targeted Delivery Using Selenium Nanoparticles
Recent innovations focus on making selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies more precise, more responsive, and more personalized. Examples include:
Ligand-targeted SeNPs
Antibodies, peptides, or sugars are attached to SeNP surfaces so they can recognize tumor markers, inflamed tissues, or infected cells with higher specificity.
Stimuli-responsive SeNPs
Systems that respond to pH, redox state, enzymes, or external stimuli can release drugs only when and where needed—for example, in tumor microenvironments or inside infected macrophages.
Hybrid SeNP-polymer or SeNP-lipid platforms
Combining SeNPs with polymers, liposomes, or cell membranes creates multifunctional carriers that improve circulation time and targeting while keeping selenium's intrinsic biological activity.
Immunomodulatory SeNPs
Some designs focus on modulating immune responses, for example, by polarising macrophages or targeting inflammatory pathways, which may be beneficial in cancer, chronic infections, or autoimmune conditions.
These innovations align well with the broader movement toward precision medicine and modular targeted delivery platforms, such as those offered by Creative Biolabs' Module Delivery Systems.
How Selenium Nanoparticles Are Made
How we make selenium nanoparticles strongly affects their size, shape, surface properties, and drug loading capacity. In turn, these factors decide how well selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies perform in real biological systems.
The three main approaches are:
1. Chemical reduction methods
- Use chemical reducing agents (such as ascorbic acid or sodium borohydride) to convert selenium salts into nanoparticles.
- Easy to scale and reproducible.
However, residual chemicals must be removed carefully to make the final product safe for drug delivery.
2. Green (plant-based) synthesis
- Uses plant extracts rich in polyphenols and other natural reducers.
- Often produces SeNPs with biocompatible surface coatings built in, which can improve stability and reduce toxicity.
Considered more sustainable and attractive for nutraceutical or food-related delivery systems.
3. Microbial and biological synthesis
- Uses bacteria, fungi, or yeast to reduce selenium salts and form nanoparticles.
- Biological components on the surface can support cell interaction and immune modulation, but process control can be more complex.
Quick rule of thumb:
- Chemical routes are great for tight size control.
- Green and microbial methods are attractive when you want eco-friendly and bio-inspired selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies.
Safety, Toxicity, and Regulatory Considerations
Safety is at the center of every selenium nanoparticle delivery strategy.
Important points to consider are:
Dose matters
Selenium has a narrow margin between deficiency and toxicity. Nanoparticle formulations should be designed to stay within safe systemic levels while reaching therapeutic effects.
Size and surface charge
Particle size, charge, and coating affect how selenium nanoparticles interact with blood proteins, cells, and organs. These parameters influence biodistribution, clearance, and immune response.
Degradation and metabolism
SeNPs may be transformed into other selenium species in the body. Understanding these pathways is key to predicting long-term outcomes.
Regulatory pathway
Because SeNPs combine nanotechnology and trace element biology, regulators will expect strong data on:
- Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution
- Acute and chronic toxicity
- Immunotoxicity and genotoxicity
Overall, current research shows that well-designed SeNPs can be safe at therapeutic concentrations, but robust preclinical and clinical data will be needed for each specific product.
Looking to develop selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) with tailored synthesis, safety, and regulatory compliance?
Share your preferred synthesis route (chemical, green, or microbial), payload type, target size/shape, and safety requirements with our SeNP Formulation Experts. We will deliver a customized solution—including optimized process parameters, surface functionalization for stability, toxicity profiling, and regulatory-aligned data generation—to turn your SeNP delivery strategy into a viable product.
Related Services You May Be Interested in
FAQs
Are selenium nanoparticles safe for human use?
When properly designed and dosed, selenium nanoparticles can be safe and show good biocompatibility. However, because selenium can be toxic at high levels, each formulation must be carefully evaluated in preclinical and clinical studies.
What is the ideal size range for selenium nanoparticles in drug delivery?
Many studies use selenium nanoparticles in the 50-200 nm range, which balances stability, circulation time, and tumor accumulation. The optimal size depends on the route of administration and the target tissue.
Can selenium nanoparticles be used for oral drug delivery?
Yes, oral selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies are being explored for nutritional supplementation and gut-related therapies. Stability in gastrointestinal fluids and controlled absorption are major design goals.
How do selenium nanoparticles help in cancer treatment?
They can carry chemotherapy or gene therapy agents to tumors, protect drugs in the bloodstream, and sometimes directly induce stress in cancer cells. Together, these effects can improve tumor killing and reduce systemic toxicity.
Are selenium nanoparticles only useful in cancer research?
No. SeNPs are also promising in antimicrobial therapy, antiviral strategies, metabolic regulation, and reproductive health, thanks to their antioxidant and immunomodulatory properties.
How do selenium nanoparticles compare to traditional selenium supplements?
Conventional supplements often use inorganic or organic selenium salts. Selenium nanoparticles can offer better stability, slower release, and targeted delivery, which may improve efficacy and reduce side effects, but they are still under evaluation.
What preclinical tests are needed before using SeNPs in humans?
Typical studies include in vitro cytotoxicity, pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, dose-escalation toxicity in animals, and immune response profiling. These tests build the safety and efficacy package required for regulatory submission.
Conclusion: Why Selenium Nanoparticles Are Becoming a Preferred Delivery Platform
Selenium nanoparticles offer an appealing blend of biological activity and engineering flexibility. They can:
- Carry and protect sensitive drugs and nutrients.
- Target diseased cells or tissues more efficiently.
- Reduce systemic toxicity compared with some traditional metal nanoparticles.
- Support innovative, stimuli-responsive, and immune-modulating delivery strategies.
As the global market grows and regulatory understanding improves, selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies are moving from concept toward practical implementation in oncology, infectious disease, nutrition, and beyond.
How Creative Biolabs Supports Selenium-Nanoparticle Delivery Research
At Creative Biolabs, we understand that selenium nanoparticle delivery strategies are not just about materials. They are about designing complete, integrated systems that work from discovery to preclinical validation.
Through our Targeted Delivery platform and specialized Module Delivery Systems, we can help you:
1. Design and optimize selenium-based nanocarriers
- Core composition, size, and surface charge
- Ligand and antibody conjugation for active targeting
2. Develop hybrid SeNP systems
- Polymer- or lipid-coated SeNPs for improved stability and circulation
- Co-delivery of multiple cargos (small molecules, nucleic acids, peptides)
3. Characterize and evaluate performance
- Physicochemical analysis (size, zeta potential, loading efficiency)
- In vitro release, cellular uptake, and cytotoxicity assays
- Mechanistic studies in disease-relevant models
4. Integrate SeNPs into broader nanoparticle strategies
- Comparison with other carriers (liposomes, polymeric nanoparticles, inorganic systems)
- Tailored modules that plug into your existing pipeline
For Research Use Only. Not for Clinical Use.
References
- Geng, L., Li, L., Sun, X., Cheng, S. & He, J. "Recent Advances Towards Selenium Nanoparticles: Synthetic Methods, Functional Mechanisms, and Biological Applications." Foods 14, 3640 (2025). https://www.mdpi.com/2304-8158/14/21/3640. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Xia, Y. et al. "Galactose-modified selenium nanoparticles for targeted delivery of doxorubicin to hepatocellular carcinoma." Drug Delivery 26, 1–11 (2019). https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10717544.2018.1556359.



