Intraventricular administration of clodronate liposomes is a specialized medical procedure that holds great potential in the field of neuroscience. By delivering these liposomes directly into the brain's ventricles, scientists and researchers hope to achieve targeted and efficient elimination of specific cell populations, leading to advancements in our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases, immune responses within the brain, and the development of new therapeutic strategies.
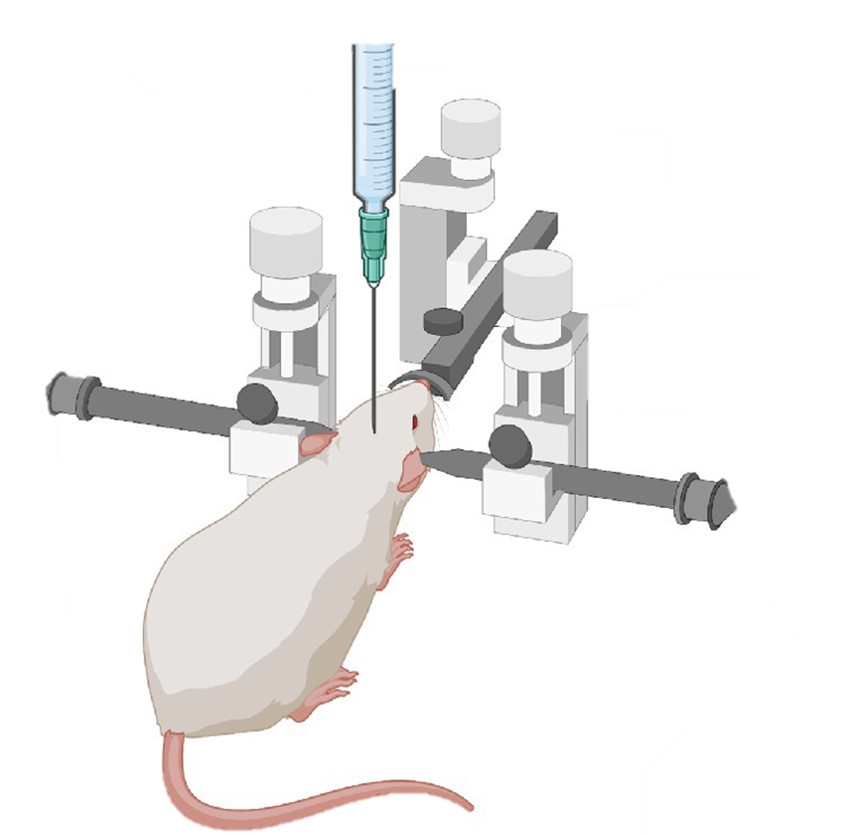 Fig.1 Stereotaxic injection into the rodent brain.1,2
Fig.1 Stereotaxic injection into the rodent brain.1,2
The power behind the intraventricular administration of clodronate liposomes resides in their unique ability to traverse the selective blood-brain barrier (BBB). The BBB serves as a safeguard, controlling the entry of a vast array of molecules from the bloodstream into the brain. Nevertheless, clodronate liposomes are engineered to be minuscule enough to successfully navigate through this barrier, enabling them to deliver their payload directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the brain's ventricles. Upon introduction, these clodronate liposomes are embraced by the central nervous system's immune cells, known as microglial cells. Once nestled within these microglial cells, the liposomes release their clodronate, initiating a transformative effect that inhibits these cells. This mechanism selectively diminishes the population of microglial cells within the brain, granting scientists a unique window to explore the multifaceted role of these cells in various neurological conditions and diseases.
In neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease, chronic neuroinflammation plays a crucial role in disease progression. By depleting microglia, clodronate liposomes can dampen the inflammatory response, potentially slowing down neuronal degeneration and disease progression.
In traumatic brain injury (TBI), the initial brain trauma triggers a cascade of inflammatory responses that can lead to secondary brain damage. Intraventricular administration of clodronate liposomes has been shown to reduce neuroinflammation and improve neurological outcomes in animal models of TBI.
Autoimmune encephalomyelitis, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), involves an aberrant immune response against the central nervous system. By targeting and depleting microglia, clodronate liposomes can modulate the immune response, potentially reducing disease severity and progression.
In brain tumors, microglia play a complex role. While they have been shown to exhibit both growth-promoting and anti-tumor properties, recent studies suggest that depleting microglia with clodronate liposomes can enhance anti-tumor immune responses and improve therapeutic outcomes.
One significant advantage of using intraventricular administration in delivering clodronate liposomes is its ability to bypass the blood-brain barrier (BBB). The BBB is a highly selective barrier that restricts the entry of many drugs into the brain, making it challenging to deliver therapeutics to the CNS. By directly administering clodronate liposomes into the ventricular system of the brain, the liposomes can readily access the CNS and target microglia. This allows for a more effective treatment approach in neuroinflammatory conditions where microglia activation plays a central role.
In addition to its targeted therapeutic effects, the intraventricular administration of clodronate liposomes offers an advantage in terms of safety. By directly targeting microglia in the CNS, systemic exposure and off-target effects are minimized. This localized approach reduces the risk of unwanted side effects, making it an attractive option for treating neurological conditions.
The selective depletion of microglia using clodronate liposomes has also shown potential in promoting tissue repair and regeneration in the CNS. By dampening neuroinflammation, the surrounding neural tissue has an improved environment for recovery and healing.
The intraventricular administration of clodronate liposomes holds great promise in advancing our understanding of neurodegenerative diseases, immune responses in the brain, and potential therapeutic avenues. The targeted depletion of macrophages and microglia through this technique allows for precise investigations into the broader implications of these immune cells, paving the way for new insights and innovative treatments in neuroscience and medicine.
Creative Biolabs has been dedicated to lipid-based drug delivery system research for over a decade of years. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry