Used as a delivery system, the internal compartment cores of vesosomes contain the drug and may vary in composition from one another. Vesosomes are easy to produce and can deliver multiple cargoes within a single carrier. As an industry leader in the field of vesicular system development, Creative Biolabs is committed to providing the most comprehensive drug delivery services for our global clients. Creative Biolabs has accumulated abundant experience in the successful completion of many lipid-based drug delivery projects. Here, we provide vesosomes development services and commercial products with the best quality and the most competitive prices to suit the exact requirements of our clients.
Vesosomes, also referred to as nested vesicles or vesicles-in-vesicles, are multicompartment structures which has distinct inner compartments separated from the external membrane. Vesosomes can take different forms, including multi-layered membrane structures that adopt an onion-like arrangement and several vesicles that are encased in a larger vesicle.
Vesosomes are formed by adding ethanol to a variety of saturated phospholipids. At temperatures below the gel-liquid crystalline transition, Tm, the interdigitated lipid-ethanol sheets are rigid and flat; when the temperature is raised above Tm, the sheets become flexible and close on themselves and the surrounding solution to form closed compartments. During this closure, the sheets can entrap other vesicles, biological macromolecules, or colloidal particles, leading to efficient and spontaneous encapsulation without disruption of even fragile materials to form biomimetic nano-environments for possible use in drug delivery, colloidal stabilization, or as microreactors.
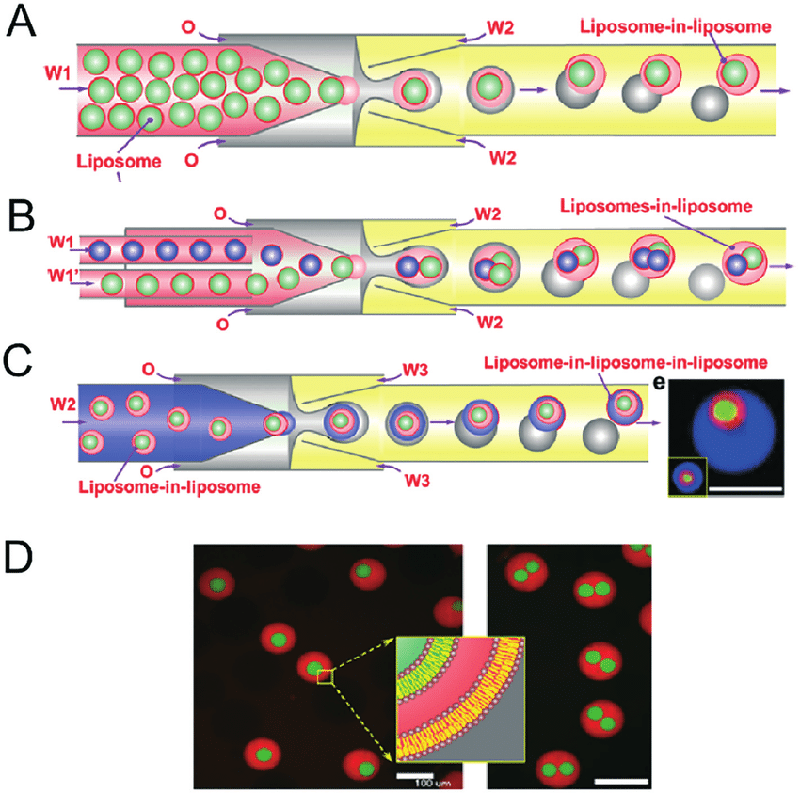 Fig.1 Microfluidic construction of vesosomes using double emulsions.1,2
Fig.1 Microfluidic construction of vesosomes using double emulsions.1,2
The vesosome structure can take full advantage of the 40 years of progress in liposome development and has been widely used in many areas these years. For instance, since each compartment of vesosome can encapsulate different materials and have different bilayer composition, vesosome could entrap both colloidal particles and biological macromolecules efficiently. Vesosomes bear an organisational similarity to multiorganelle eukaryotic cells. Building on this analogy, vesosomes containing a nucleus-like inner compartment were constructed, which contained the components necessary for in vitro transcription of RNA from a DNA template.
Aided by our well-established platforms and experienced scientists, we can provide comprehensive vesosomes services, varying from lipid-based drug delivery characterization, delivery system construction services to in vitro efficacy validation, in vivo PK/PD validation. A wide spectrum of customized delivery products is available for your choice.
Vesosomes are large lipid bilayer enclosing many smaller liposomes, serving as a support for the customization of separate environments for multiple therapeutics and release. If you are interested in the vesosomes services that we provide for drug delivery, please get in touch with us. Creative Biolabs also provides other lipid-based drug formulation. For more details and information, please feel free to contact us.
References
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry