Cardiolipin is an acidic lipoprotein which is abundant in the inner mitochondrial membrane and is required for normal respiratory chain enzyme activity. It is the only known dimeric phospholipid, and its unique structure plays a major role in maintaining the function of membrane-associated proteins in the mitochondria. Creative Biolabs is a leading service provider that focuses on all kinds of liposome development services. Our strong expertise in delivery system design allows us to help clients tackle challenges and accelerate the design and development of drug delivery.
Cardiolipin (CL) is an evolutionarily conserved phospholipid which exists almost exclusively in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) of mammalian cells and plasma membranes of bacteria. This phospholipid plays an important role in mitochondrial bioenergetics by affecting the activity of key proteins of IMM. The structure of CL is characterized by a glycerol backbone connected to two phosphatidyl lipids. Two chiral carbons and four fatty acyl chains in CL result in a flexible body allowing interactions with respiratory chain complexes and mitochondrial substrate carriers. The biosynthesis of CL is a little more complex than that of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) and phosphatidylserine (PS), and it involves two pathways: de novo synthesis and remodeling steps.
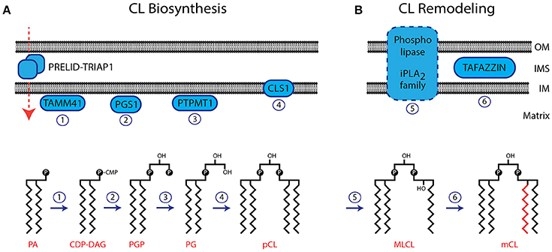 Fig.1 Biosynthesis and remodeling of CL.1,2
Fig.1 Biosynthesis and remodeling of CL.1,2
The use of liposomes to assist drug delivery has had a major impact in many biomedical fields. They have been shown to be beneficial for stabilizing therapeutic compounds, overcoming barriers to cellular and tissue uptake, and improving the biodistribution of compounds to target sites in vivo. Liposomes are defined as phospholipid vesicles composed of one or more concentric lipid bilayers surrounding a discrete aqueous space. The unique ability of the liposome system to capture lipophilic and hydrophilic compounds enables these vesicles to encapsulate multiple drugs. Liposomes containing CL, reportedly reduced cardiotoxicity associated with doxorubicin by altering the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of the drug and hence cardiolipin may also exert similar results in LEP-ETU. LEP-ETU is the potential liposomal formulations of paclitaxel which is an anti-cancer chemotherapy drug. LEP-ETU formulations composed of DOPC, cholesterol and cardiolipin in 90:5:5 molar ratio were prepared by the modified thin-film hydration method. Higher doses of LEP-ET can be safely administered compared to paclitaxel alone. Moreover, in cardiotoxicity, positively charged doxorubicin's affinity for negatively charged CL is thought to be involved in drug localization in the heart tissue. Therefore, the use of CL in liposome formation can effectively reduce cytotoxicity.
Drug delivery systems (DDS) can be designed to increase the bioavailability of the drug, control drug delivery and maintain complete delivery of the drug to the site of action while avoiding the non-diseased host tissues. In short, using a minimum dose to achieve optimal therapeutic effect in a suitable dosage and mode of administration is the research goal of DDS. As main components of cellular membrane, phospholipids have excellent biocompatibility. CL, as a phospholipid, has important applications in the composition of drug delivery systems. In addition to liposomes composed of CL, Creative Biolabs offers other customized formulations based on our lipid-based drug delivery (LDD) platform. Please contact us for more information.
References
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry