Creative Biolabs has extensive experience in lipid-based drug delivery system production and can provide a full range of custom lipid-based anti-infective drug delivery formulations and services with the highest quality and most competitive price for global clients.
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases or transmissible diseases, are a group of disorders caused by the invasion of infectious microorganisms or produced toxins, including bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. Infectious diseases are one of the leading threats of life-health all over the world as it is difficult to control when the pathogens evolve resistance to drugs. Generally, human hosts can initiate immune responses, mainly involving inflammations followed by an adaptive response, to fight against infections. Specific medications should be used to treat infections when immune responses are not enough.
Infectious diseases can be treated with anti-infective drugs, and the corresponding antibacterial drugs include antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, depending on the type and severity of the infection. However, there are many challenges for these antimicrobial agents, such as poor bioavailability, lack of penetration, severe side effects and non-specificity, and the most significant limitation is drug resistance.
To overcome these challenges, many pharmaceutical scientists introduced and confirmed a novel drug delivery system to increase the effective delivery and therapies of these anti-infective drugs, namely is lipid-based drug delivery systems, including liposomes, lipid nanoparticles, niosomes, ethosomes, transferosomes, etc. There are several antibacterial drugs that have been successfully formulated based on novel lipid-based carriers, among which antibiotics encapsulation into liposomes is the most extensively researched due to their noted advantages, which include but are not limited to:
Anti-infective drug encapsulation to a lipid-based drug carrier also shares some characteristics with others, such as targeted release, better stability and bioavailability, reduced toxicity and side-effects.
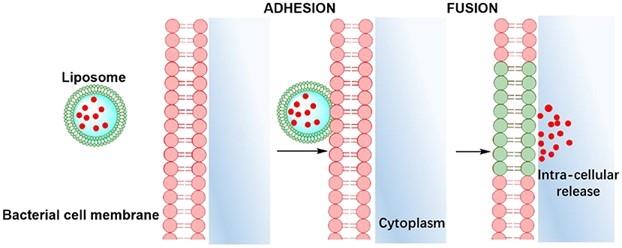 Fig.1 Similarity-mediated fusion of liposomes into bacterial cell membranes and release of antimicrobial cargo into a bacterium.1,2
Fig.1 Similarity-mediated fusion of liposomes into bacterial cell membranes and release of antimicrobial cargo into a bacterium.1,2
Based on first-in-class technology and experienced expert staff, Creative Biolabs has developed extensively novel lipid-based drug delivery platforms to offer one-stop services, including but not limited to:
If you are interested, please contact us, and we can customize our offering to meet your specific project needs.
References
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseApplications
Online Inquiry