Cholesterol is a membrane constituent widely found in biological systems and serves uniquely in modulating membrane fluidity, elasticity, and permeability. Creative Biolabs develops and commercializes a full range of drug delivery services, which are based on its liposome development platform. The company’s seasoned scientists are pleased to meet each of the most specific requirements and provide a comprehensive knowledge of its LDD system.
Cholesterol is an indispensible structural building block for cell membranes, responsible for membrane fluidity and permeability, intracellular transport, signal transduction and cell trafficking. It is a white and waxy substance, an essential type of fat called lipoproteins carried in the blood stream of particles. Cholesterol plays an essential role in the maintenance of the integrity of biologic membranes and serves as a precursor in the synthesis of many endocrine mediators. It is also synthesized in mammalian cells via the mevalonate pathway. It has demonstrated a possible linkage of cholesterol to some diseases, such as prostatic cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia, coronary heart disease, and cerebral thrombosis. Cholesterol has many biological functions. Depending on the cell types, the cholesterol content of cell membranes varies. The membranes of most cells have an intermediate cholesterol/phospholipid ratio and possess both protective and metabolite-transport functions.
Among various hydrophobic moieties, cholesterol has gained considerable interest in recent years to improve the hydrophobicity of drug delivery systems. As is well-known, cholesterol plays a strategic role in liposome composition. It is a very important variant in the liposomal structure that could control the stoutness for drug delivery. Moreover, conjugation of cholesterol moiety to active compounds for either cancer treatment or diagnosis is a suitable delivery system for poorly soluble chemotherapeutic drugs. This approach is widely used in the delivery of the anticancer agents to tumor tissues selectively. For example, it is demonstrated that the cholesterol conjugated poly(D,L-Lactide) (PLA)-based polymeric micelles (mPEG-PLA-Ch) for improved delivery of curcumin in cancer can improve the hydrophobicity of the core in mPEG-PLA micelles. In this case, conjugation of the cholesterol moiety to active medicinal compounds for either cancer disease diagnosis or treatment is an attractive approach for targeted drug delivery. There are many additional areas in which this targeting tactic could be applied to improve the chemotherapeutic efficacy and to reduce the toxicity to normal cells. Utilization of cholesteryl drug conjugates for targeted delivery provides a novel approach to enhance the therapeutic efficacy and better the medical treatment of various human diseases.
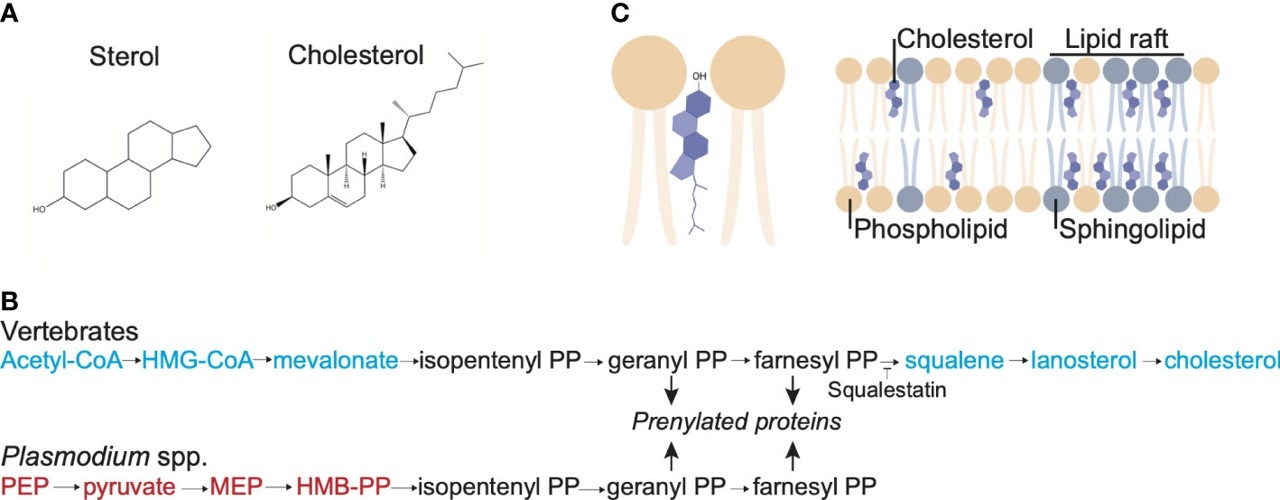 Fig.1 Cholesterol structure, membrane localization and synthesis pathway.1,2
Fig.1 Cholesterol structure, membrane localization and synthesis pathway.1,2
Due to the hydrophobicity and excellent biocompatibility, cholesterol has been extensively used to improve the hydrophobicity, biocompatibility and biodegradability of drug delivery system without using slow-degrading polymers of high molecular weights. Creative Biolabs is able to offer the most comprehensive services and products based on its LDD platform, which including but not limited to emulsions, vesicular system, lipid particulate system, and lipid-core micelles. If you want more types of formulations, please feel free to contact us for a detailed quote.
References
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry