At Creative Biolabs, we leverage decades of expertise in lipid-based drug delivery (LDD) systems to advance the frontiers of pharmaceutical research. Our comprehensive understanding of emulsion systems enables us to optimize drug formulation and enhance bioavailability through cutting-edge technologies and methodologies.
Emulsions are mixtures of two immiscible liquids, typically oil and water, with one dispersed in the other as tiny droplets. These systems, essential in many pharmaceutical and biomedical applications, exist in forms such as oil-in-water (O/W) or water-in-oil (W/O), determined by which liquid is the continuous phase. Due to their versatility, emulsions are ideal for encapsulating both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs, helping to improve drug solubility, stability, and bioavailability.
Emulsions serve as versatile carriers that can accommodate both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs, providing a significant advantage for compounds with poor solubility. Their diverse structures allow for multiple applications in drug delivery, from oral to intravenous routes, making them ideal for enhancing drug bioavailability and stability.
Emulsions are characterized by unique optical and stability properties. The dispersion of droplets within the continuous phase results in light scattering, often giving emulsions a cloudy or milky appearance. Microemulsions and nanoemulsions, with droplet sizes below 100 nm, often appear translucent due to the reduced scattering of light. The Tyndall effect and particle size are influential in the physical stability of emulsions. Particle size, viscosity, and the choice of stabilizers, such as surfactants or solid particles, dictate the emulsion's overall stability and resistance to destabilizing forces.
To form stable emulsions, it is critical to understand the mechanisms of stabilization:
The stability of an emulsion is essential for its effectiveness in drug delivery, as stability impacts drug release, bioavailability, and shelf life.
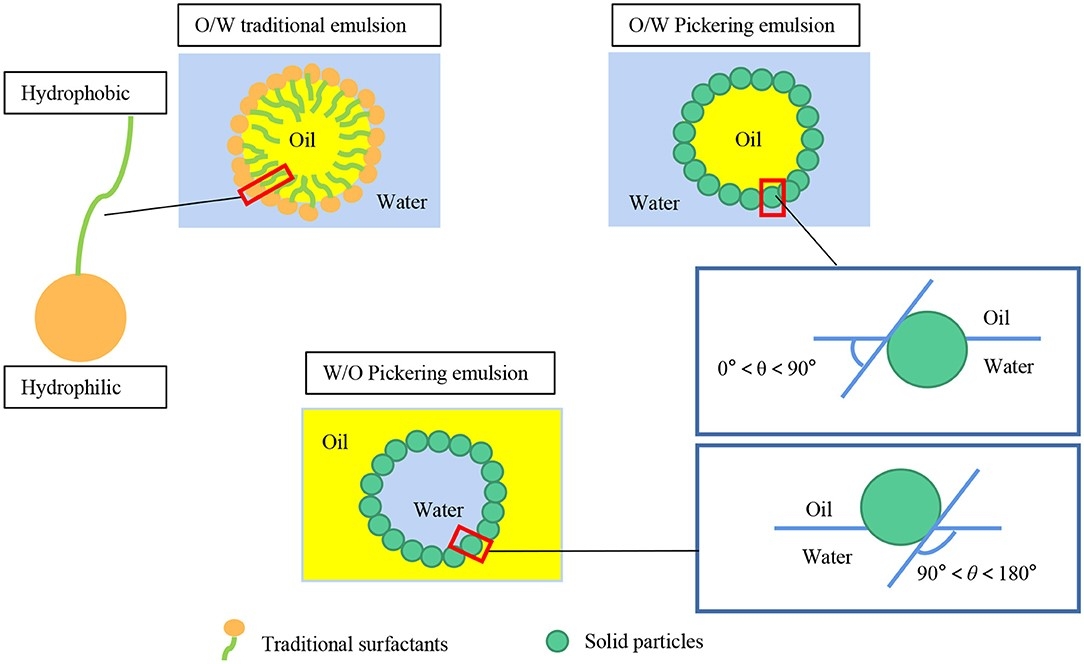 Fig.1 Sketch of traditional emulsions and pickering emulsions.1
Fig.1 Sketch of traditional emulsions and pickering emulsions.1
Creative Biolabs provides comprehensive emulsion formulation and production services, including custom-designed emulsion systems that address specific drug delivery needs. Leveraging decades of expertise, we offer a full suite of services to optimize emulsion stability, bioavailability, and release profiles.
Our laboratories employ state-of-the-art technologies and techniques to ensure the highest quality in emulsion formulation. By integrating traditional and modern engineering methods, Creative Biolabs delivers innovative solutions that align with industry standards and client requirements.
We offer a range of customizable solutions tailored to meet the unique needs of each project, including bioavailability enhancement, sustained release options, and targeted delivery systems. Our experienced team collaborates closely with clients to design formulations that optimize efficacy and stability. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
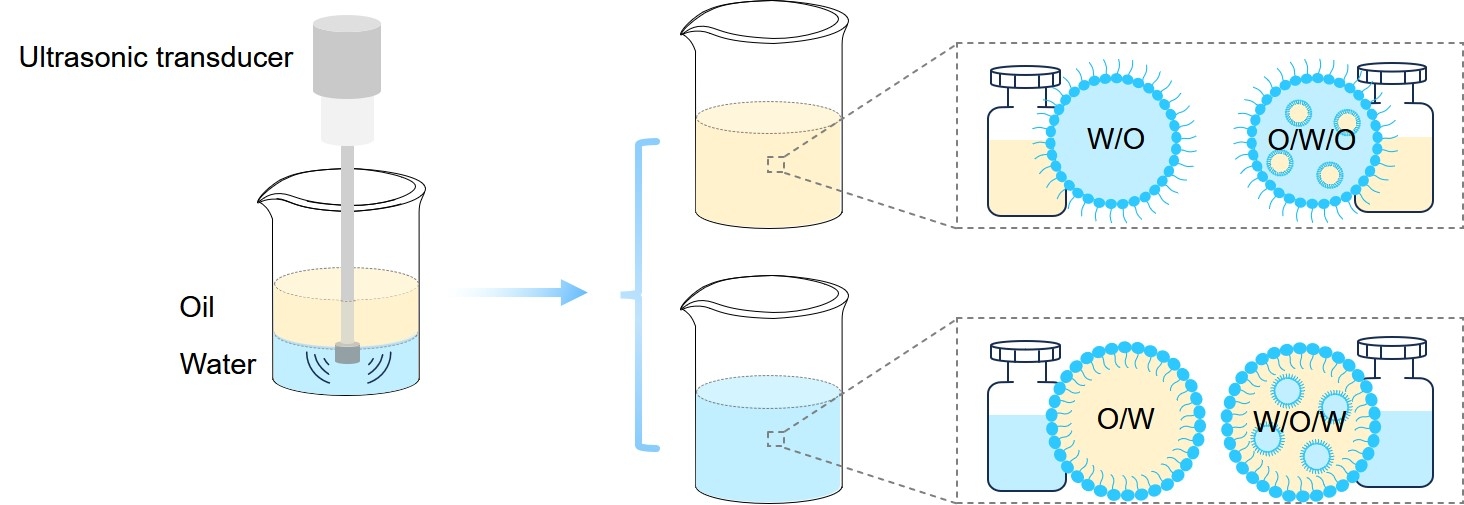 Fig.2 Diagrammatic representations of emulsion system.
Fig.2 Diagrammatic representations of emulsion system.
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Oral Drug Delivery | Emulsions enhance the solubility and bioavailability of hydrophobic drugs, facilitating more efficient absorption in the GI tract, particularly beneficial for drugs with low intrinsic bioavailability. |
| Topical Formulations | Used in creams, lotions, and ointments, emulsions allow for the incorporation of both lipophilic and hydrophilic drugs, enabling enhanced skin penetration and promoting the permeation of active ingredients in dermatological products. |
| Parenteral Drug Delivery | Lipid-based emulsions aid in intravenous and intramuscular drug administration, reducing injection site irritation and enhancing stability for lipophilic drugs, with applications such as propofol and parenteral nutrition solutions. |
| Ocular and Nasal Delivery | Emulsions formulated for eye drops and nasal sprays improve drug retention and facilitate permeation through mucosal barriers, allowing for sustained release in localized delivery. |
| Vaccine Adjuvants | Emulsions serve as effective vaccine adjuvants, boosting immune response by enhancing antigen uptake and providing controlled release, strengthening the immune response against specific antigens. |
| Cosmeceutical Use | Emulsions in cosmeceuticals enhance skin penetration of active ingredients such as vitamins and antioxidants, providing a stable vehicle for compounds that improve skin health and appearance. |
At Creative Biolabs, a wide spectrum of LDD formulation services is available for your choice. Aided by our well-established platforms and experienced scientists, we can tailor a one-stop solution to meet your needs with the best quality and most competitive price.
Reference
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry