Liposomes are effective carriers for drug delivery, including small and large molecules (proteins, peptides, and DNA). Generally, we can classify liposomes based on the preparation method, the number, and size of vesicle bilayers, etc.
According to the size and number of bilayer membranes (lamellarity) forming vesicles, liposomes can be divided into the following categories:
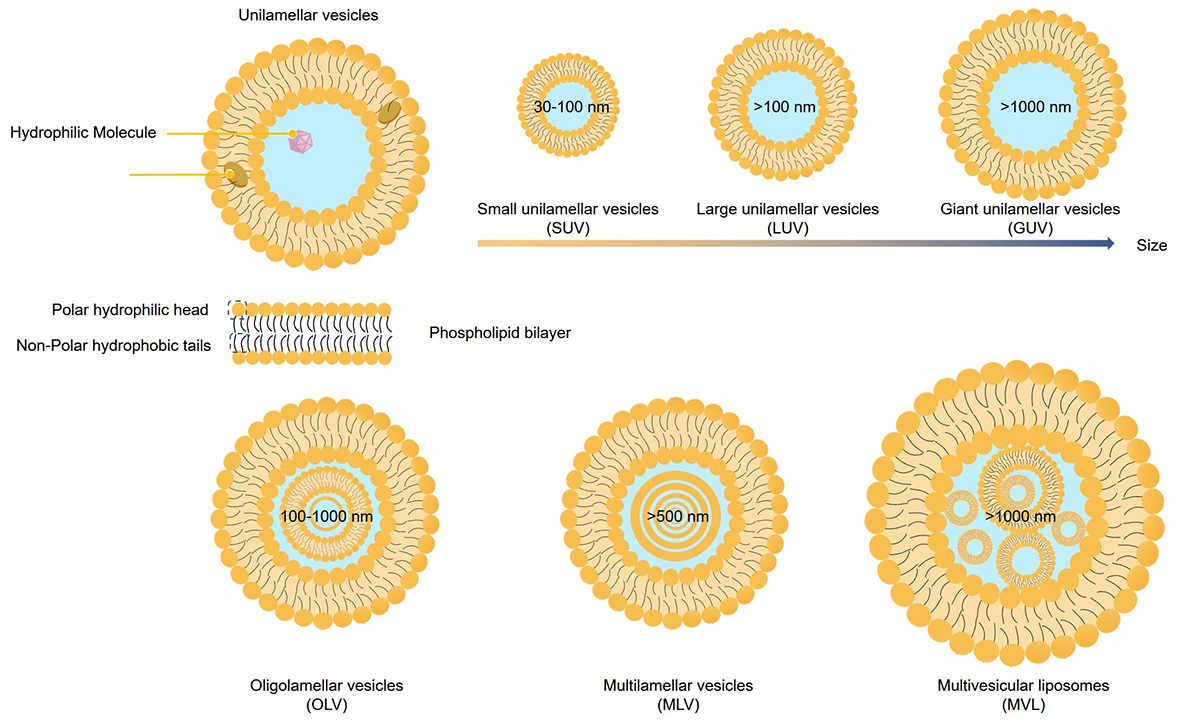 Fig.1 Schematic representation of different sizes and lamellar structures of liposomes.
Fig.1 Schematic representation of different sizes and lamellar structures of liposomes.
Liposomes can be divided into several different types according to their composition and application, including:
Conventional liposomes are the first generation of liposomes. They are lipid bilayer molecules surrounding the aqueous chamber and are the basis of all subsequent liposomes.
Immunoliposomes are vesicles specially designed for active targeting of the drug substances inside the body.
The surface modification or PEG modification of liposomes is called PEGylation of liposomes, and the modified liposomes are called long circulating liposomes or stealth liposomes. Compared with conventional liposomes, PEG liposomes can avoid phagocytosis and circulate for a long time in systemic circulation.
Cationic liposomes can be prepared by adding cationic phospholipid into bilayer membrane. This allows high rates of DNA incorporation, and for this reason, such liposomes may be more suitable for gene and antisense therapy.
Liposomes can be easily functionalized through the introduction of functional materials, such as stimulus-response materials. Their structure, configuration, and other properties can be changed under certain in vivo or in vitro stimulation, such as the change of heat, light, and pH value.
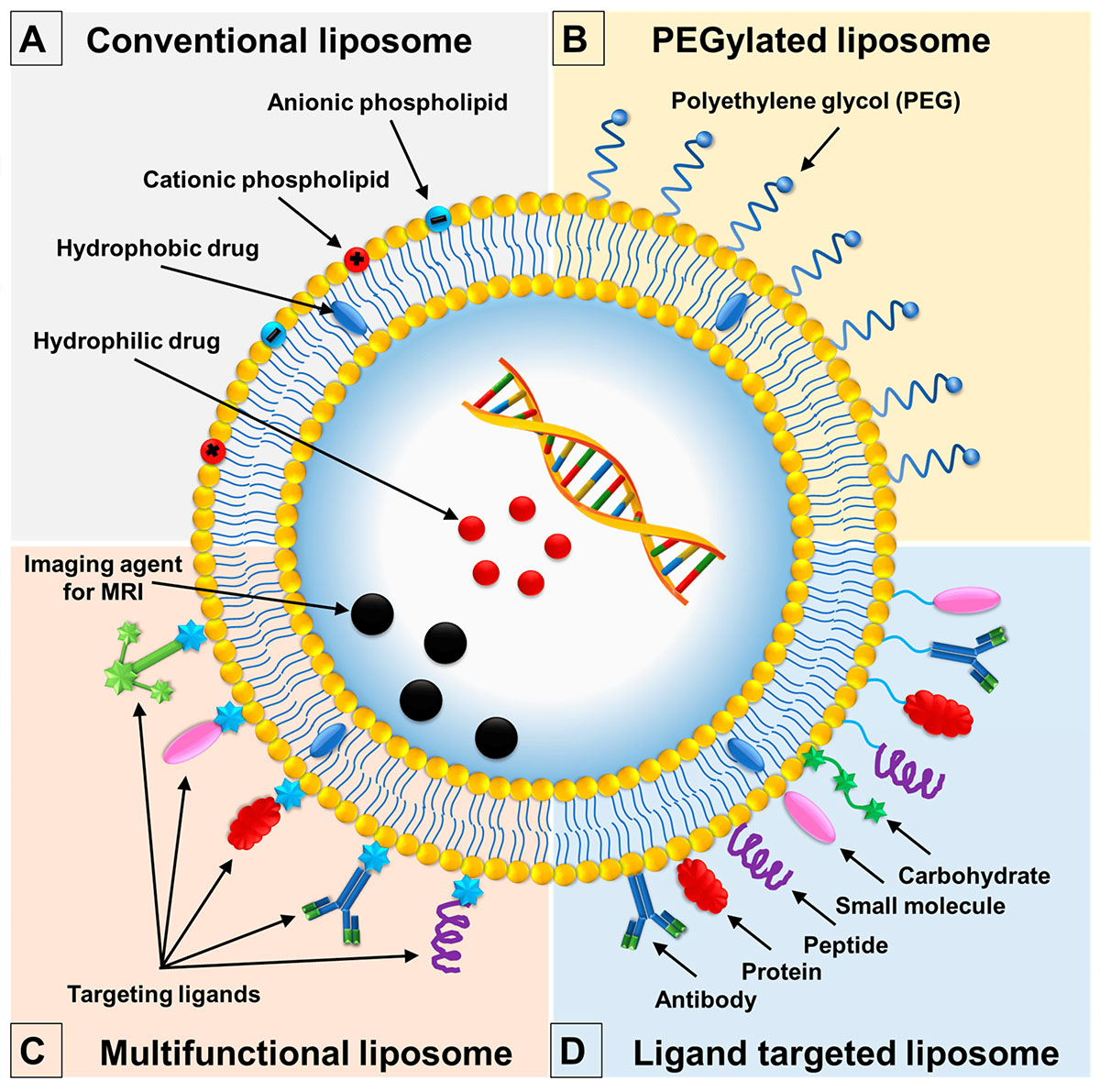 Fig.2 Classification of liposomes based on composition and application.1,2
Fig.2 Classification of liposomes based on composition and application.1,2
In addition to the above two classification methods, liposomes will also be classified according to their preparation methods. This classification depends on using the organic solvents, obtaining different lamellarity of liposomes, changing the size and applications of liposomes.
REV SUVs/OLVs/MLVs: made by reverse-phase evaporation method
SPLV: stable plurilamellar vesicle
DRV: made by dehydrated rehydrated method
VET: vesicles prepared by extrusion technique
FATMLVs: frozen and thawed MLVs.
As a liposome development service provider with decades of experience, Creative Biolabs provides a variety of liposomes. For more details about our services, please directly contact us.
References
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry