Phosphatidylethanolamine is one of the most abundant phospholipids in biological membranes, and due to its unique properties, it has received more and more attention in the pharmaceutical field in recent years. Thus, Creative Biolabs is committed to continuously providing more and better phospholipid-based pharmaceutical preparation services for its customers around the world, assisting them in achieving their strategic goals.
Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is a phospholipid found in all living organisms. Together with phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylinositol (PI), PE represents the backbone of most biological membranes. PE is the second-most abundant phospholipid in mammalian membranes ranging from 20 to 50%. In healthy cells, PE resides predominantly in the inner leaflet of the cell membrane. In dead or dying cells, it’s externalized to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane.
In mammalian cells, the biosynthesis of PE occurs mainly through two major pathways: by the decarboxylation of PS, which takes place at the mitochondrial membrane via phosphatidylserine decarboxylase (Psd) 1, or at the Golgi and vacuolar membranes through Psd2, and by the cytosine diphosphate (CDP)-ethanolamine pathway or Kennedy pathway at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane. Besides, the cells may employ other less quantitative synthetic routes, such as acylation of lyso-PE, and PS synthase-2-catalysis, as well as the base-exchange reaction between PS and ethanolamine. The relative contributions of the different PE biosynthetic pathways have been suggested to be dependent on the cell type.
PE has a variety of physiological and biochemical functions, including but not limited to, chaperoning membrane proteins to their folded state; stimulating OXPHOS activity; attaching covalently to the autophagy protein Atg8, which initiates autophagosome formation; catalyzing the conversion of prions from the nontoxic to the toxic conformation; being an essential substrate for the synthesis of GPI-AP; being a precursor of other lipids; and it is associated with ER stress involving diabetes and neurodegeneration. More shockingly, PE with an arachidonic acyl chain is a target of lipoxygenase, which oxidizes an unsaturated acyl chain into a cytotoxic lipid hydroperoxide to facilitate ferroptosis. In addition, PE is a target of plant natural products that have potent anti-cancer activity, and the mitochondrial protein LACTB is a tumor suppressor that targets PSD for degradation.
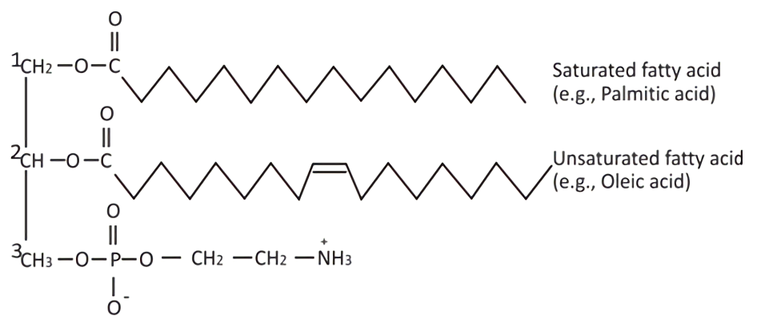 Fig 1 The Structure of the Phosphatidylethanolamine.
Fig 1 The Structure of the Phosphatidylethanolamine.
With years of experience and high-end technologies, Creative Biolabs provides our clients with products and custom services to help you get a milestone development in your drug delivery project. If you need help with this, please feel free to contact us.
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry