As one of the leading companies in lipid-based drug delivery (LDD) development, Creative Biolabs is devoted to simplifying your research processes. We are providing various kinds of high-quality lipids produced by our advanced technology platform specialized for biomedical research. All of our products are guaranteed with high purity and technical backup.
Sphingolipids are commonly believed to be a component of the plasma membrane lipid bilayer, which also play important roles in cell recognition and signal transduction. The compound is composed of a sphingoid base backbone, a fatty acid chain, and a polar headgroup. Changes in the fatty acid chains and headgroups derivates several major classes of sphingolipids include sphingosine, ceramide, sphingomyelin, and glycosphingolipid.
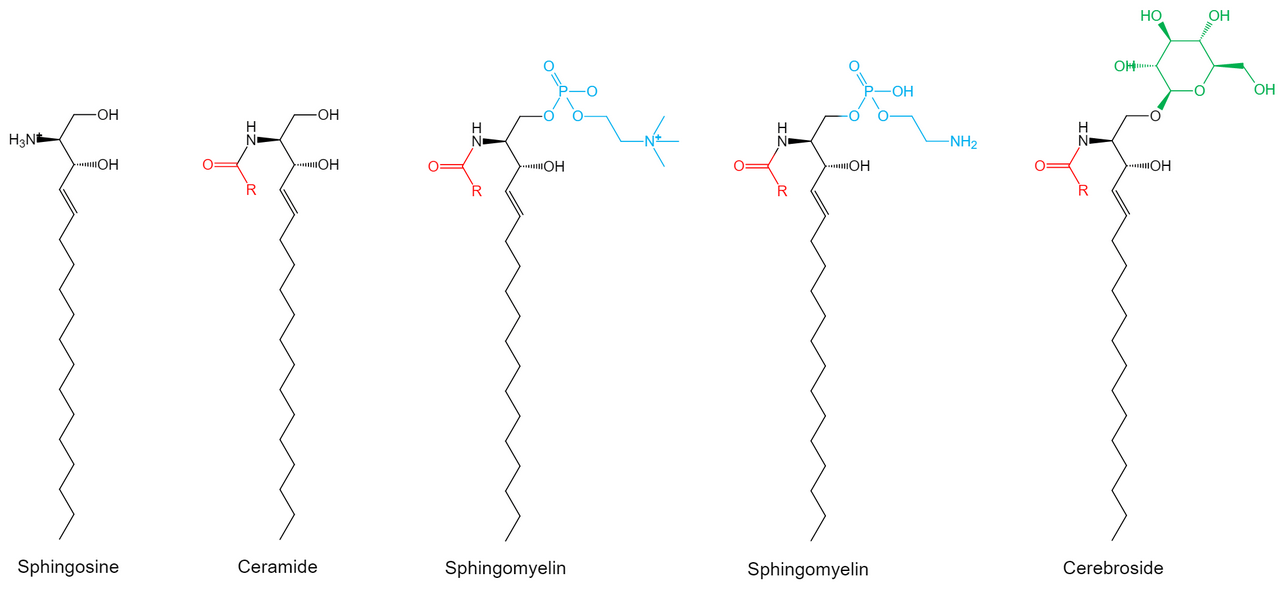 Figure 1. Structures of sphingolipids
Figure 1. Structures of sphingolipids
Sphingosine ((2S,3R,4E)-2-amino-4-octadecen-1,3-diol), is the simplest kind of sphingolipid without alkyl chain or R group and is the most abundant sphingolipid in mammals. Sphingolipids vary considerably in the alkyl chain, R group, branching, the number of double bonds, and other features. For example, ceramides consist of a fatty acid chain amide to the amino group of the backbone and a hydrogen atom R group. Ceramides are the main components of skin and are widely used in cosmetic products, which also serve as precursors of more complex sphingolipids. Sphingomyelins have a phosphocholine or phosphoethanolamine molecule linked at the 1-hydroxy group of a ceramide, while glycosphingolipids are ceramides with various sugar monomers or dimers at the 1-hydroxyl position, yielding cerebrosides and globosides, respectively.
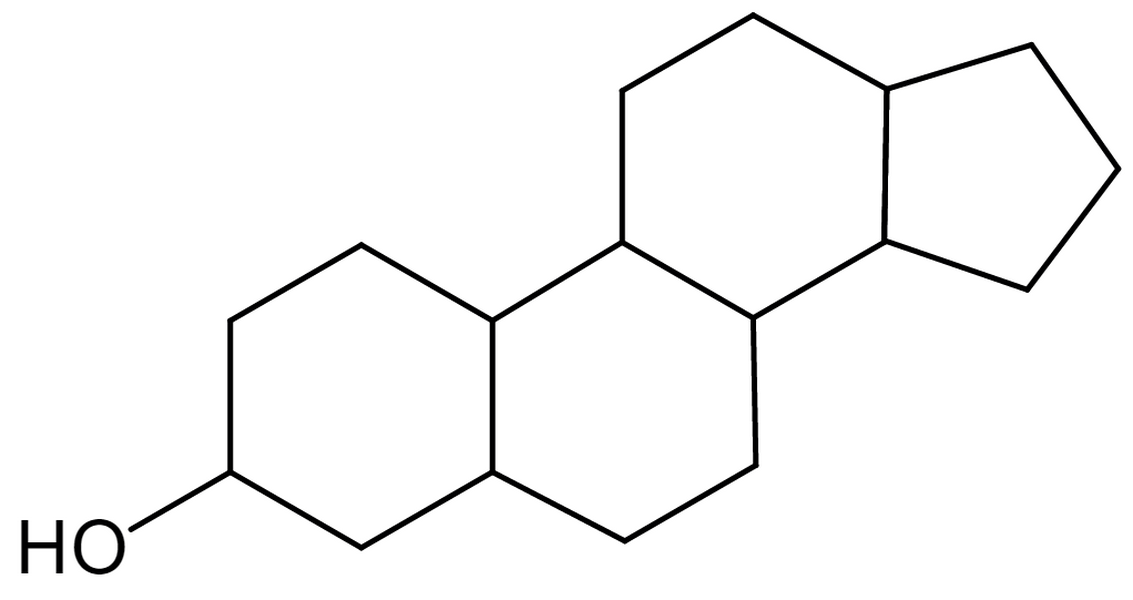 Figure 2. Molecular structure of sterols
Figure 2. Molecular structure of sterols
Sterol consists of a cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene backbone with a hydrogen atom in position 3 replaced by a hydroxyl group, which widely exists in tissues of animals and plants. Cholesterol is the most abundant sterol in animal tissues and plays a vital role in cells membrane fluidity and cellular signaling. Additionally, cholesterol also serves as a precursor of vitamin D and bile acid, both of which are important to growth and metabolism.
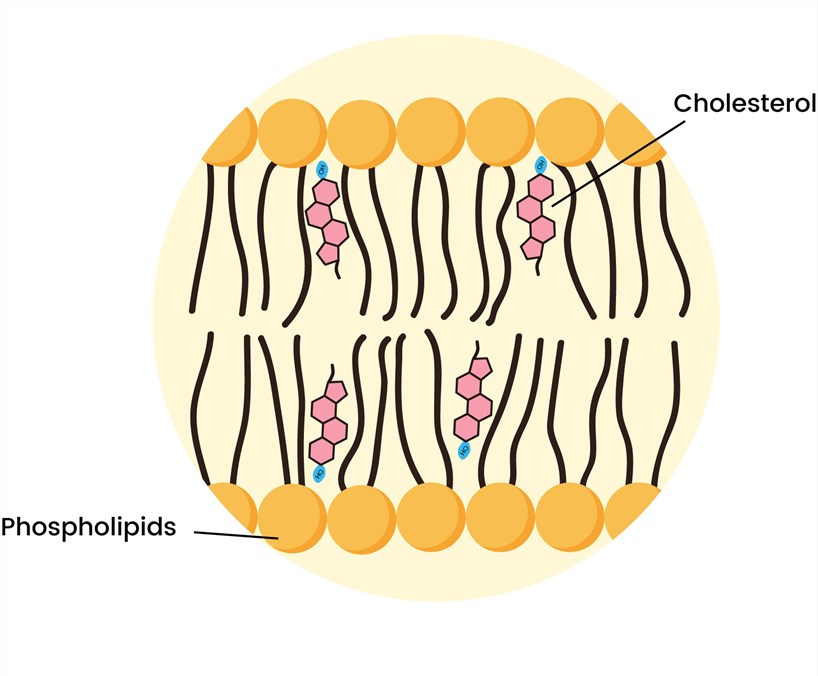 Figure 3. Cholesterol in the liposomal bilayers
Figure 3. Cholesterol in the liposomal bilayers
As is well-known, cholesterol is a strategic composition in liposome development, which controls the stoutness of liposomal structure. Studies on the use of cholesterol in liposomes showed that this steroid can fill in the gaps between other lipids, thus improving the tightness of the bilayer and preventing the vesicles from aggregation. Moreover, cholesterol can also conjugate to active compounds for cancer diagnosis or treatment due to its excellent biocompatibility.
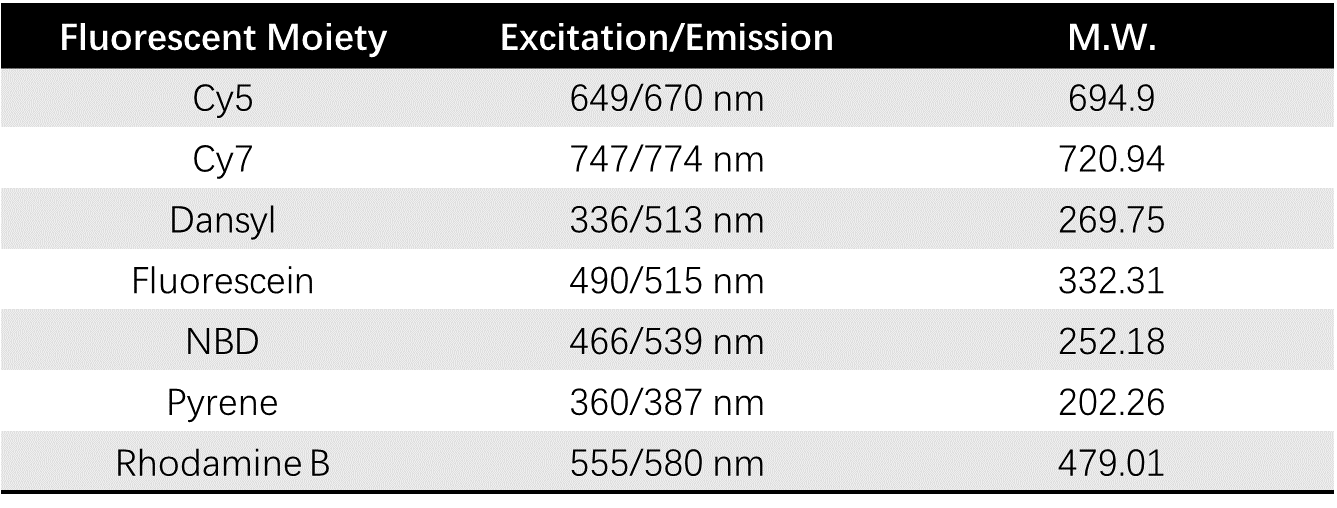
Installation of fluorescent moieties attaches lipids additional functions such as signaling and fluorescent reporting other than the natural functions. Such products are widely used in biological research and drug carrier development. Creative Biolabs offers a variety of fluorescent lipids to fulfill your needs. We provide fluorescent installation of phospholipids, sphingolipids, sterols, glycolipids, etc. Characteristics of fluorescent moieties are shown below.
Table 1 Fluorescent moieties for fluorescent lipids
Some synthetic lipids such as cationic lipids and polymerizable lipids are critical in the development of lipid-based carriers. Cationic lipids have been used as a component of nucleic acids carriers for gene therapy since the 1990s, and are still the major carriers for gene delivery. The cationic liposomes can encapsulate anionic nucleic acids through electrostatic interactions effectively and have the advantages of chemical and physical stability, biocompatibility, and wide availability over other carriers. Polymerizable lipids such as PEGylated lipids are also widely used in the development of drug carriers. PEGylation of lipids provides the carriers with a longer circulation half-life because of the escape of capture and phagocytosis by various organs. We provide these lipids of the highest quality to support your pioneering studies, and custom synthesis of other uncommon lipids is welcomed to consult.
Apart from the lipids mentioned above, Creative Biolabs is working on the development of a wider range of lipid products. Please feel free to contact us for any other kind of lipid of your interest, we provide custom service to meet your needs.
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use| Cat | Product name | CAS No. | Formula Weight | Formula | Data sheet | MSDS | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLP007 | 1,2-didecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphate (sodium salt) | 321883-64-1 | 502.554 | C₂₃H₄₄O₈PNa |
|
Inquiry | |
| CLP154 | 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (DOPE) | 4004-05-1 | 744.034 | C₄₁H₇₈NO₈P |
|
Inquiry | |
| CLP001 | ALC-0159 | 1849616-42-7 | (C₂H₄O)nC₃₁H₆₃NO₂ |
|
Inquiry | ||
| CLP002 | ALC-0315 | 2036272-55-4 | C₄₈H₉₅NO₅ |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY1 | C8 PEG2000 Ceramide | 212116-76-2 | 2522.183 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY2 | C16 PEG2000 Ceramide | 212116-78-4 | 2634.399 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY3 | C8 PEG5000 Ceramide | 212116-76-2 | 5517.787 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY4 | C16 PEG5000 Ceramide | 212116-78-4 | 5630.003 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY5 | C8 PEG750 Ceramide | 212116-76-2 | 1244.646 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY6 | C16 PEG750 Ceramide | 212116-78-4 | 1356.862 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY7 | 16:0 PEG5000 PE | 474922-84-4 | 5745.030 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY8 | 14:0 PEG5000 PE | 474922-82-2 | 5688.920 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY9 | 18:0 PEG5000 PE | 474922-77-5 | 5801.140 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY10 | 18:1 PEG5000 PE | 474922-90-2 | 5797.100 |
|
Inquiry | ||
| LDLY-0223-LY11 | 16:0 PEG3000 PE | 474922-84-4 | 3718.590 |
|
Inquiry |
Online Inquiry