Creative Biolabs is a biopharmaceutical company that holds a leadership position in the global market and focuses on improving human health through biotechnology. Our mission is to develop high-quality innovative tools and services to accelerate drug discovery.
There are six major phospholipid species in eukaryotes, each of which has unique structural and functional roles. Of them, phosphatidylinositol (PI) accounts for only about 2-10% of the total membrane lipids, but it plays a key role in the regulation of several fundamental processes, such as membrane dynamics and signal transduction pathways. The de-novo biosynthesis of PI occurs only in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and begins with the precursor glycerol-3-phosphate or dihydroxyacetonephosphate. These molecules undergo two groups of acylations by the action of an acyltransferase; the first acylation forms the lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), and the second acylation step produces the phosphatidic acid (PA).
PI consists of a glycerol backbone with an inositol ring and a phosphate at the sn-3 position and two acyl chains esterified at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. The inositol ring can be phosphorylated at multiple locations, which produces seven unique species called phosphoinositides (PIPns) (Figure 1). PIPns maintain synergistic effects of PI-kinase and phosphatase in different subcellular compartments in space and time. PIPns species control several different cellular processes, such as regulation of ion channels, actin-cytoskeletal dynamics, vesicle transport, endocytosis, exocytosis, and signal transduction pathways.
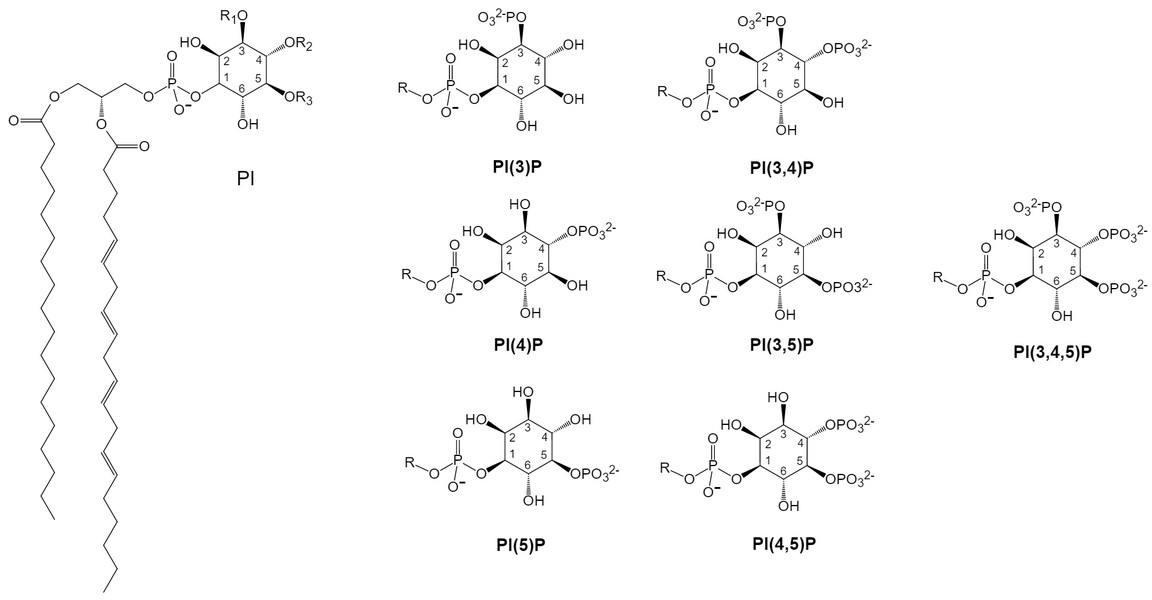 Fig.1 Structures of different phosphatidylinositol polyphosphates.
Fig.1 Structures of different phosphatidylinositol polyphosphates.
The biological importance of phosphoinositides lies in their use as universal signal molecules in eukaryotic cells. These lipids are not only precursors to other soluble and lipid second messengers, but phosphoinositides together form the chemical basis for important and diverse signal coding. Their inherent signal properties come in several forms. For example, phosphoinositide facilitates the assembly of chemically distinct platforms on the membrane surface that allow for spatial and temporal regulation of protein activity recruited from the cytoplasm. In addition, phosphoinositide also serves as key allosteric regulators of many enzymes (such as GTPase and phospholipase D) and ion channels.
As a leading source provider in the field of biological research and drug discovery, Creative Biolabs is committed to ensuring that every process is focused on delivering the highest level of service and satisfaction, and we are proud to exceed industry standards with our timely and helpful responses to customer inquiries. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for more details.
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry