Since their discovery, cochleates have attracted considerable interest, due to their remarkable structural properties and their potential use as drug delivery vehicles. Until now, cochleates have been successfully utilized for the delivery of multiple active ingredients such as antifungal agents, DNA, and vaccines. Therefore, the cochleate delivery system is a very promising technology platform for the formulation and administration of efficacious but problematic therapeutic molecules.
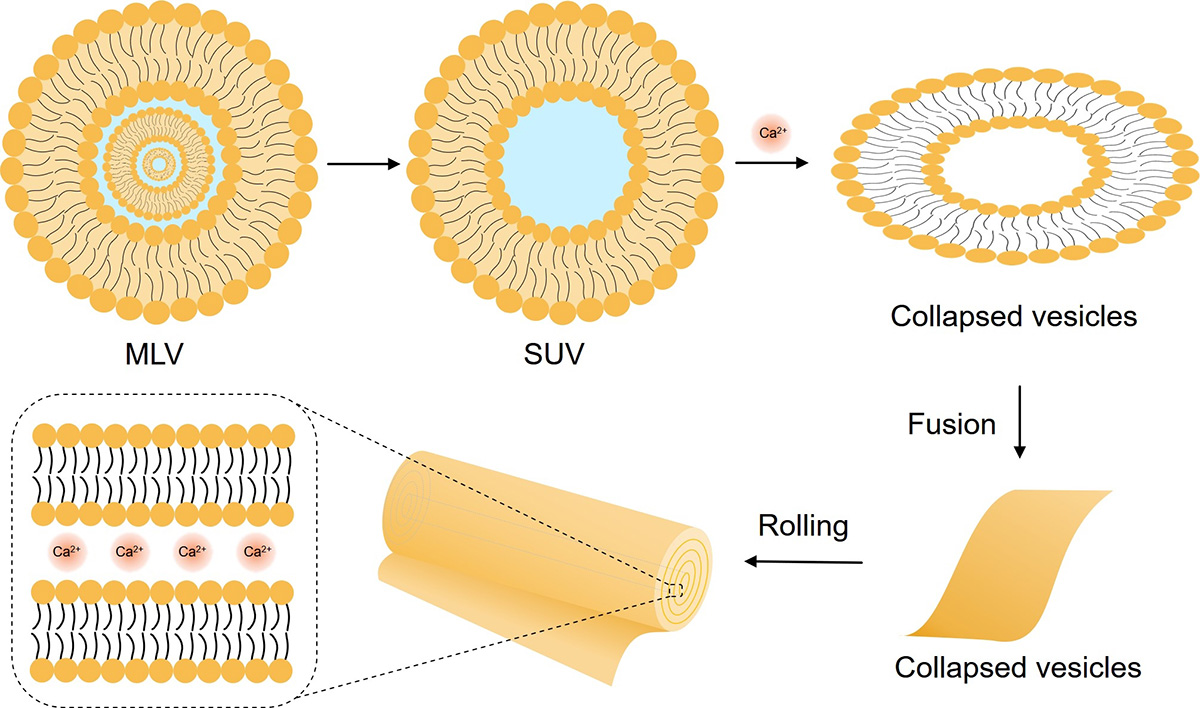 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the structures of cochleates.
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the structures of cochleates.
Cochleates (Co) are phospholipid-calcium precipitates derived from the interaction of anionic lipid vesicles with divalent cations such as calcium. They have a multilayered structure consisting of large and continuous lipid bilayer sheets rolled up in a spiral structure with no internal aqueous phases. The unique structure of the tightly packed cochlea can protect molecules contained within the lipid bilayer from degradation. In addition, the cochleates themselves are non-toxic and non-inflammatory, therefore, they have been used to formulate drugs or antigens. Since the cochleate crystal structure consists of a series of solid layers, even if the structure is exposed to acidic pH or enzymes, the internal bioactive molecules remain intact.
Cochleates are mainly formed by phosphatidylserine (PS) and calcium. PS shows a significant binding affinity for calcium because calcium tends to lose part of its hydration shell and to displace water upon complex formation. Due to the neutralization of the electrostatic charge, calcium causes the liposomes composed of PS to aggregate and fuse with each other.
Cochleates deliver the material to the cell by the fusion of the outer layer of the cochleate with the cell membrane. Several naturally occurring membrane fusion events involve the interaction of calcium with negatively charged phospholipids, typically phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylglycerol. Perturbations of membranes induced by calcium containing negatively charged lipids and subsequent membrane fusion events are an important mechanism in many natural membrane fusion processes. Therefore, cochleates can be envisioned as membrane fusion intermediates that result in the delivery of a small amount of material into the cytoplasm of the cell. Alternatively, cochleates can be absorbed by endocytosis and deliver their contents to the cytoplasm by fusion with endocytic vesicle membranes.
Cochleates has many advantages, including the following:
In order to prepare the drug-cochleates, three methods can be used. The first method is called trapping/high pH. The second is the trapping/film method that utilizes the hydrophobicity of the drug and its easy inclusion into the lipid bilayer. A third method uses a biocompatible hydro Cochleates gel, two-phase system that results in the formation of small nanocochleates particles. The physicochemical properties of the drug cochlea prepared by different methods are different (particle size, aggregation) and are therefore expected to result in different biological activities.
Creative Biolabs has developed procedures for the preparation of cochleate formulations containing a wide variety of biologically important molecules, including proteins, peptides, DNA plasmids, antisense oligonucleotides, drugs, and lipid-soluble compounds. If you provide us with your medicine or other biological materials, we are sure to give you the best cochleate formulation in the world.
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry