Lipoproteins are complex aggregates of lipids and proteins, which have proven themselves to be effective and versatile delivery agents. They can be modified in numerous ways, such as loading with drugs, paramagnetic lipids, fluorophores, nanocrystals, radioactive nuclei, boron compounds and nucleic acids. Creative Biolabs has integrated multiple cutting-edge technologies and established a powerful lipid-based drug delivery (LDD) system. Our strong expertise in delivery system design allows us to help clients tackle challenges and accelerate the design and development of drug delivery.
Lipoproteins are a set of natural nanoparticles responsible for the transport of cholesterol and other lipids in the blood circulation. They are complex particles and each has a central hydrophobic core of non-polar lipids, primarily cholesterol esters and triglycerides. This hydrophobic core is surrounded by a hydrophilic membrane consisting of phospholipids, free cholesterol, and apolipoproteins, which facilitates lipoprotein formation and function. Since lipids are insoluble in water, these lipids must be transported in association with proteins in the circulation. Large quantities of fatty acids from meals must be transported as triglycerides to avoid toxicity. Lipoproteins play a key role in the absorption and transport of dietary lipids by the small intestine, the transport of lipids from the liver to peripheral tissues, and the transport of lipids from peripheral tissues to the liver and the intestine. A secondary function is to transport toxic foreign hydrophobic and amphipathic compounds, such as bacterial endotoxin, from areas of invasion and infection.
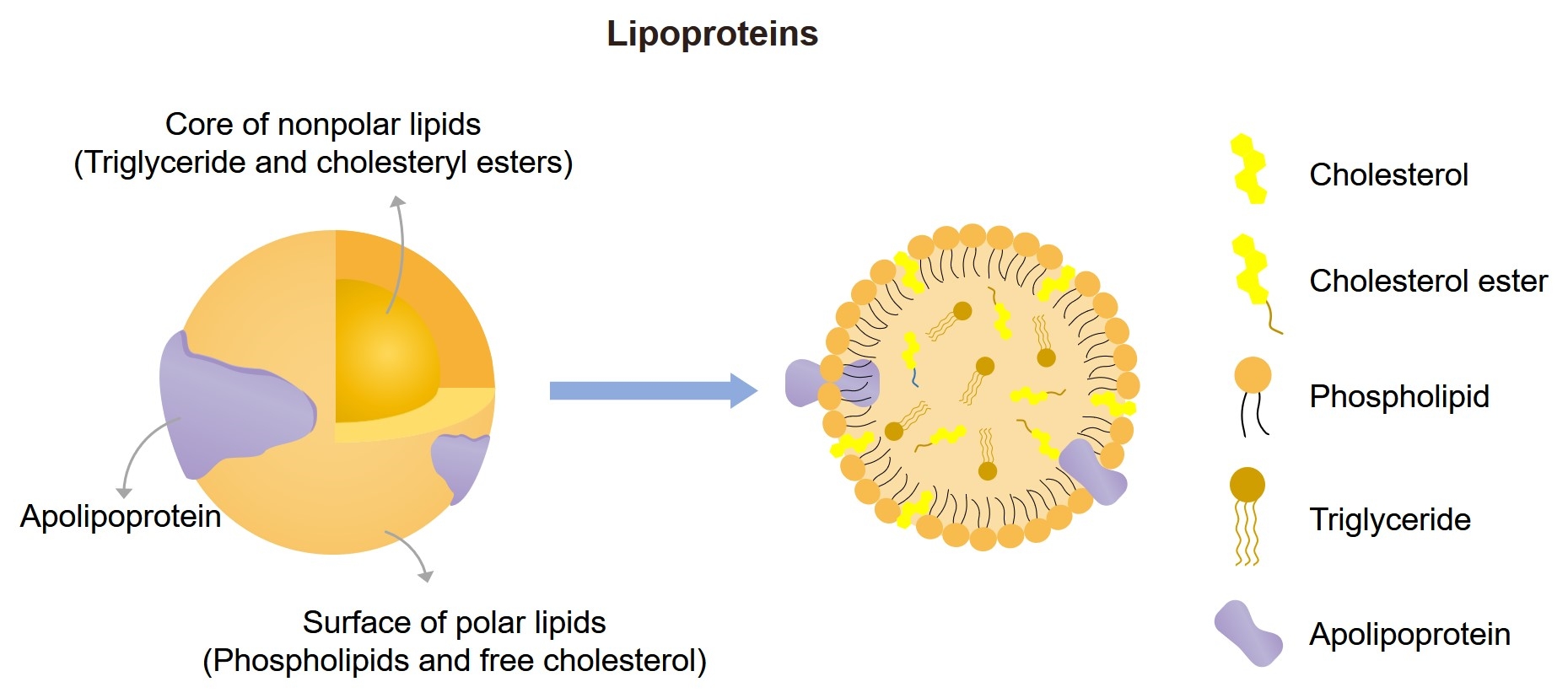 Fig.1 Schematic representation of a lipoprotein.
Fig.1 Schematic representation of a lipoprotein.
In drug delivery, nanoparticle based agents are starting to form a significant part of an array of disease treatments while natural nanoparticles would be likely to be non-immunogenic, biocompatible and degradable. That makes lipoproteins the focus of research. Lipoproteins have many applications. They are endogenous; they can deliver a range of payloads (contrast media, drugs and nucleic acids); they naturally accumulate at several important targets; they can be re-routed to other targets, carry lipophilic drugs, be modified via numerous different methods; moreover, imaging their behavior is of fundamental importance. Based on their sizes and surface composition, lipoproteins may demonstrate relatively long circulation half-lives, compared with non-lipoprotein nanoparticles. They have been considered as natural nanoparticle delivery candidates and can be modified to act as contrast agents in many ways, such as to provide contrast for computed tomography by inserting gold cores. They can be loaded with drugs, nucleic acids, photosensitizers or boron to act as therapeutics. These all enable attributes render lipoproteins to be attractive and versatile delivery vehicles.
Lipoproteins have a number of natural targets, but the addition of ligands results in their rerouting to other targets. These attributes have led to applications in imaging and therapy of cardiovascular diseases, cancer and Alzheimer's disease. Lipoproteins have proven themselves to be effective and versatile delivery agents. They can be modified in numerous ways, such as loading with drugs, paramagnetic lipids, fluorophores, nanocrystals, radioactive nuclei, boron compounds and nucleic acids. Equipped with multiple leading technologies and abundant expertise, Creative Biolabs is confident in its drug delivery system and first-class professional service. In addition to the formulation composed of lipoproteins, we offer other customized formulations based on our LDD platform. Please feel free to contact us for a detailed quote.
 For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical UseSupports
Online Inquiry