Custom RNA Longmer Synthesis Service
Introduction
Accelerate drug discovery with our Custom RNA Longmer Synthesis service. We deliver high-quality, sequence-verified long RNA oligonucleotides tailored to your research and therapeutic needs. Using advanced chemical and enzymatic technologies, we provide custom modifications and ensure construct integrity for applications in gene therapy, functional genomics, and viral research. Our expertise overcomes challenges in synthesizing complex RNA sequences, enabling novel therapeutic strategies and breakthrough discoveries.
[Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation]
Custom RNA Longmer Synthesis
RNA longmers are chemically synthesized RNA oligonucleotides typically ranging from 100 to several hundred bases in length. These extended RNA molecules are crucial for applications requiring full-length functional RNAs, such as mRNA for protein expression, tRNA for specific amino acid delivery, and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) involved in complex gene regulatory networks. Their unique secondary and tertiary structures, influenced by sequence and environmental factors, are essential for their biological activity and play a significant role in gene regulation and viral replication.
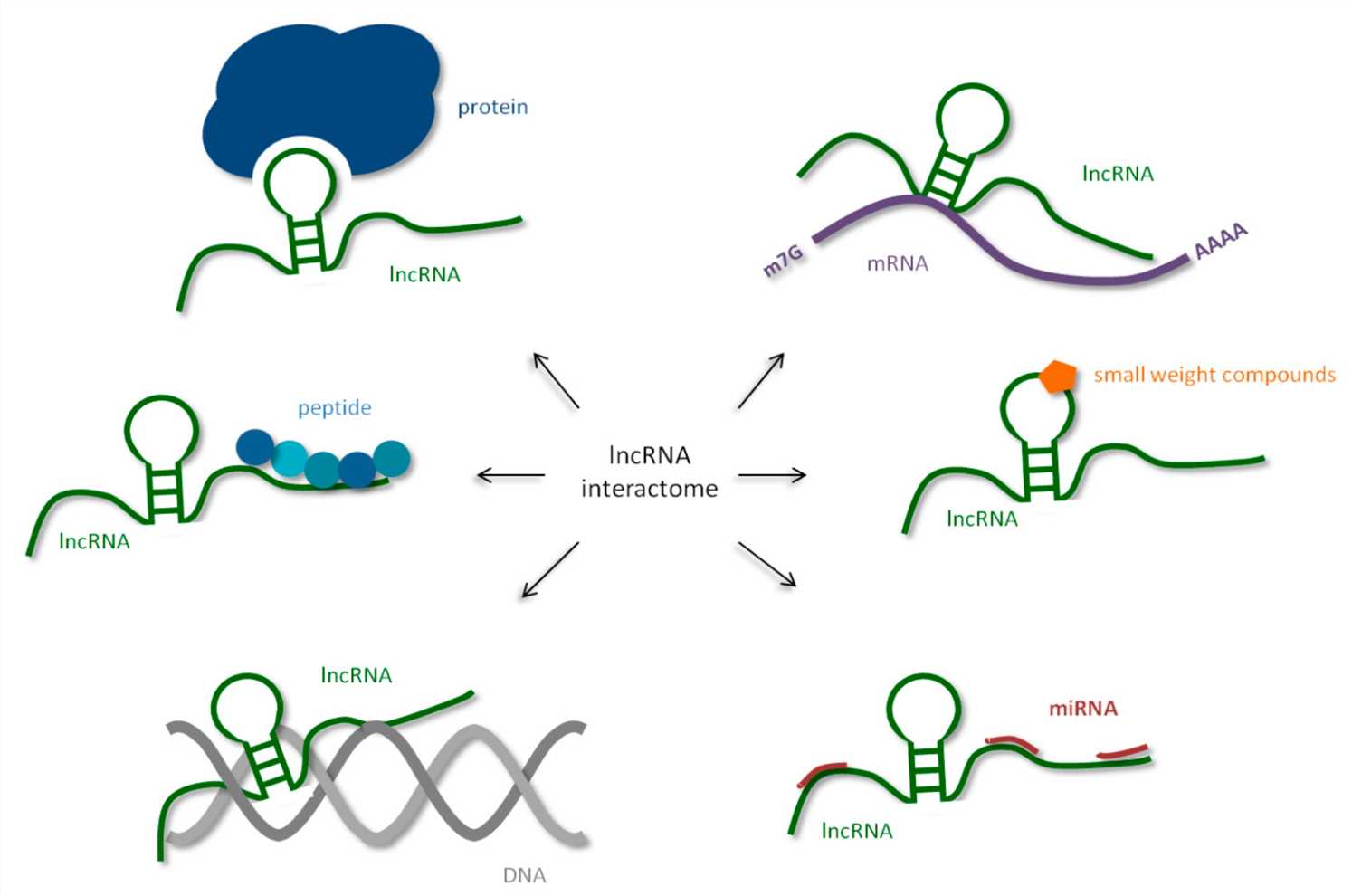 Fig.1 The interaction between human lncRNA and cellular biomolecules.1
Fig.1 The interaction between human lncRNA and cellular biomolecules.1
Workflow
-
Synthesis
Creative Biolabs uses advanced chemical synthesis to produce custom RNA longmers up to 300 bases with high coupling efficiency, via solid-phase synthesis for precise base-by-base addition and sequence accuracy. For longer transcripts, advanced enzymatic transcription from DNA templates is employed. We enable the incorporation of diverse modifications and labels at specific sites, providing tailored solutions for research and therapeutic needs.
-
Purification
High purity is critical for functional RNA longmers, as impurities disrupt downstream applications. Post-synthesis, all undergo rigorous purification using advanced HPLC and/or PAGE to remove truncated sequences, unreacted reagents, and other impurities. This multi-step process ensures highly pure products, reducing experimental variability and boosting research efficacy.
-
Quality Control
At Creative Biolab, every custom RNA longmer undergoes strict quality control to ensure integrity and suitability for critical experiments. This includes ESI-MS for accurate molecular weight and sequence verification, plus PAGE and HPLC for detailed purity assessment, providing visual and quantitative data on homogeneity. This multi-faceted approach guarantees integrity, sequence accuracy, and high purity, offering researchers reliable tools.
-
Final Deliverables
Clients receive their purified RNA longmer product, a comprehensive ESI Mass Spectrometry report confirming sequence and molecular weight, and detailed HPLC/PAGE purity analysis data.
-
Estimated Timeframe
The typical timeframe for this service ranges from 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the length of the RNA, the complexity of any requested modifications, and the specific purification requirements.
What we can offer
Tailored Solutions
Fully customized RNA longmer synthesis, matching unique sequence, length, and modification needs for all applications.
Broad Length Capabilities
Chemical synthesis (up to 300 bases) and enzymatic transcription to meet diverse project demands.
Extensive Modification Portfolio
Wide range of modifications/labels (fluorescent tags, biotin, phosphorothioate) for enhanced function and stability.
Optimized Synthesis Protocols
More than 20 years of expertise enable high coupling efficiency, superior yields, and consistent quality.
Dedicated Expert Support
Biology specialists provide full consultation from design to delivery, ensuring seamless execution.
[Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today]
FAQs
What is the maximum length of RNA longmers Creative Biolabs can synthesize?
Creative Biolabs can chemically synthesize custom RNA longmers up to 300 bases in length with high precision. For even longer RNA transcripts, we can produce kilobase-length RNAs from a DNA template, offering unparalleled flexibility for your most ambitious projects and ensuring you have the right tools for your research.
Can I include specific modifications or labels in my RNA longmer?
Absolutely. We offer a comprehensive range of modifications and labels, including fluorescent dyes, biotin, phosphorothioate linkages, 2'-O-methyl modifications, and more. Our advanced synthesis allows for precise placement of these modifications to meet your exact experimental requirements, enhancing the utility of your RNA longmers.
How does Creative Biolabs ensure the quality and purity of its RNA longmers?
We employ a multi-stage quality control process, including ESI Mass Spectrometry for accurate sequence and molecular weight verification, and HPLC/PAGE for rigorous purity analysis. This meticulous approach ensures that every RNA longmer delivered meets the highest standards of quality and integrity, providing you with confidence in your results.
What applications are best suited for Custom RNA Longmer Synthesis?
Our custom RNA longmers are ideal for a wide array of cutting-edge applications, including gene therapy research (e.g., mRNA vaccine development, ASO design), functional genomics studies (e.g., lncRNA analysis), RNA structure-function investigations, and as templates for in vitro transcription.
What information do I need to provide to initiate a Custom RNA Longmer Synthesis project?
To get started, we typically require your target RNA sequence, details on any desired modifications or labels, and information about the intended application of the RNA longmer. This helps us tailor our synthesis strategy to your specific needs and ensure optimal project outcomes.
Creative Biolab is your trusted partner for high-quality Custom RNA Longmer Synthesis, delivering precisely engineered RNA molecules for groundbreaking research and therapeutic development. With advanced technology, strict quality control, and customer-centric service, we ensure project success, empowering scientific discovery.
[Contact Our Team for More Information and to Discuss Your Project]
Reference
- Kazimierczyk, Marek, et al. "Human long noncoding RNA interactome: detection, characterization and function." International journal of molecular sciences 21.3 (2020): 1027.DOI: 10.3390/ijms21031027. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
