Peptide-Conjugated Antisense Oligonucleotide (ASO) Development Service
Peptide-oligonucleotide conjugate (POC) is one of the effective methods to improve the cellular uptake, tissue delivery, bioavailability, and overall efficiency of oligonucleotides. Peptides are composed of 4-50 amino acids and can deliver drugs to the target site by energy-dependent or non-dependent means, so they are becoming an important tool for ASO delivery. Creative Biolabs provides services for POC design, synthesis, and custom conjugation solutions based on the characteristics and delivery requirements of ASO drugs.
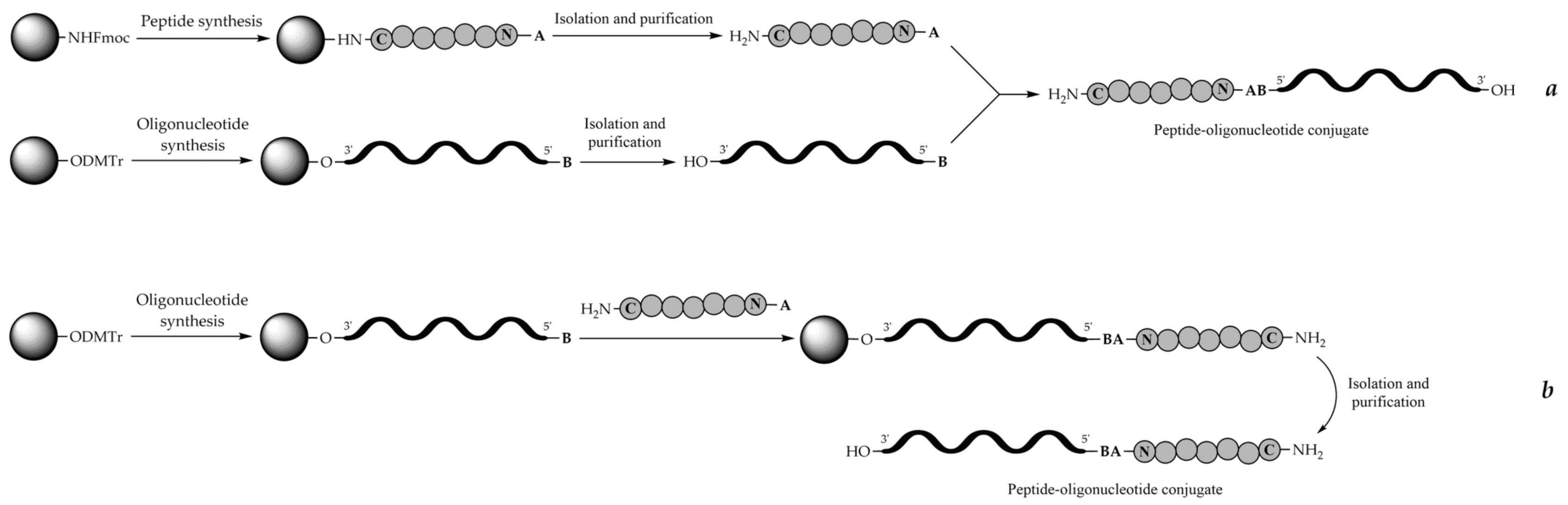 Figure 1 Solid-phase and liquid-phase coupling method of POC.1,3
Figure 1 Solid-phase and liquid-phase coupling method of POC.1,3
Antisense Oligonucleotide
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are a revolutionary class of drugs that work by regulating gene expression at the pre-translational level. These synthetic nucleic acid fragments, typically consisting of 15 to 30 nucleotides, are designed to hybridize with specific messenger RNA (mRNA) or precursor mRNA targets via Watson-Crick base pairing. This precision of targeting allows drugs to intervene in disease pathways with high specificity, thereby tackling traditionally "undruggable" targets in the genome or transcriptome.
Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy: Advancing the Nucleic Acid Frontier
The development of antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) therapy has moved from theoretical concepts to clinical applications, providing transformative treatment options for a variety of genetic diseases, neurological disorders, and infectious diseases. Early ASOs faced numerous challenges, including nuclease degradation, poor pharmacokinetic properties, and low cellular uptake efficiency. These challenges were primarily overcome through extensive chemical modifications.
Key advantages include:
- High specificity
- Comprehensive target space
- Rapid development timeline
What Is Peptide-Coupled Antisense Oligonucleotide (P-ASO)?
- Definition: P-ASO is a next-generation conjugate in which an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) therapeutic agent is chemically linked to a peptide molecule (e.g., receptor ligand, cell-penetrating peptide (CPP)) that imparts targeting or cell-penetrating properties via a chemical linker.
- Mechanism of Action: The peptide moiety guides the ASO to specifically bind to receptors on the surface of target cells. This complex enters the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis, thereby achieving highly efficient and targeted gene silencing within the cell.
Why Use Peptide to Conjugate with Antisense Oligonucleotide?
Peptides are characterized by small molecular weight, adjustable charge, and resistance to enzymatic hydrolysis. Peptides conjugated to ASOs improve target cell permeability and mediate selective tissue targeting. In addition, POC has the following features:
- Efficient delivery
- Precise Targeting
- Enhanced stability
- Improved therapeutic efficiency
- Reduced toxicity and side effects
- A broad scope of applications
Mechanism of Peptide-mediated Delivery
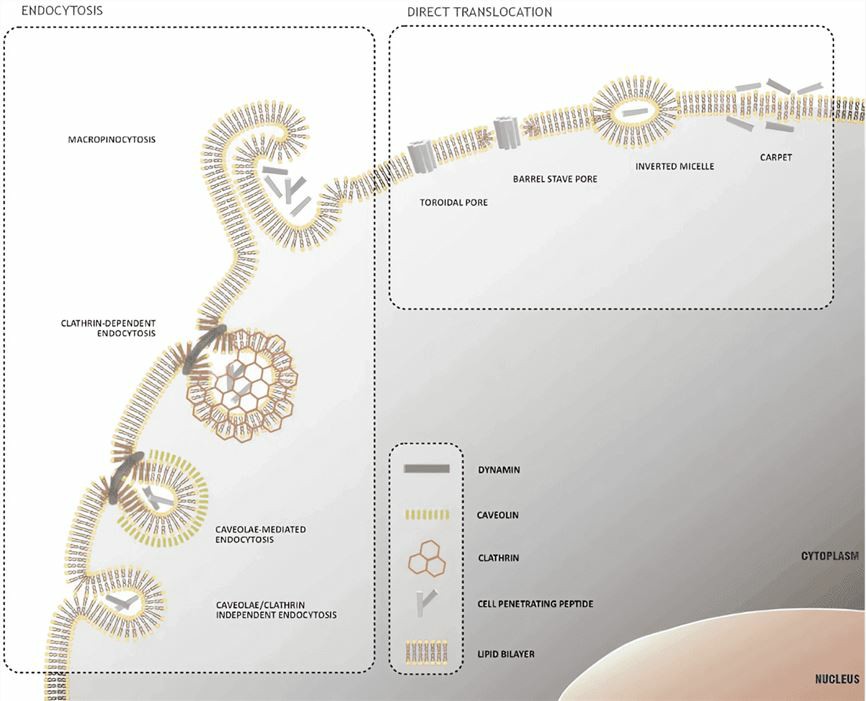 Figure 2 Mechanisms of cellular internalization of CPP.2,3
Figure 2 Mechanisms of cellular internalization of CPP.2,3
Direct translocation (energy independent):
Mechanism 1: positively charged CPP interacts with negatively charged membrane components and phospholipid bilayer;
Mechanism 2: A pH gradient is formed on the plasma membrane. At high pH values, the carboxyl group of fatty acids in the lipid bilayer binds to the guanidine group of extracellular CPP and mediates the transfer of CPP through the plasma membrane due to the formation of ring pores.
Endocytosis:
Phagocytosis: a process which occurs only in specialized cells, such as macrophages;
Pinocytosis: active in most cells and includes macropinocytosis, clathrin-mediated pinocytosis, caveolae-mediated pinocytosis, and other less well-characterized pathways.
How to Design Peptide-Coupled Antisense Oligonucleotides?
A. ASO Sequence and Chemical Optimization
The initial step is to select a suitable ASO sequence for the target RNA. We utilize advanced bioinformatics and computer simulation tools to predict optimal binding sites, considering factors such as secondary structure, accessibility, and potential off-target binding. Once the sequence is determined, we strategically select the ASO backbone and glycosyl modifications (e.g., PS, 2'-MOE, LNA).
B. Target Peptide Selection and Engineering
Peptide selection is crucial. We utilize a rich library of validated target ligands, including cell-penetrating peptides (CPPs), receptor-specific peptides, and tissue-homing peptides. Peptide selection depends on the desired therapeutic application and the receptor expression profile of the target cells. Key design considerations include:
- Affinity and specificity
- Toxicity characteristics
- Charge and hydrophobicity
C. Linker Strategy and Geometry
The linker for linking peptides and antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) is often the most critical yet most easily overlooked component. The linker must be chemically stable in systemic circulation to facilitate intracellular ASO release. Our design platform systematically screens various linker groups to optimize:
- Coupling yield
- Steric Freedom
- Pharmacokinetics
Conjugation Chemistry & Process Optimization
Covalent linking of peptide and oligonucleotide components requires specialized chemical approaches adapted to the unique properties of these molecular entities. Our platform integrates multiple coupling strategies, each with specific advantages for different applications.
Chemical Linking Methods
01 Native Chemical Linking
This method enables the formation of native peptide bonds between oligonucleotides and peptide components, typically using C-terminal thioesters and N-terminal cysteine residues.
02 Enzymatic Linking
Certain enzymes, such as sorting enzymes or transglutaminases, can catalyze specific coupling reactions under mild conditions, thereby maintaining the structural integrity of both components.
03 Click Chemistry
Copper-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloaddition involves introducing an azide or alkyne functional group into the corresponding component, thereby forming a triazole bond with excellent stability.
Process Optimization Parameters
01 Reaction Conditions
Key parameters, including pH, temperature, solvent composition, and reactant concentration, are systematically optimized to maximize coupling efficiency while minimizing side reactions.
02 Purification Methods
Advanced chromatographic techniques, including reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), ion-exchange chromatography, and size exclusion chromatography, are employed to separate the target conjugates with high purity.
03 Analytical Monitoring
Multiple orthogonal techniques are used to monitor the coupling process to ensure complete reaction and detect potential byproducts.
Highlights of Peptide-Coupled Antisense Oligonucleotide
Creative Biolabs has a professional team and extensive experience in providing a comprehensive POC service:
- POC design and synthesis: Provide a one-stop solution from peptide design, and ASO synthesis to POC conjugation.
- POC purification and characterization: Using advanced purification technology to ensure the high purity and stability of POC and providing a full range of analytical services, including MS, NMR, EP, etc.
- POC functional modification: Provide fluorescent labeling, biotinylation, and other functional modification services.
- POC drug delivery and functional evaluation: Provide evaluation services of cell uptake, tissue distribution, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of POC to provide strong support for drug development of customers.
Our Services
Our company provides end-to-end development services for peptide-conjugated antisense oligonucleotides, supporting projects at every stage from initial concept to preclinical development. Our services aim to address the multifaceted challenges of conjugate development by integrating expertise from multiple scientific fields.
- Peptide Discovery and Design: Custom synthesis of novel targeting peptides or optimization of known ligands.
- Compound Conjugate Synthesis: Synthesis of ASO components at gram scale, followed by conjugation with peptides.
- Analytical Characterization: Detailed physicochemical and structural analyses of the final P-ASO conjugates.
Partnership and Success Stories
Creative Biolabs is driven by collaborative innovation. Our partnerships with leading pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies are based on rigorous scientific principles and mutual respect for intellectual property. While specific client information is confidential, our past successes include advancing multiple P-ASO drug candidates from exploratory research to preclinical development. These successes span a wide range of therapeutic areas, including genetic diseases, oncology, and chronic inflammatory diseases, demonstrating the breadth and adaptability of our platform.
Why Choose Our Services?
Targeted Delivery Platform
- High-throughput screening of peptide libraries for primary cells and tissues
- In vivo phage display technology for identifying organ-homing peptides
- Computational modeling of receptor-ligand interactions
- Validation of target specificity using advanced imaging techniques.
Endosomal Escape Enhancement Platform
- Endosomal lysis peptide libraries with different mechanisms of action
- High-content screening for quantitative assessment of cytoplasmic delivery
- Structure-activity relationship optimization of escape domains
- Compatibility with various targeting ligands and oligonucleotide chemistry systems.
Stability Optimization Platform
- Systematic evaluation of proteolytic cleavage sites and stabilization strategies
- Introduction of non-natural amino acids with enhanced stability
- Conformational confinement through cyclization and backbone modification
- Comprehensive stability assessment in biological matrices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the main advantages of P-ASO compared to traditional ASO?
A: P-ASO utilizes receptor-mediated endocytosis, enabling more effective targeting of extrahepatic tissues and improved cellular uptake efficiency, thereby significantly increasing the therapeutic index and achieving targeting of previously difficult-to-target cells.
Q: How to address the challenges of scaling up complex conjugates?
A: Our R&D process considers scale-up from the early stages, with particular emphasis on the selection of conjugation chemistry methods and purification strategies. Our platform approach has proven successful in scaling from milligram to gram levels.
Q: What criteria should be considered when selecting different conjugation chemistry methods?
A: Multiple factors influence the selection of conjugation chemistry methods, including stability requirements, functional group compatibility, scalability, and analytical characterization considerations. We typically evaluate multiple methods in the initial R&D phase to determine the optimal strategy for each specific conjugate.
Q: What chemical modifications are typically used in ASO components?
A: We typically employ second- and third-generation chemical methods, primarily using a thiophosphate backbone to improve nuclease stability, and modifying with 2'-O-methoxyethyl (2'-MOE) or LNA to enhance binding affinity and reduce toxicity.
Q: How do you select the optimal targeting peptide?
A: Selection is based on the target cell receptor expression profile, peptide stability (resistance to proteolysis), and its ability to mediate efficient internalization. We screen for peptides with high affinity binding and favorable physicochemical properties.
Q: Can you process ASOs of non-standard lengths or chemical structures?
A: Yes, our platform is fully customizable. We focus on synthesizing and conjugating ASOs with unique backbone chemical structures, alternative sugar modifications, and varying lengths to meet new research needs.
Q: What is the typical purity level of the final conjugate?
A: Our standard purification protocols typically yield P-ASO conjugates with a purity exceeding 95%, and are validated using a variety of orthogonal analytical techniques, including HRMS and various HPLC/CE methods, to ensure clinical readiness.
Connect with Us Anytime!
Peptide-conjugated antisense oligonucleotides represent the next stage of development in oligonucleotide therapy, providing a powerful strategy for expanding the scope and efficacy of gene silencing. Creative Biolabs is ready to be your trusted partner, offering PhD-level expertise, an integrated technology platform, and rigorous quality control to address the complex challenges of P-ASO development. If you have any needs or questions about POC, please feel free to contact us, we will be glad to serve you.
References
- Trabulo, Sara, et al. "Cell-penetrating peptides—mechanisms of cellular uptake and generation of delivery systems." Pharmaceuticals 3.4 (2010): 961-993. 10.3390/ph3040961
- Klabenkova, Kristina, Alesya Fokina, and Dmitry Stetsenko. "Chemistry of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates: a review." Molecules 26.17 (2021): 5420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175420
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
