Antisense Oligonucleotide (ASO) Development Service
What is Antisense Oligonucleotide (ASO)
Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) are nucleotide chains created in a lab. They typically consist of 12-28 bases. As a kind of therapeutic drugs that target RNA, they can latch onto complementary sequences of target mRNA or pre-mRNA. They can precisely control gene expression through multiple mechanisms. In the cell nucleus, these antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) can quietly affect the splicing and tailing process of precursor mRNA, and may even be directly "cut off" by the RNase H enzyme; in the cytoplasm, they have a new task - either to block the "production line" of protein synthesis, or to pull the RNase enzyme to decompose the mature mRNA. Their "targets" are particularly wide: whether it is mRNA responsible for encoding proteins, or RNA that does not directly encode proteins such as microRNA and lncRNA, they can be accurately "targeted". Because they can handle both coding and non-coding RNA at the same time, and can play a role in different locations in the cell, ASOs have become "all-rounders" in the fight against genetic diseases - especially those caused by disordered gene expression or splicing errors.
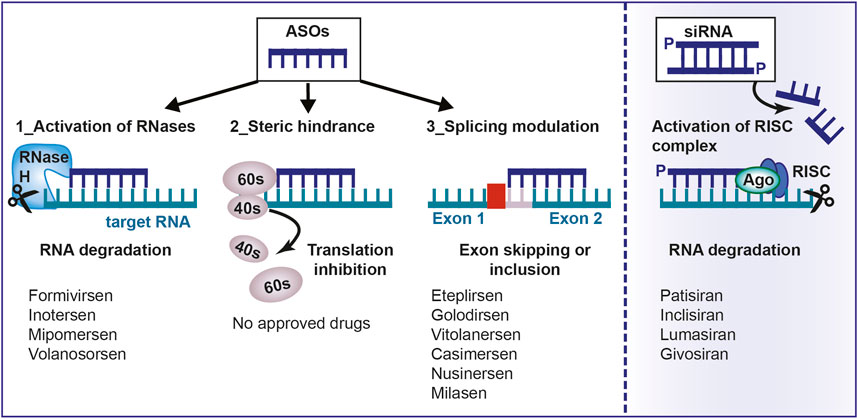 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of antisense oligonucleotides.1
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of antisense oligonucleotides.1
At Creative Biolabs, we provide one-stop ASO development services, integrating cutting-edge design, synthesis and optimization technologies to customize solutions around your therapeutic goals. From early research to preclinical development, our team will become your exclusive partner, providing reliable, scalable, high-quality ASOs to help you accelerate the development of RNA-targeted therapies.
Strategic Advantage in RNA-Targeted Therapy
There are indeed many complex steps in the process of developing ASO, from sequence design to in vivo delivery, but these should not become stumbling blocks that hinder your progress. With our professional experience, technical capabilities and in-depth cooperation, we can help you overcome difficulties and achieve R&D milestones faster.
Full-process integration: Our team eliminates traditional silos between computational design, chemical synthesis, and in vivo validation by implementing a unified platform that connects every development phase—from initial sequence modeling through manufacturing. there are no gaps between synthesis and validation. You don't have to juggle different stages alone—we handle the entire workflow, so you can focus on what matters most.
Precision Customization by Expert Teams
Our PhD team acts like an extension of your lab, fine-tuning every detail just for you:
Sequence Design: We optimize your target RNA sequence to ensure it hits the right spot with precision.
Chemical Modifications: Need a stronger backbone (like phosphorothioate) or specific add-ons (e.g., 2'-O-methyl groups)? We design them to boost stability and effectiveness for your disease model.
Delivery Systems: Whether it's lipid nanoparticles or conjugate carriers, we pick the best fit to get your therapy where it needs to go.
No cookie-cutter solutions here—every change serves your unique research needs.
Regulatory-Ready Quality: Our quality control starts from the first step of development, and each step is designed according to global regulatory requirements. The production workshop is built directly according to GMP standards and is equipped with real-time monitoring equipment, which can not only ensure that each batch of products is stable and reliable, but also generate a complete set of application materials (such as production process data, animal experiment reports, etc.), directly helping you prepare materials for IND application and subsequent clinical trials.
Workflow: A Clear Path from Design to Delivery
Our "phased-gate" methodology divides the development journey into clearly defined stages (Discovery, Preclinical Readiness, Manufacturing, Regulatory Submission), each anchored to objective validation metrics. We strictly control every key stage - from computational model verification, in vitro effect testing to biodistribution research, every step is carefully checked. This has two advantages: first, it can eliminate the risk of problems at each stage in advance; second, you can clearly know what results you can get next and how long it will take to advance the project.
-
Phase 0: Target Identification and Validation
This phase is fundamental to ensuring the scientific validity and clinical relevance of the selected RNA targets, thereby preventing misallocation of subsequent development resources. We employ a multi-dimensional validation strategy combining bioinformatics and experimental methods: We utilize large-scale omics databases (such as TCGA and GTEx) and proprietary algorithms to analyze differential expression profiles to screen RNA targets with high specificity, strong disease relevance, low druggability risk, and low off-target risk. We then use intervention models (such as RNA interference) in disease-relevant cell lines (such as patient-derived primary cells) to verify whether regulating the target can reverse the disease phenotype. We use tools such as BLAST to compare sequence homology across different species (human, mouse, and rat), prioritizing targets with highly conserved core binding regions for subsequent in vivo validation. We also collect clinical samples (such as patient tissues) to detect target expression and analyze its correlation with clinical indicators (such as prognosis) to confirm clinical value.
-
Phase 1: Design & Optimization
Collaborative sequence design using advanced in silico tools to predict target affinity, minimize off-target binding, and optimize RNase H recruitment (for Gapmers). We engineer Gapmer structures (central DNA gap flanked by modified RNA) and avoid self-complementarity or G-quadruplex formation (e.g., replacing guanine with 7-deaza-dG) to enhance stability.
-
Phase 2: Synthesis & Purification
Scalable synthesis from small-scale screening (10 nmol) to large-scale production (kilogram), with the capacity to process 5 to >1000 sequences in a single run. We use optimized solid-phase synthesis, with purification options including SePOP desalting (default) or HPLC (for high-purity needs).
-
Phase 3: Functional Validation & Safety Assessment
In the ASO development workflow, analysis services play a critical role in validating efficacy, specificity, and safety. Below is a detailed breakdown of the key analysis services—Dual-Fluorescent Reporter Assay, In Vitro ASO Screening, In Vivo Study, and Off-target Analysis—integrated into our one-stop development solutions.
The dual fluorescence reporter gene assay utilizes a dual-plasmid system containing a target gene fragment (fused to GFP) and a reference gene (RFP). The fluorescence intensity ratio accurately measures the binding specificity and activity of the ASO with the target RNA. This allows rapid screening of optimal sequences with low cross-reactivity within 24-48 hours, providing efficient verification for early-stage design.
In vitro ASO screening utilizes multi-dimensional evaluation in cell models, using qPCR and Western blotting. Blot analysis assesses target gene knockdown efficiency, MTT and flow cytometry analyses analyze cytotoxicity, and fluorescence tracking is used to observe cellular uptake and localization. This comprehensive approach, encompassing a range of systems, including primary cells and disease-specific models, comprehensively validates the efficacy and safety of ASOs in vitro.
In vivo studies further evaluate ASOs in animal models, using imaging to track the biodistribution and clearance pathways of ASOs in target organs (such as the liver, brain, and muscle). Biomarker assays (such as SMN protein in SMA models) are used to assess efficacy. Systemic toxicity and immunogenicity are analyzed through hematology, histopathology, and cytokine assays, laying a critical foundation for clinical translation.
Off-target analysis uses RNA-seq to compare global gene expression, computationally predict highly similar sequences, and validate and map binding sites through qPCR. This accurately identifies non-target RNA binding risks and recommends sequence modifications to mitigate off-target effects. These services are seamlessly integrated into the development process, ensuring comprehensive control from specificity, efficacy, and safety, accelerating the transition of ASOs from design to clinical application.
-
Phase 4: Comprehensive QC & Delivery
We have done a comprehensive quality inspection - using HPLC to measure purity (guaranteed ≥95%), mass spectrometry to confirm molecular weight, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and functional testing. Each batch of goods comes with a super detailed quality analysis report (CoA) to ensure that all quality inspection data are clear and reliable. It can be used directly for research or submitted to regulatory authorities for approval.
We provide full transparency and robust data to ensure confidence in your ASOs. All batches undergo rigorous testing before release:
- Purity & Integrity: HPLC (purity ≥95%), mass spectrometry, NMR (structural confirmation).
- Functional Efficacy: In vitro knockdown efficiency (qPCR), splice modulation activity (RT-PCR).
- Safety & Toxicity: Endotoxin assay (LAL), cytotoxicity testing, off-target analysis (RNA-seq), and assessment of immunostimulatory motifs.
- Stability: Accelerated and real-time stability testing under various storage conditions.
Advanced ASO Technology Platform
Our platform uses the most advanced technology available today. The ASO we produce can accurately find the target, is extremely stable, and has very good treatment effects.
Precision Design Tools
We have a special "intelligent design assistant": using computer algorithms to help you design sequences, whether it is for human genes or experimental animals such as mice and rats, it can be easily handled. We will also verify the effect in the corresponding animal model to ensure that what works in mice is also effective in humans, so there is no need to worry about "cross-species effects" at all.
Tailored Chemical Modifications
We will tailor chemical modifications to ASOs according to needs, so that they are stable and can work accurately. For example, adding "phosphorothioate (PTO)" is like wearing anti-corrosion armor to withstand the damage of enzymes in the body; "2'-methoxyethyl (2'-MOE)" can prolong life and reduce body rejection; "locked nucleic acids (LNAs)" are like super glue, making ASO and the target hold tighter; "peptide nucleic acids (PNAs)" help to find the target more accurately; "morpholino oligonucleotides" adjust splicing without accidentally damaging other RNAs; connecting "GalNAc" is like putting a special label on the liver, taking less medicine but with better results.
In addition, we have to help ASO "get through the last mile" - use "lipid nanoparticles (LNPs)" as small trucks to take them through the "garbage recycling station" of cells and enter cells smoothly; wrap them with "invisible cloaks" (PEG modification) to slow down the body's clearance and stay in the blood for a while longer; use "antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates (AOCs)" as precision missiles, and antibodies take ASO directly to specific cells (such as cancer cells and nerve cells). In short, from "wearing armor" to "finding the right path", every detail is in place, just to make ASO work both steadily and accurately.
Enabling Breakthroughs Across Diverse Applications
Our ASOs have proven success in a range of research and therapeutic areas, with a track record aligning with the evolution of ASO therapeutics—from first-generation drugs like Fomivirsen (anti-viral), to second-generation Mipomersen (5-10-5 gapmer structure), and third-generation Miravirsen (LNA-modified):
Genetic Disease Therapy
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA): Modulating SMN2 pre-mRNA splicing to restore functional SMN protein.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD): Skipping mutated exons in dystrophin pre-mRNA to produce truncated but functional protein.
- hATTR Amyloidosis: Targeting TTR mRNA for degradation, reducing amyloid formation.
- Ophthalmology: Treating retinal diseases via local delivery of ASOs targeting pathogenic RNAs in retinal cells.
Non-Coding RNA Targeting
ASOs designed to modulate microRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs, enabling research into previously "undruggable" genomic regions.
Splice Modulation Research
Custom ASOs to correct aberrant splicing events, including exon skipping, inclusion, or cryptic splice site inhibition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between "Research Grade" and "GMP Grade" ASOs?
A: Research Grade ASOs are optimized for in vitro studies and early screening. Each batch of GMP-grade ASO must pass a strict "quality checkpoint" - the basic step is to purify it with HPLC first, then check whether the purity is sufficient (at least 95%) and whether the knockdown effect of the target RNA is effective; GMP-grade ASO is more stringent, and the entire process from synthesis to packaging is operated according to the pharmaceutical production standards. In addition to basic inspections, additional tests are required for endotoxins (to avoid inflammation), stability (whether it will become ineffective after being stored for a long time), toxicity (whether it will damage cells), and even off-target risks are clearly checked. It can be directly used in animal experiments or human clinical trials.
Q: How do I choose the right chemical modifications for my ASO?
A: If you want it to directly degrade RNA (for example, to silence pathogenic genes), you can choose "Gapmer with thiophosphate backbone + 2'-MOE/LNA modification", which can not only accurately cut the target, but also withstand the damage of enzymes in the body; if you want to adjust RNA splicing (for example, skip the wrong exon), it is more appropriate to use "Morpholino or 2'-MOE modification", which can guide the correct splicing without triggering degradation. We will also help you choose the most suitable combination based on your target RNA and delivery method.
Q: What delivery system is best for my application?
A: For example, if you want to accurately target specific cells (such as cancer cells), you can use "antibody-ASO conjugates (AOCs)", which is equivalent to equipping ASO with "antibody navigation" to directly deliver it to the target cells without harming innocent people. No matter what your needs are, we can help you build a "transportation line".
References
- Collotta, D et al. "Antisense oligonucleotides: a novel Frontier in pharmacological strategy." Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 14 1304342. 17 Nov. 2023, https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1304342.
- Khuu, Alexandre et al. "Clinical Applications of Antisense Oligonucleotides in Cancer: A Focus on Glioblastoma." Cells vol. 13,22 1869. 11 Nov. 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13221869.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
