CDC5L and Associated Diseases
The CDC5L gene encodes an in vivo cell division 5-like protein with a striking similarity to the S. pombe cdc5 gene product. CDC5L and the protein it expresses are very active in humans, DNA damage and molecular experiments confirmed that CDC5L interacts with the cell cycle checkpoint protein Rad3-related kinase (ATR) and activates effectors downstream of ATR, including Chk1 and Rad17, interfering with CDC5L inactivates the S-phase cell cycle checkpoint, thereby increasing drug sensitivity.
In addition to affecting the cell cycle, the CDC5L protein is also a member of the spliceosome complex. Both precursor messenger RNA processing factor 19 and CDC5L are highly conserved eukaryotic proteins that together play a unique and direct role in the splicing of the precursor messenger RVA. With the development of molecular biology, the pathological changes caused by CDC5L mutation have also been reported and proposed as a new therapeutic target for malignant tumors.
 Fig 1. Prediction of transcription factors related to CDC5L. (Zhang, 2021)
Fig 1. Prediction of transcription factors related to CDC5L. (Zhang, 2021)
CDC5L in Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Molecular biological assays demonstrated selective binding of CDC5L and hTERT promoters in all four colon cancer cell lines, while CDC5L was shown to be a transcriptional activator of hTERT, whose expression was positively correlated with hTERT, a key promoter in CRC cells. To some extent, it suggests that CDC5L may serve as a novel target for human colorectal cancer therapy.
CDC5L in Bladder Cancer
The immunohistological evaluation found that CDC5L was highly expressed in fresh bladder cancer tissues, and knockdown or expression inhibition of CDC5L could significantly inhibit bladder cancer cell migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and induced bladder cancer cell apoptosis. The molecular biological analysis also showed that the expression of CDC5L was significantly correlated with the expression of ki67, a gene related to the pathological grade of bladder cancer.
CDC5L in Melanoma
Bioinformatics and gene silencing analyses identify an essential role of CDC5L in melanoma. The enzyme fumaric acetoacetate hydrolase (FAH) is highly expressed in melanoma and affects melanoma cell survival. The latest experiments identified CDC5L as an important transcription factor regulating FAH expression in melanoma cells.
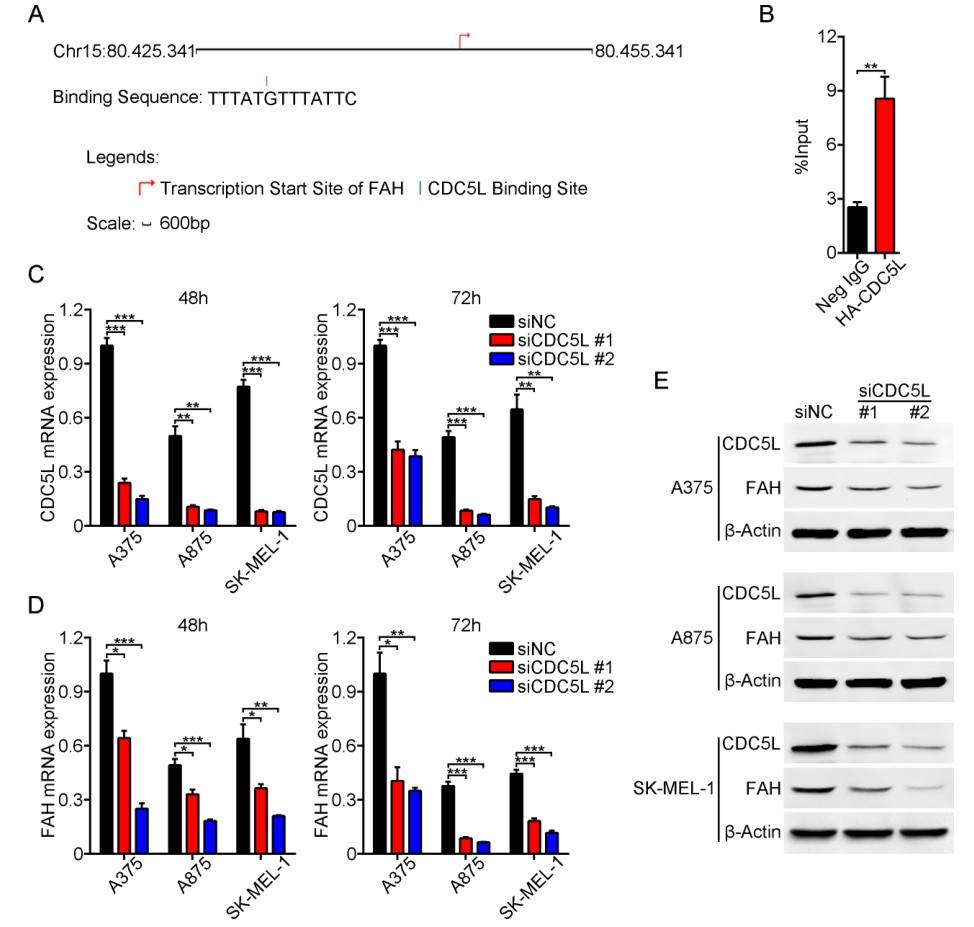 Fig 2. CDC5L drives FAH expression. (Gu, 2017)
Fig 2. CDC5L drives FAH expression. (Gu, 2017)
CDC5L and Other Diseases
CDC5L can regulate the G2/M transition process of cells and participate in pre-messenger RNA splicing and DNA damage repair. For property, CDC5L has been used as a candidate oncogene in diseases such as osteosarcoma and cervical tumors in recent studies. At the same time, the disorder of the CDC5L gene can also lead to renal dysplasia, neutropenia, atrial septal defect, and other symptoms.
References
- Zhang, Z.W.; et al. Depletion of CDC5L inhibits bladder cancer tumorigenesis. Journal of Cancer. 2020, 11(2): 353-363.. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
- Gu, Z.C.; et al. CDC5L drives FAH expression to promote metabolic reprogramming in melanoma. Oncotarget. 2017, 8(69): 114328-114343. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
