Creative Biolabs offers an UV-activated site-specific antibody labeling service to help you achieve precise and efficient antibody-label conjugates through our advanced photoaffinity labeling technology. This service addresses the challenges of inconsistent antibody labeling, which can hinder assay development and analysis, and ensures high-quality and reproducible results.
Traditional antibody labeling methods, often relying on chemical reactions with lysine residues, typically result in heterogeneous mixtures containing several DNA strands per antibody at varying positions. This heterogeneity complicates purification and can compromise target recognition. To improve these limitations, Creative Biolabs develops an efficient approach that offers a solution by enabling fast, efficient, and modular production of conjugates with defined sites and minimal impact on antigen binding, addressing the growing demand for high-quality antibody-DNA conjugates, crucial for advancing DNA-assisted protein analysis.
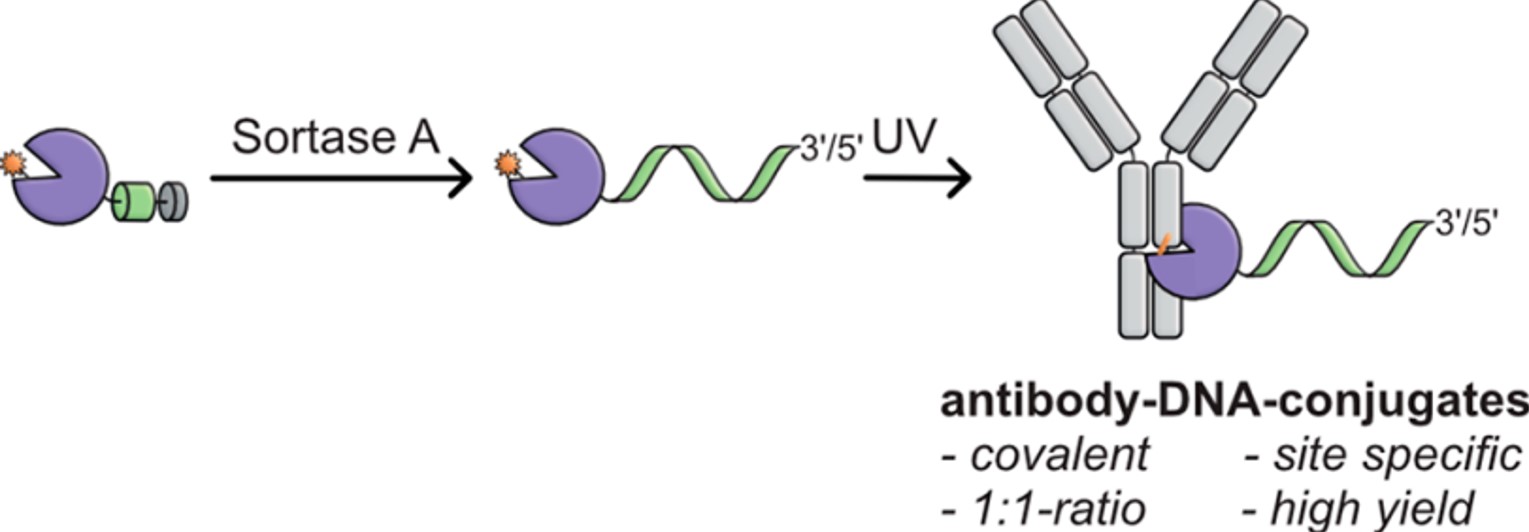 Fig.1 Light-mediated antibody-DNA conjugate.1
Fig.1 Light-mediated antibody-DNA conjugate.1
Creative Biolabs' UV-activated site-specific antibody labeling service provides a streamlined solution for generating antibody-label conjugates. Our site-specific antibody labeling method employs a light-activated technique. This method uses a specialized targeting molecule with a light-sensitive component. Upon exposure to a specific wavelength of light, a stable bond is formed between a reagent and the antibody, allowing for the attachment of various labels to the Fc region of antibodies. This process ensures that the label does not interfere with antigen binding and offers robust buffer compatibility. The labeling process is rapid, requires minimal hands-on time, and produces homogeneous conjugates.
Purified immunoglobulin samples are received from customers for subsequent processing.
A specialized targeting molecule with a light-sensitive component is introduced and permitted to attach to a designated, precise area on the antibody.
The desired labels (e.g., fluorophores, enzymatic reporters, or affinity tags) are introduced and spatially aligned with the targeting ligand-antibody assembly.
Controlled irradiation at optimized wavelengths activates the ligand's photoreactive group, inducing site-directed covalent linkage between the antibody and the conjugated label.
Excess, unbound targeting molecules and labels are removed through purification steps.
Conjugates undergo rigorous assessment using spectrophotometric analysis, ligand-binding ELISA, and SDS-PAGE to quantify labeling efficiency (molar ratio), verify structural integrity, and confirm retained antigen recognition capacity
Sterile-filtered conjugates meeting predefined specifications are transferred to collaborators with accompanying analytical certificates and storage/stability guidelines
This UV-activated site-specific approach is versatile in that it allows researchers freedom in their experimental design by conjugating a great range of payloads without compromising the antigen-binding site of the antibody. Generally speaking, our site-specific antibody labelling system is very appropriate for many targets, including:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Summary: This study uses a modified Z domain from protein A, incorporating a light-activatable unnatural amino acid (BPA), to specifically label the antibody's Fc region. The Z domain is also engineered to carry a DNA oligonucleotide through an enzymatic coupling step. This allows for efficient and controlled generation of conjugates from common IgG antibodies, maintaining both the antibody's and the DNA's functionality, as demonstrated in a protein analysis assay. The modular nature of this method and the stability of intermediate products make it a convenient platform for generating and testing various antibody-DNA combinations.
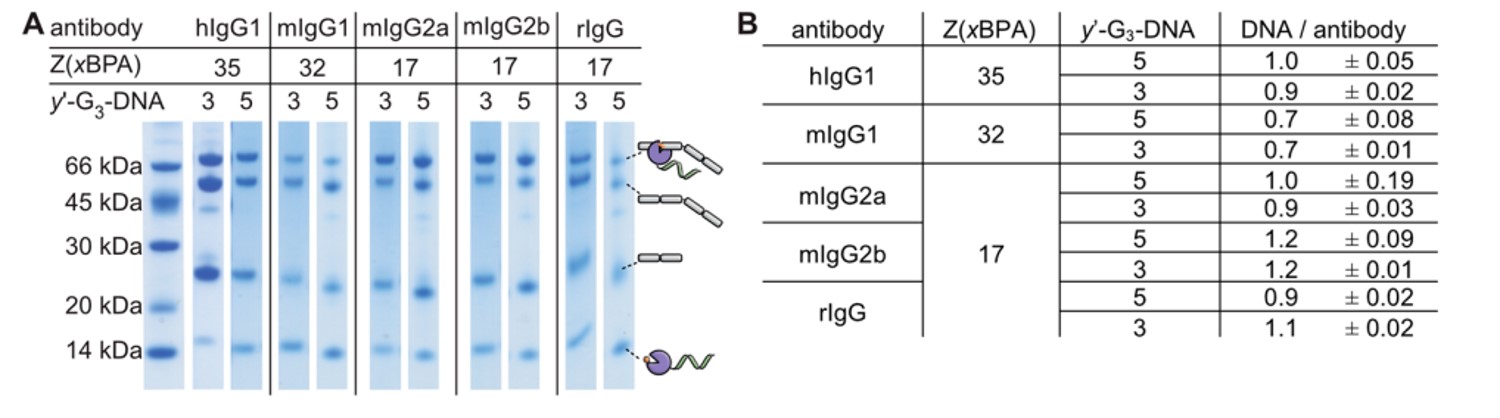 Fig.2 Photoaffinity labelling analysis of human, mouse, and rabbit IgG subclasses employing the modified C terminus of Z domain from protein A.1
Fig.2 Photoaffinity labelling analysis of human, mouse, and rabbit IgG subclasses employing the modified C terminus of Z domain from protein A.1
Q1: Is the labeling process likely to affect antibody function?
A1: Our bioconjugation methodology is engineered to preserve native antibody functionality through spatially resolved modification. The approach employs precision targeting of non-complementarity-determining regions, ensuring topological separation between conjugation sites and paratope architecture. This spatial segregation maintains full antigen recognition capability, as verified through comparative binding affinity assays. Empirical validation of epitope conservation and structural analysis data are available upon request.
Q2: How long does the service process take?
A2: The regular schedule for this service is determined by project complexity; it usually runs two to four weeks.
If you would like additional information about our UV-activated site-specific antibody labelling system and how we may be of help to your project, please do not hesitate to directly get in contact with us.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION