The quest for efficacious personalized cancer immunotherapies confronts a persistent barrier: the reliable identification of immunogenic neoantigen-TCR pairings amidst a combinatorial landscape of potential interactions. Current methodologies often falter in discriminating high-avidity binders from bystander interactions, a bottleneck exacerbated by tumor heterogeneity and HLA allelic diversity. Machine learning-guided TCR-neoantigen interaction profiling platform at Creative Biolabs circumvents these limitations through an ensemble architecture integrating convolutional neural networks with biophysical docking simulations.
Our platform synergizes three computational strata:
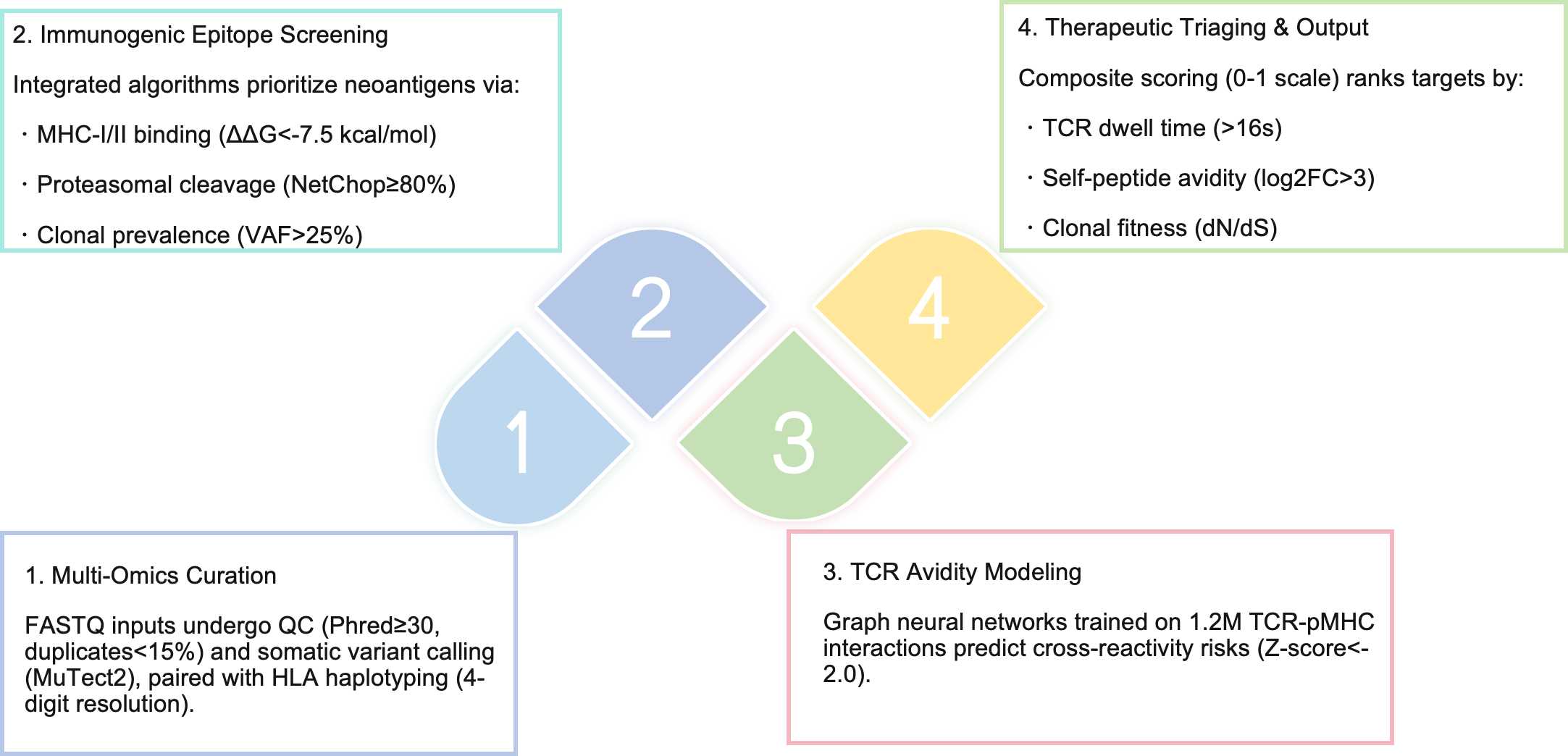
1. Epitope Fitness Prediction: Quantifies neoantigen immunogenicity via MHC-I/II binding stability and proteasomal cleavage likelihood (≥80% prediction confidence)
2. TCR Clonotype Optimization: Employs graph-based attention networks to model CDR3β loop conformational dynamics, predicting clonotype-specific avidity (pMHC-TCR dwell time >15s)
3. Cross-Reactivity Mitigation: Leverages adversarial neural networks to minimize off-target recognition against human peptidome databases (UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot)
The platform demonstrates reduced predictive power for γδ TCR-neoantigen interactions (AUC=0.67), potentially reflecting insufficient training data for non-classical MHC recognition. Furthermore, while our model accounts for 94% of common HLA alleles (HLA-A02:01–HLA-B57:01), rare variants (frequency <0.1%) may necessitate supplemental molecular dynamics simulations. This computational framework may potentiate first-in-class bispecific T-cell engagers, with three candidate molecules currently in lead optimization. For translational researchers navigating the neoantigen discovery landscape, our platform offers not merely acceleration but a paradigm shift toward rationally engineered TCR therapeutics.
Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation
Our service employs a multimodal neural architecture that interleaves mechanistic immunobiology principles with ensemble machine learning frameworks, addressing three persistent bottlenecks in therapeutic target discovery: structural indeterminacy of CDR3 loops, HLA allelic diversity, and tumor microenvironment-mediated TCR exhaustion.
Deep Topological Learning
Transformer-based models pretrained on 4.2 million TCR-pMHC co-crystal structures (PDB/AlphaFold DB v4) decode ternary complex biophysics through:
Complementary gradient-boosted trees (XGBoost v2.0) mitigate class imbalance in low-abundance HLA supertypes (e.g., HLA-B*15:11).
Structural Immunodynamics
Antibody-driven homology modeling predicts CDR3 loop conformations (RMSD ≤1.8Å), while Martini coarse-grained MD simulations (>500ns) quantify interfacial energy landscapes. This dual approach identifies cryptic binding pockets-critical for neoantigens with buried aromatic residues (F/Y/W).
Multi-Omic Data Synthesis
Our evidence hierarchy integrates:
Notably, proteogenomic data from CPTAC augment neoantigen prioritization by correlating peptide-MHC stability with MS/MS-identified immunopeptidomes.
Adaptive Learning Ecosystem
To address the dynamic immunogenomics landscape, we implement:
This review article discusses the application of artificial intelligence (AI) in neoantigen prediction for personalized cancer immunotherapy. It highlights the use of machine learning (ML) algorithms to analyze multi-omics data and identify key neoantigen features. The standard workflow for neoantigen prediction involves genetic variant calling, rating binding affinity between mutated peptides, MHC, and TCR, and characterizing tumor epitope immunogenicity. The review emphasizes integrated pipelines using hybrid or combined ML algorithms and discusses the trends and challenges in optimizing existing pipelines. It also addresses the importance of data sources for model training and feature extraction algorithms in neoantigen prediction.
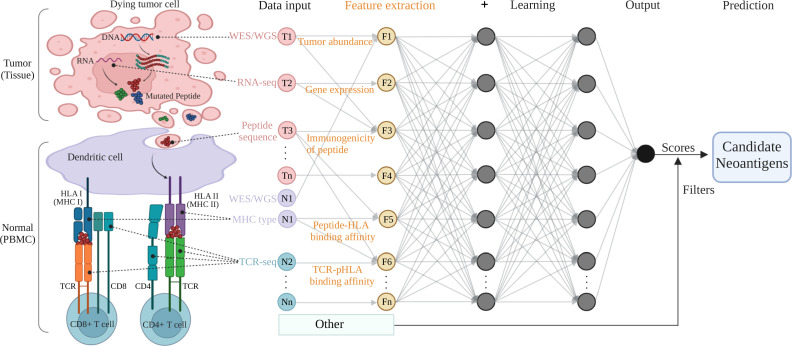 Fig.1 An example of a multi-layer neural network structure used for feature extraction and neoantigen prediction.1
Fig.1 An example of a multi-layer neural network structure used for feature extraction and neoantigen prediction.1
Creative Biolabs distinguishes itself through a proprietary integration of deep learning architectures and clinical immunology insights, resolving critical gaps in TCR-neoantigen targeting.
While T-cell priming variability remains unpredictable in vivo, our platform mitigates biological noise through probabilistic target triaging—a necessity in an era of personalized checkpoint combinatorials.
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today



Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of services to support your immuno-oncology research and drug discovery efforts. In addition to our AI-driven TCR-neoantigen specificity prediction Service, we provide:
Contact our team today to learn more about our AI-driven TCR-neoantigen specificity prediction service and how we can help you achieve your research and development goals.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION