Lymph nodes are essential for the activation and coordination of T cell-mediated immune responses, where T cells engage with antigens and differentiate into effector cells to address infections. To tackle the challenges of T cell activation ex vivo in T cell therapies, researchers have developed a dynamic immune-stimulating scaffold known as an artificial lymph node (aLN). This innovative platform effectively replicates the roles of antigen-presenting cells and lymphatic tissue, facilitating direct in vivo stimulation of antigen-specific T cells. It recruits and organizes host immune cells, fostering an immuno-stimulatory environment that supports the in situ activation and proliferation of T cells specific to the target antigens, thus eliminating the necessity for ex vivo activation.
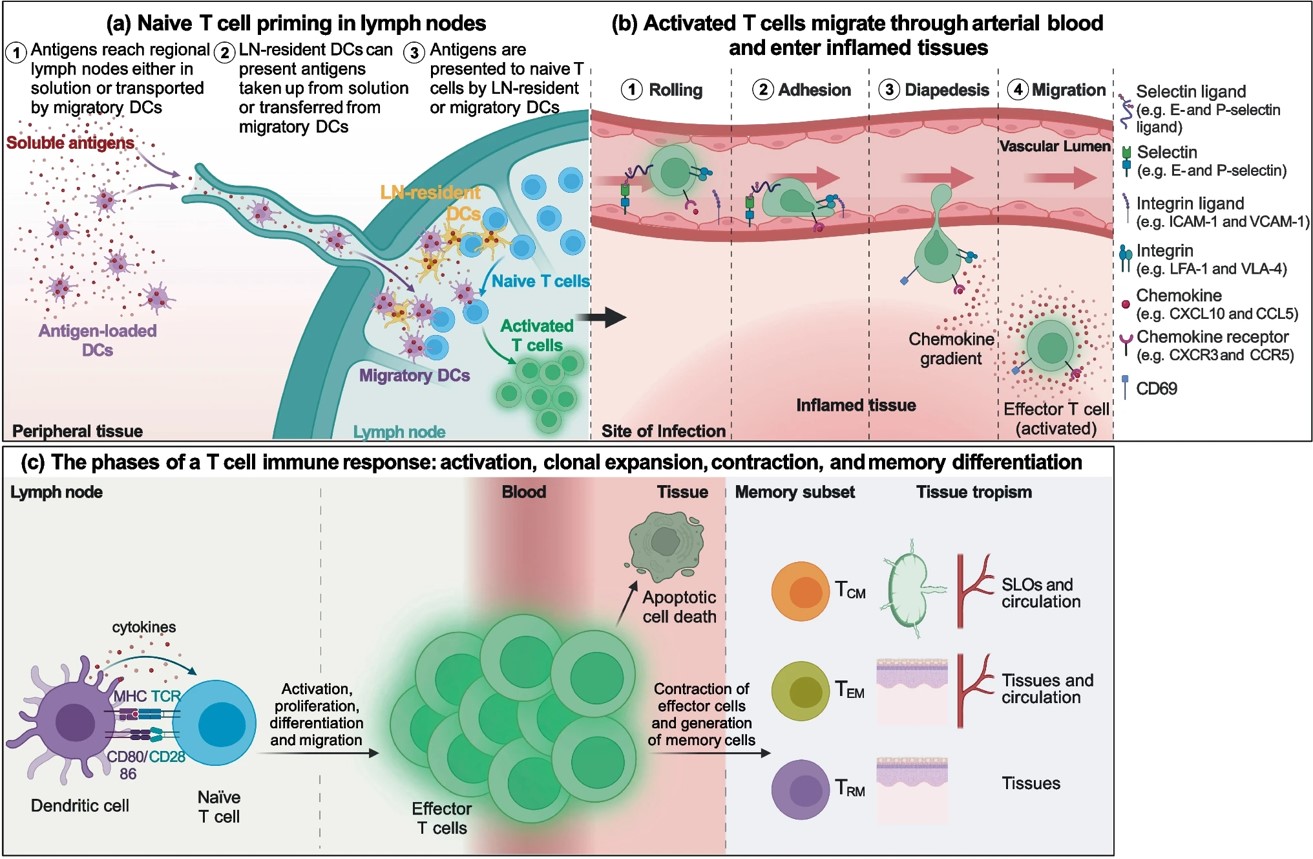 Fig.1 T cell activation and trafficking.1
Fig.1 T cell activation and trafficking.1
aLN shows great potential in improving T cell therapy. Here are a few of aLN's salient characteristics:
Creative Biolabs offers a custom aLN-based artificial T cell-stimulating platform development service designed to accelerate cancer immunotherapy research. Our strategy harnesses cross-linking materials between different hydrogels to offer tailored T cell stimulation and activation in situ, incorporating user-specified T cell-stimulating signals. To enable effective platform development. We work directly with customers to customize the aLN, including hydrogels, ligands, costimulatory agents, and cytokines. At the same time, we continue to optimize the component concentrations and physical qualities for maximum T cell activation based on the testing results. Flexible, our service is suitable for a wide range of research purposes ranging from small and large-scale research initiatives.
As a one-stop service provider, we also provide comprehensive characterization services to identify platforms in phenotype and function. At Creative Biolabs, we are always committed to offering fast, high-quality solutions that help customers build more effective and long-lasting cancer T cell treatments.

Associated Services
In addition to aLN, we also offer tailored solutions for various hydrogel-based materials, including aTM and immunomodulatory macroporous scaffolds, to develop advanced artificial T cell stimulation platforms that cater to our customers' unique requirements. Leveraging our profound knowledge in biomaterial engineering and T cell biology, we are adept at designing custom platforms that replicate particular lymphoid microenvironments, thereby improving the effectiveness and applicability of T cell-centric therapies.
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of T cell therapy enhancement, combining deep theoretical insights with hands-on expertise in crafting innovative T cell stimulation platforms. Our specialization lies in the design and engineering of bespoke aLN-based solutions specifically aligned with your distinct research objectives. Reach out to us today to explore your specific requirements and discover how our expertise can help you create a highly effective aLN platform for the activation of T cells.
Reference
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION