Target Background
MET (c-Met), also known as HGFR (hepatocyte growth factor receptor) is a single pass tyrosine kinase receptor whose precursor is post-translationally cleaved at a furin site to generate an intensively glycosylated extracellular α subunit and a transmembrane β subunit, and the two subunits are disulfide bridged with each other. Subsequent processing of the β subunit yields an M10 peptide identified to reduce lung fibrosis.
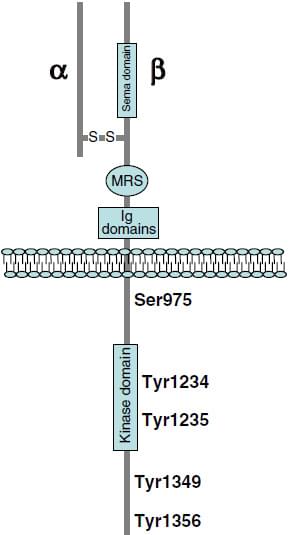 The structure of c-Met Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, without modification, from Wiki.
The structure of c-Met Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, without modification, from Wiki.
Physiologically, MET only expresses in stem cells and progenitor cells, and distributes mainly on epithelial cells, also on endothelial cells, neurons, hepatocytes, hematopoietic cells, melanocytes and neonatal cardiomyocytes. The activation of MET via binding of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) endows cells with the essential ability for mitogenesis, morphogenesis, embryogenesis and wound healing. Since MET is originally identified as an activated oncogene in a human osteosarcoma cell line, accumulative evidences prove that cancer cells can hijack the ability of normal stem cells to overexpress MET, and subsequently stimulate the growth, persistence and metastasis of multiple human malignancies (cancers of kidney, lung, liver, stomach, breast and brain) via activation of several key oncogenic pathways (RAS, PI3K, STAT3 and beta-catenin), angiogenesis and cell scattering due to metalloprotease production. On account of MET's critical role depicted above, MET has emerged as a potential biomarker and target for anti-cancer therapies. Creative Biolabs will help researchers open up the brightening future for the anti-MET CAR-T cell therapy in the scientific community.
Anti-MET CAR-T Cell Therapy
Despite the current ongoing phase 1 clinical trial which is aiming to test the efficiency of autologous cMet redirected T cells administered intratumorally (IT) in patients with metastatic breast cancer, no other preclinical or clinical studies are reported. Thus, Creative Biolabs helps researchers make progress together to design and initiate the subtle anti-MET CAR-T cell therapy.
Animal Models for in vivo Study of anti-MET CAR-T Cell Therapy
Creative Biolabs offers researchers almost all the animal models (murine, canine, etc.) generated from the major techniques including the conventional carcinogen-induced models, the mosaic transposon- or virus-induced models, the transgenic models and the subcutaneous or patient-derived xenograft models for multiple human malignancies (cancers of kidney, lung, liver, stomach, breast and brain). In addition, Creative Biolabs is always passionate about introducing our well-established animal models to in vivo tests of adoptive cell therapy and providing assistance in creating the most clinically relevant animal models with customized requirements.
In vivo Assay Parameters and Techniques
At Creative Biolabs, we offer the most exquisite and comprehensive service platform for preclinical MET CAT-T cell therapy research.
Efficacy Test
Tumor remission monitored by tumor volume recording or bioluminescence imaging and survival curve tracking
Viability and Bio-distribution Studies
Durability, bio-distribution studies
Toxicity Evaluation
Pilot tolerability (MTD, The route of administration, Dose regimen/response/onset)
Clinical observation (body weight, feed consumption, ophthalmologic and clinical pathology)
Cytokine storm surveillance (fever, hypertension, prolonged cytopenia)
Complete necropsy, organ weight
Histopathology
Tumorigenicity study
Creative Biolabs is thrilled to create the most scientific pre-clinical assay design in vivo with the most clinically relevant animal models with the consideration of every elementary detail to innovate the miraculous future of CAR-T cell therapy for conquering the most malignant cancers.
For any technical issues or product/service related questions, please leave your information below. Our team will contact you soon.
All products and services are For Research Use Only and CANNOT be used in the treatment or diagnosis of disease.
 NEWSLETTER
NEWSLETTER
The latest newsletter to introduce the latest breaking information, our site updates, field and other scientific news, important events, and insights from industry leaders
LEARN MORE NEWSLETTER NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
CellRapeutics™ In Vivo Cell Engineering: One-stop in vivo T/B/NK cell and macrophage engineering services covering vectors construction to function verification.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
NOVEL TECHNOLOGY
Silence™ CAR-T Cell: A novel platform to enhance CAR-T cell immunotherapy by combining RNAi technology to suppress genes that may impede CAR functionality.
LEARN MORE NOVEL TECHNOLOGY NEW SOLUTION
NEW SOLUTION
Canine CAR-T Therapy Development: From early target discovery, CAR design and construction, cell culture, and transfection, to in vitro and in vivo function validation.
LEARN MORE SOLUTION